Current issue
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Current issue
Research Articles
- [English]
- Finite Element and Discrete Element Analyses of Anisotropic Powder Compaction for Axial Flux Motor Cores
- Jeong Ah Lee, Do Won Lee, , Hyojeong Ha, Ki Hyuk Kwon, Eon Byeong Park, Taeyoung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):451-458. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00409
- 875 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
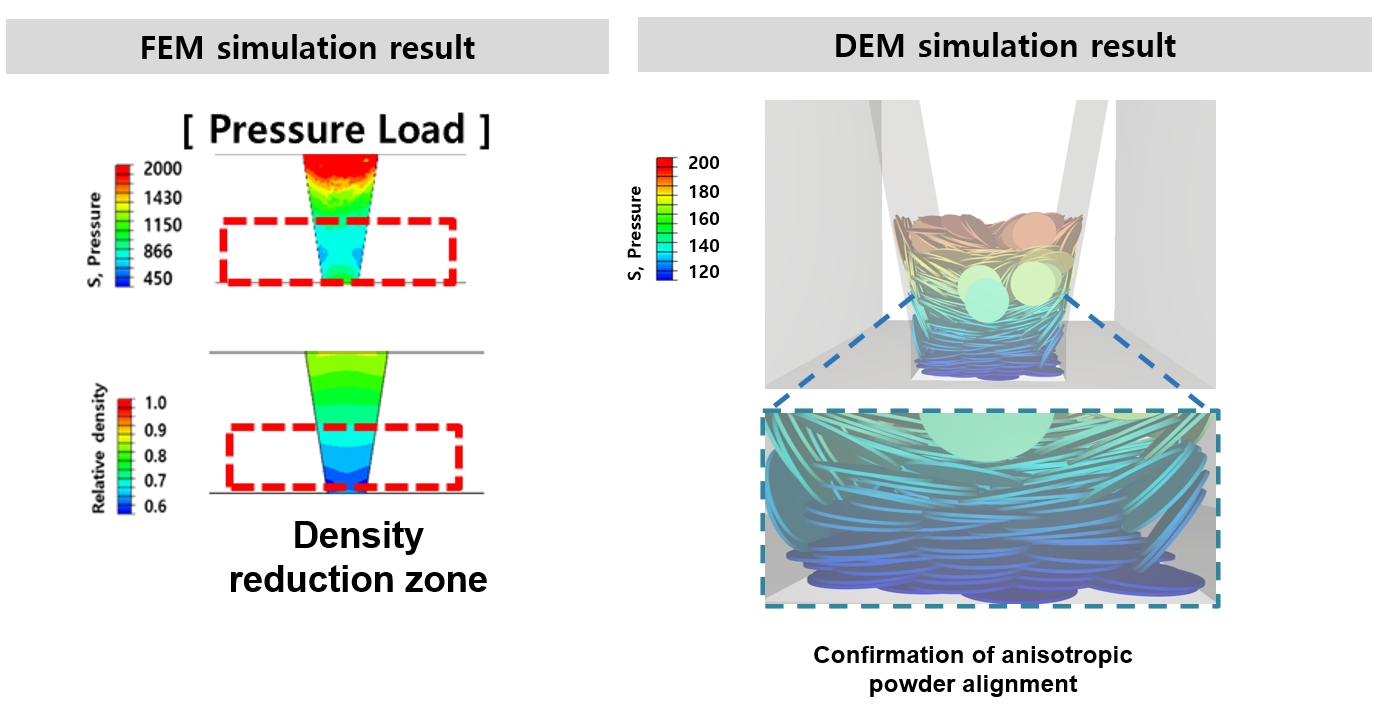
PDF - This study investigates the compaction behavior of anisotropic, plate-like powders used in axial flux motor cores through a combined FEM–DEM approach. A porous continuum FEM model captures stress and density evolution during die pressing, revealing strong gradients along the compaction direction, with higher stress and densification near the upper punch and reduced compaction in the lower region. Guided by these results, DEM simulations examine particle packing, orientation, and contact pressure in representative zones. The DEM analysis shows that higher local pressure promotes denser packing and in-plane particle alignment near the upper punch, while the lower region exhibits more random orientations and lower contact forces. As a result, the multi-scale FEM–DEM framework clarifies how anisotropic particle behavior governs local densification and offers practical guidance for die design and process optimization to achieve more uniform density and controlled magnetic-property-relevant particle alignment in axial flux motor cores.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA3003 Tube for Heat Exchanger Processed by Floating Plug Drawing
- Hyeon-Jun Heo, Sung Jun Oh, Seong-Hee Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):459-465. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00346

- 729 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An AA3003 tube was severely deformed by cold floating plug drawing, and then annealed at temperatures from 210 to 460℃. The as drawn Al tube exhibited a typical deformation structure in which the grains were greatly elongated along the drawing direction. The hardness increased with increasing the reduction of cross-sectional area (RA), became 68Hv after RA= 99%. Up to 310℃, the Al tube still mainly exhibited a deformed structure. While complete recrystallization occurred at temperatures above 360℃. The hardness decreased with increasing the annealing temperature, and it became 33Hv after annealing at 410℃. Both the tensile and yield strengths also decreased with increasing the annealing temperature, but the decrease was larger in yield strength than in tensile strength. The elongation increased with increasing the annealing temperature. The changes in the strength and the elongation with the annealing temperature were the largest at 360℃, in which the complete recrystallization occurred.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Porous W-Cu by Freeze Casting of Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry Mixed with WO3-CuO Powder
- Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Minju Son, Wonyong Kwon, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):466-471. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00437
- 729 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
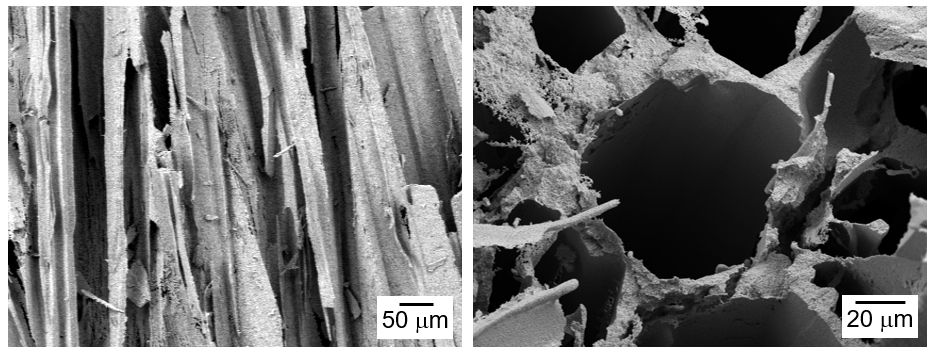
PDF - The influence of process conditions on the microstructure of porous W-Cu, fabricated by freeze casting using tert-butyl alcohol as the freezing agent, was investigated. The slurries containing 10 vol% of WO3-CuO powder were prepared by milling with a small amount of citric acid and polyethylene glycol as dispersants. The slurries with dispersion stability were frozen in a mold with the lower part cooled to -25°C, followed by sublimation in a vacuum to remove the freezing agent. The sintered W-1 vol% Cu in a hydrogen atmosphere exhibited aligned pores with the size of 50 μm, which were generated by sublimation of directionally solidified tert-butyl alcohol crystals. In the cross-section of the specimen, hexagonal pores corresponding to the crystal structure of tert-butyl alcohol was observed. Microstructure analysis of the struts revealed that Cu was distributed non-uniformly due to the mutual insolubility and low wettability of the W-Cu system.
- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Properties of Rare-Earth Zirconate Thermal Barrier Coatings for Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbines
- Gun-Woong Lee, Min-Soo Nam, Min-Ji Kim, HyunSuk Jung, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):472-480. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00423

- 786 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) for hydrogen-fueled gas turbines withstand higher combustion temperatures and increased steam concentrations compared to conventional natural-gas systems. These harsh operating conditions significantly accelerate the thermal degradation of widely used YSZ coatings, emphasizing the need for alternative top-coat materials with improved phase stability and reduced thermal conductivity. In this study, rare-earth zirconate ceramics, Gd2Zr2O7 (GdZO), Tm2Zr2O7 (TmZO), and a mixed composition (Gd0.5Tm0.5)2Zr2O7 (Gd/TmZO), are synthesized and investigated as potential next-generation TBC candidates. Each material was comparatively examined with a focus on crystal structure, thermophysical properties, and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, high-temperature steam exposure experiments were performed to simulate hydrogen combustion environments. Microstructural analyses, high-temperature degradation behavior, and phase stability evaluations were carried out to obtain fundamental experimental data. This study provides essential baseline information for the design and development of high-performance TBC materials suitable for the hydrogen-fueled gas turbine systems.
- [English]
- A Self-Powered Cationic Microfiber-Based Triboelectric Air Filter for High-Speed Particulate Matter Removal and Smart Monitoring
- Tae-hyung Kim, Jin-Kyeom Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):481-491. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00465
- 888 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
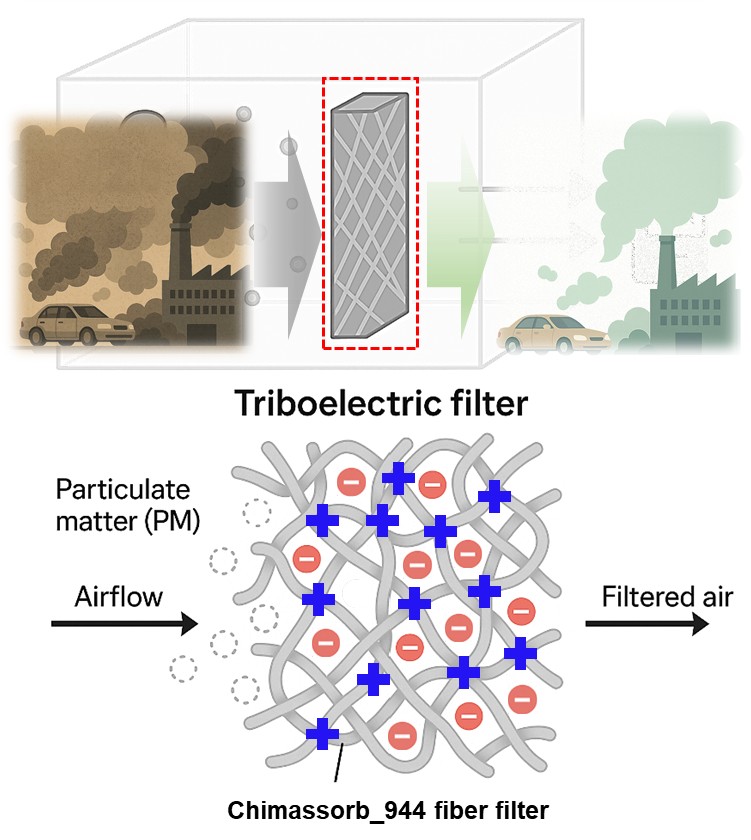
PDF - Particulate matter (PM) pollution demands air filters that combine high efficiency with low pressure drop. Here, we report a self-powered electrostatic filter based on an electrospun cationic microfiber web of Chimassorb 944 (C-fiber). The C-fiber functions as a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), generating a surface charge density of 85.8 85.8 μC/m2 when paired with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which creates a strong electrostatic field for capturing sub-micron particles, including the most penetrating particle size (MPPS). As a result, the triboelectrically charged C-fiber filter maintains >80% filtration efficiency at a high wind speed of 60 cm/s, far exceeding uncharged mechanical filters (<20%) while retaining low air resistance. Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) visualizes the surface-potential change after particle capture, and the gradual decay of TENG output provides a built-in indicator of dust loading. This strategy offers a promising platform for next-generation smart air purification systems.
- [Korean]
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):492-500. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00332
- 763 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
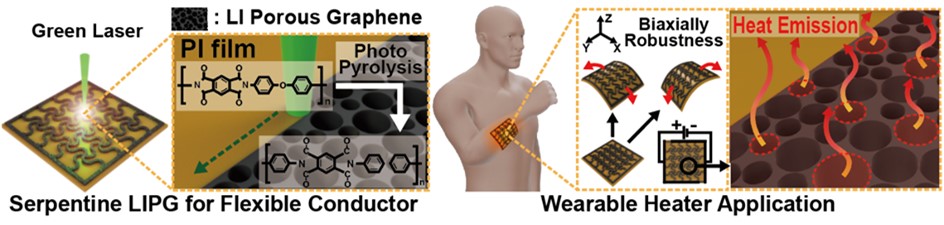
PDF - A flexible heater with high thermal efficiency and mechanical durability was developed by fabricating laser-induced porous graphene (LIPG) electrodes on polyimide films using a 532 nm green laser. Laser power, scan speed, and line distance were precisely optimized based on photothermal simulations to generate uniform porous graphene structures with large surface area and excellent heat dissipation characteristics. Raman, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses confirmed that the optimized LIPG exhibited highly graphitized features with low oxygen defects. Scanning electron microscope analysis revealed that porous morphologies formed only within a specific laser scan speed range, whereas excessive or insufficient irradiation resulted in collapsed or absent porosity. The serpentine-patterned LIPG heater maintained stable electrical resistance under repeated multidirectional bending, demonstrating excellent flexibility and mechanical stability. The heater also achieved rapid and uniform heating up to 80 °C within seconds, maintaining consistent temperature distribution even on curved surfaces.
- [Korean]
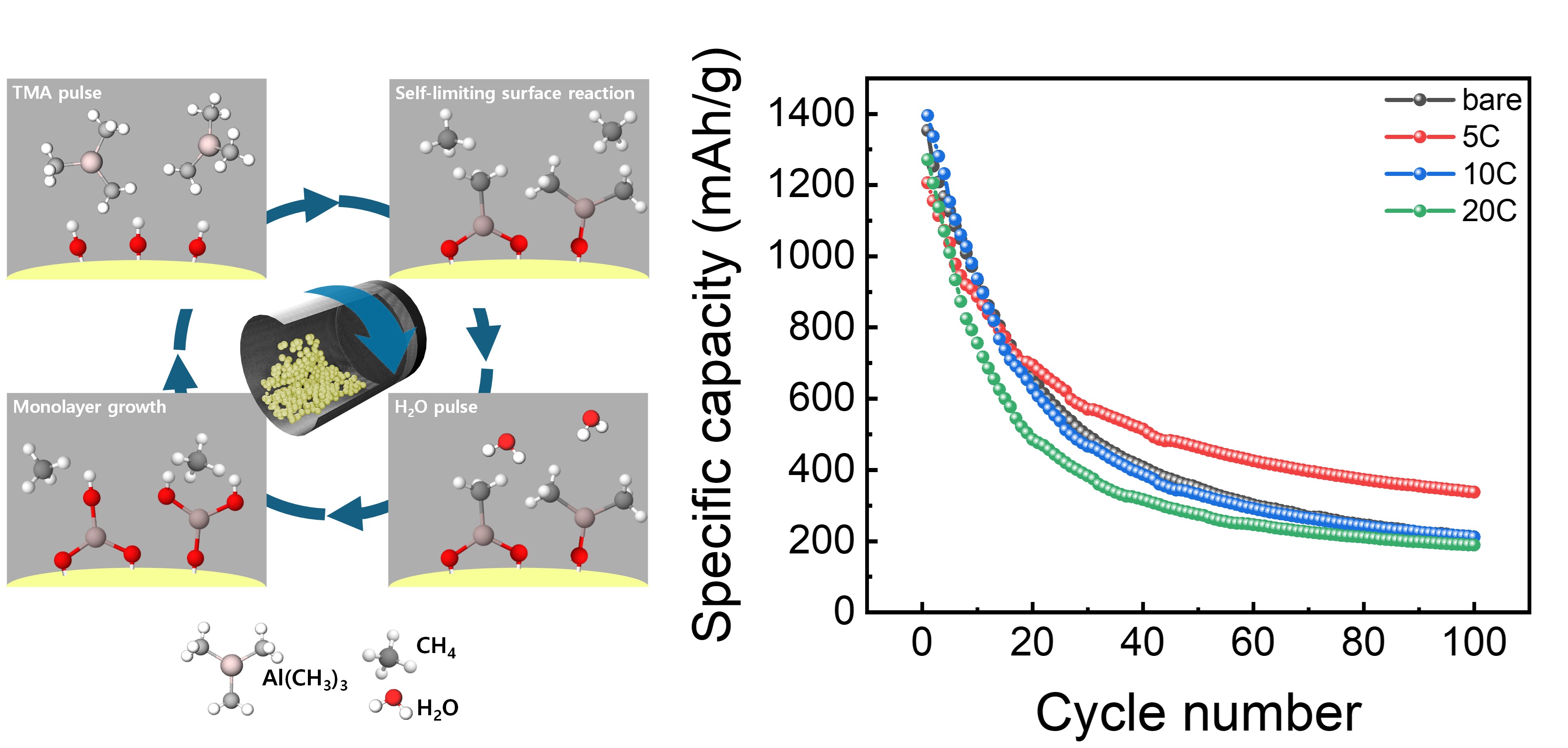
- Enhancement of the Electrochemical Performance of SiOx Anodes by Al2O3 Coating via Powder Atomic Layer Deposition
- Donggeon Shin, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):501-508. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00416
- 718 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Silicon based anode materials offer high theoretical capacity but suffer from severe volume expansion and unstable interfacial properties during repeated lithiation and delithiation, resulting in rapid performance degradation. In this study, a thin aluminum oxide coating layer was deposited on Si/SiOx Carbon anode materials using a powder atomic layer deposition (PALD) process to address these limitations. EDS mapping and XRD analyses confirmed the uniform formation of an amorphous aluminum oxide coating with increasing thickness as the deposition cycles increased. Electrochemical evaluation showed that the electrode coated with 5 PALD cycles exhibited approximately 78% higher capacity retention after 100 cycles at 1 A g-1 and a higher initial Coulombic efficiency compared to the bare electrode. The coated electrode also delivered approximately 22% higher capacity at a high current density of 5 A g-1, indicating enhanced rate capability. Cyclic voltammetry analysis revealed increased surface controlled reaction contributions and improved reaction kinetics. These results demonstrate that PALD derived aluminum oxide coatings effectively stabilize the electrode electrolyte interface and enhance the electrochemical performance of silicon based anodes, highlighting their potential for next generation high capacity lithium ion batteries. generation high capacity lithium ion battery anode materials.
- [Korean]
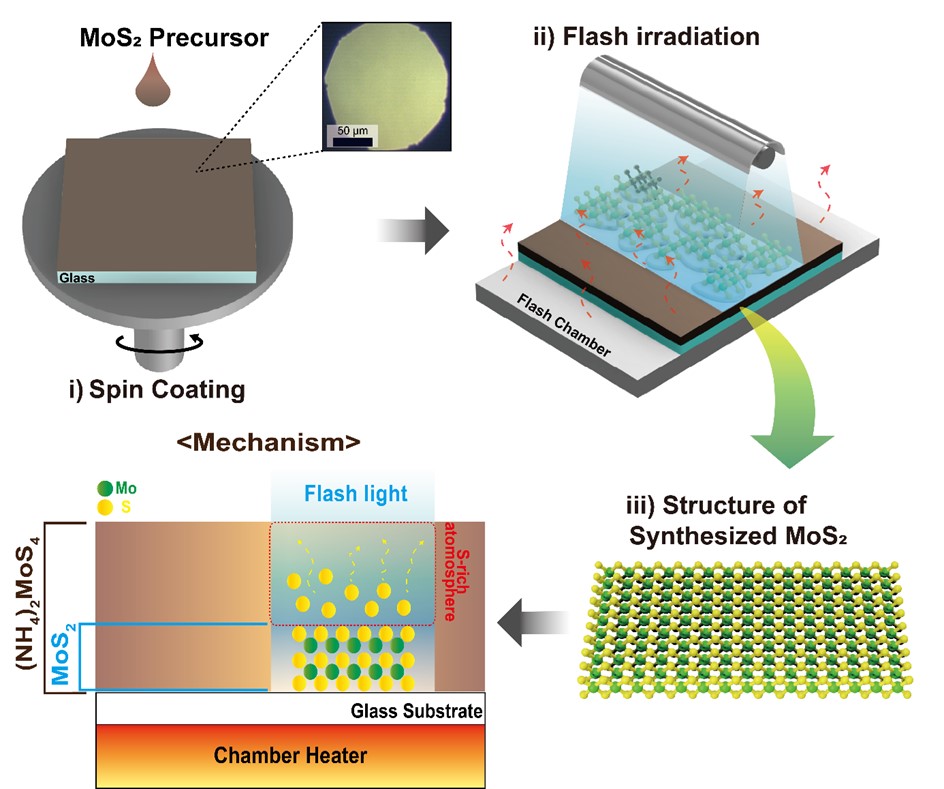
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):509-516. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00339
- 697 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents the synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) using flashlamp annealing and provides a comprehensive investigation of its structural and physical properties. The proposed flash-induced approach enables rapid production of high-quality MoS₂, offering superior process efficiency compared to conventional synthesis techniques. The structural, electronic, and thermal characteristics of the synthesized MoS₂ were systematically examined using multiple analytical methods, with particular attention to how synthesis conditions influence layer structure, crystallinity, and defect density. The results indicate that MoS₂ produced through this method exhibits material properties suitable for high-performance electronic devices and energy storage applications. Moreover, this work demonstrates the potential of flash-induced synthesis for scalable and practical fabrication of MoS₂-based nanomaterials, thereby contributing to the broader advancement of transition metal dichalcogenide technologies across diverse nanotechnology applications.
Critical Reviews
- [Korean]
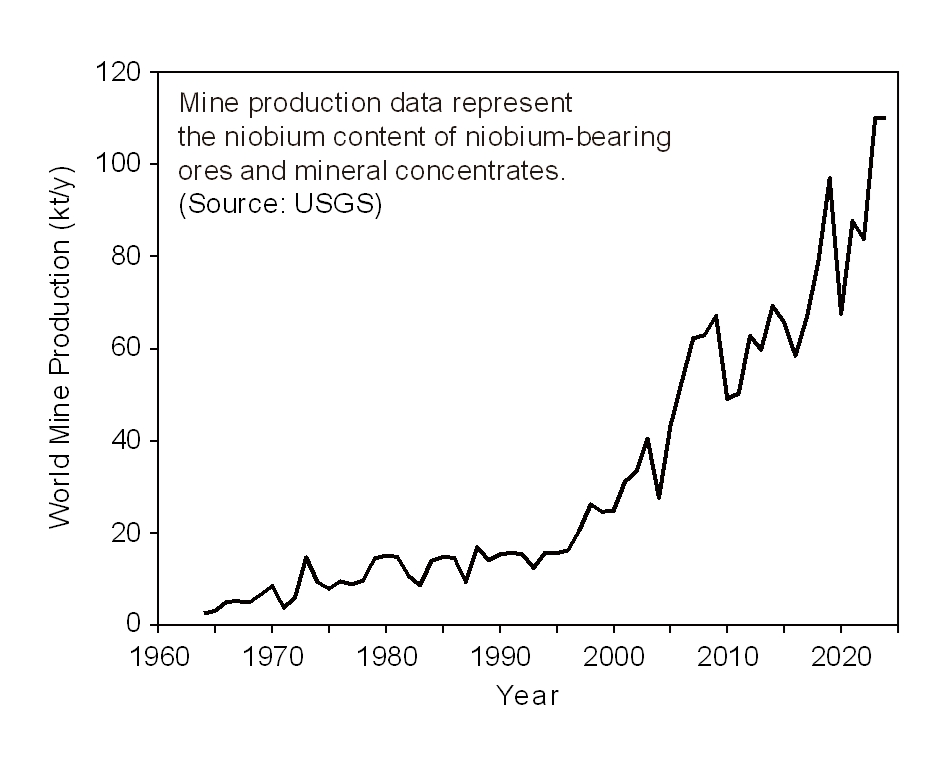
- Smelting and Recycling of Niobium
- Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):517-528. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00367
- 734 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Global annual production of niobium is only around 100,000 tonnes; however, it is a critical metal for modern industry and is mined in only a limited number of regions. This study reviews the current status of niobium smelting and recycling technologies. Approximately 90% of niobium is produced as ferroniobium (FeNb) for use in steel alloys, although niobium is also utilized in superalloys, superconductors, capacitors, semiconductors, and other applications. Niobium coexists with tantalum in columbite and tantalite ores. These ores are decomposed by hydrofluoric acid digestion or alkali fusion, followed by solvent extraction to separate Nb2O5 and Ta2O5. Niobium metal and FeNb are produced from Nb2O5 primarily via aluminothermic reduction, although metallic niobium can also be manufactured by thermal reduction using Mg, Ca, or C, as well as by molten salt electrolysis. Crude niobium is subsequently refined into high-purity niobium through molten salt electrolytic refining, high-temperature vacuum treatment, and electron beam melting. Because most niobium is used as an alloying element in stainless steel and high-strength low-alloy steel, recycling practices for niobium remain poorly documented.
- [Korean]
- Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
- So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):529-541. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00493
- 802 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magneto-mechano-electric (MME) energy harvesters have emerged as a promising solution for maintenance-free power generation in rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT) environments, where replacing or wiring batteries is impractical. MME devices convert weak alternating magnetic fields, ubiquitous around power infrastructures, into useful electrical energy through sequential magnetic, mechanical, and electrical transduction processes. This review summarizes recent advances across triboelectric-, piezoelectric-, and hybrid MME architectures. Triboelectric MME generators employing nano-engineered polymer surfaces, flash-induced surface modification, and nanoscale pattern replication demonstrate low-cost fabrication routes while achieving significantly enhanced voltage and current outputs. Piezoelectric MME systems based on Mn-doped PMN-PZT single crystals highlight strategies for improving mechanical quality factors and resonance-driven power generation. Further, hybrid MME designs that integrate piezoelectric and electromagnetic induction mechanisms enable high-power outputs exceeding tens of milliwatts, sufficient to operate multifunctional IoT platforms and charge practical energy-storage devices. Collectively, these studies illustrate a transition of MME harvesting technologies from laboratory concepts to application-ready self-powered systems. Future opportunities lie in broadband resonance design, modular harvester integration, advanced power management, and multi-source hybridization for robust long-term operation in real environments.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI



 First
First Prev
Prev


