- [English]
- Influence of milling atmosphere on thermoelectric properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te based alloys by mechanical alloying
-
Suk-min Yoon, Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Dong-won Shin, Chul-hee Lee, Babu Madavali, Soon-jik Hong, Kap-ho Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):357-363. Published online October 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.357
-
-
1,270
View
-
4
Download
-
7
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
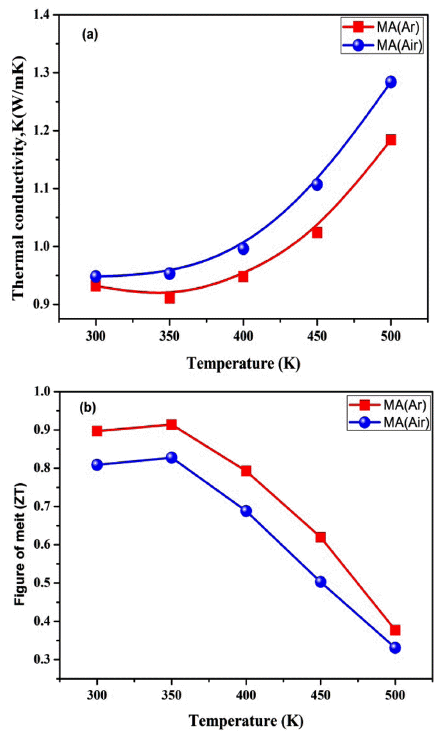
In this study, Bi-Sb-Te thermoelectric materials are produced by mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). To examine the influence of the milling atmosphere on the microstructure and thermo-electric (TE) properties, a p-type Bi-Sb-Te composite powder is mechanically alloyed in the presence of argon and air atmospheres. The oxygen content increases to 55% when the powder is milled in the air atmosphere, compared with argon. All grains are similar in size and uniformly, distributed in both atmospheric sintered samples. The Seebeck coefficient is higher, while the electrical conductivity is lower in the MA (Air) sample due to a low carrier concentration compared to the MA (Ar) sintered sample. The maximum figure of merit (ZT) is 0.91 and 0.82 at 350 K for the MA (Ar) and MA (Air) sintered samples, respectively. The slight enhancement in the ZT value is due to the decrease in the oxygen content during the MA (Ar) process. Moreover, the combination of mechanical alloying and SPS process shows a higher hardness and density values for the sintered samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Grain Size‐Dependent Thermoelectric Performances of Al2O3 Addition into BiSbTe Alloy During Heat Treatment Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying
Ji‐Won Ha, Vasudevan Rathinam, Eun‐Ha Go, Soon‐Jik Hong
Advanced Engineering Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Revealing the improved thermoelectric performances of (BiSb)2Te3 alloy through rapid solidification of cold-water assisted water atomization approach
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Ji-Won Ha, Sung-Jae Jo, GeonWoo Baek, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1010: 177548. CrossRef - Microstructural and Thermoelectric Properties of Heat-treated Al2O3 Doped BiSbTe Alloy
Jiwon Ha, Vasudevan Rathinam, Eunha Go, Soonjik Hong
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2025; 72(Supplement): S983. CrossRef - Advancement of thermoelectric performances through the dispersion of expanded graphene on p-type BiSbTe alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Babu Madavali, Peyala Dharmaiah, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 722. CrossRef - Influence of milling atmosphere on the structure and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed Fe40Co30Ni30
Alex Abraham Paul, Anuj Rathi, Ganesh Varma Thotakura, Tanjore V. Jayaraman
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2021; 258: 123897. CrossRef - Enhancement of mechanical properties and thermoelectric performance of spark plasma sintered P-type Bismuth Telluride by powder surface oxide reduction
Ahmed A. Abdelnabi, Vickram Lakhian, Joseph R. McDermid, Yu-Chih Tseng, James S. Cotton
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 858: 157657. CrossRef - Solid solution evolution during mechanical alloying in Cu-Nb-Al compounds
Kaouther Zaara, Mahmoud Chemingui, Virgil Optasanu, Mohamed Khitouni
International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials.2019; 26(9): 1129. CrossRef
- [English]
- Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
-
Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):115-121. Published online April 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.115
-
-
1,380
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this work, p-type Bi−Sb−Te alloys powders are prepared using gas atomization, a mass production powder preparation method involving rapid solidification. To study the effect of the sintering temperature on the microstructure and thermoelectric properties, gas-atomized powders are consolidated at different temperatures (623, 703, and 743 K) using spark plasma sintering. The crystal structures of the gas-atomized powders and sintered bulks are identified using an X-ray diffraction technique. Texture analysis by electron backscatter diffraction reveals that the grains are randomly oriented in the entire matrix, and no preferred orientation in any unique direction is observed. The hardness values decrease with increasing sintering temperature owing to a decrease in grain size. The conductivity increases gradually with increasing sintering temperature, whereas the Seebeck coefficient decreases owing to increases in the carrier mobility with grain size. The lowest thermal conductivity is obtained for the bulk sintered at a low temperature (603 K), mainly because of its fine-grained microstructure. A peak ZT of 1.06 is achieved for the sample sintered at 703 K owing to its moderate electrical conductivity and sustainable thermal conductivity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites
Seok-Min Yong
Journal of Ceramic Processing Research.2019; 20(1): 59. CrossRef
- [English]
- Investigation of Ball Size Effect on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type BiSbTe by Mechanical Alloying
-
May Likha Lwin, Sang-min Yoon, Babu Madavali, Chul-Hee Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):120-125. Published online April 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.120
-
-
1,466
View
-
5
Download
-
4
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
P-type ternary Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloys are fabricated via mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). Different ball sizes are used in the MA process, and their effect on the microstructure; hardness, and thermoelectric properties of the p-type BiSbTe alloys are investigated. The phases of milled powders and bulks are identified using an X-ray diffraction technique. The morphology of milled powders and fracture surface of compacted samples are examined using scanning electron microscopy. The morphology, phase, and grain structures of the samples are not altered by the use of different ball sizes in the MA process. Measurements of the thermoelectric (TE) transport properties including the electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and power factor are measured at temperatures of 300- 400 K for samples treated by SPS. The TE properties do not depend on the ball size used in the MA process. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 115. CrossRef - Flexible Thermoelectric Device Using Thick Films for Energy Harvesting from the Human Body
Han Ki Cho, Da Hye Kim, Hye Sun Sin, Churl-Hee Cho, Seungwoo Han
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2017; 54(6): 518. CrossRef - Investigation of the Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of P-Type BiSbTe Alloys by Usage of Different Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) During Mechanical Milling
S.-M. Yoon, B. Madavali, Y.-N. Yoon, S.-J. Hong
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1167. CrossRef - Mechanical and thermoelectric properties of Bi2−xSbxTe3 prepared by using encapsulated melting and hot pressing
Woo-Jin Jung, Il-Ho Kim
Journal of the Korean Physical Society.2016; 69(8): 1328. CrossRef
|