- [Korean]
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
-
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):492-500. Published online December 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00332
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
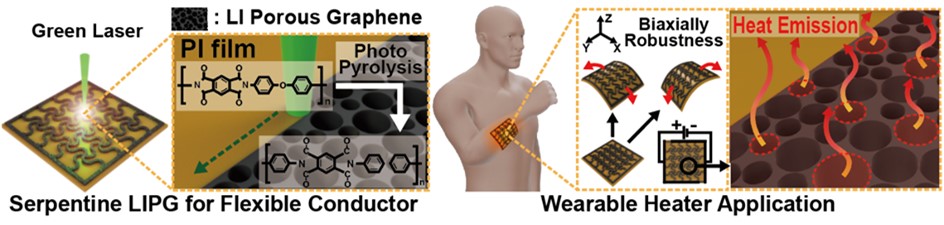
- A flexible heater with high thermal efficiency and mechanical durability was developed by fabricating laser-induced porous graphene (LIPG) electrodes on polyimide films using a 532 nm green laser. Laser power, scan speed, and line distance were precisely optimized based on photothermal simulations to generate uniform porous graphene structures with large surface area and excellent heat dissipation characteristics. Raman, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses confirmed that the optimized LIPG exhibited highly graphitized features with low oxygen defects. Scanning electron microscope analysis revealed that porous morphologies formed only within a specific laser scan speed range, whereas excessive or insufficient irradiation resulted in collapsed or absent porosity. The serpentine-patterned LIPG heater maintained stable electrical resistance under repeated multidirectional bending, demonstrating excellent flexibility and mechanical stability. The heater also achieved rapid and uniform heating up to 80 °C within seconds, maintaining consistent temperature distribution even on curved surfaces.
- [Korean]
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
-
Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):509-516. Published online December 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00339
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
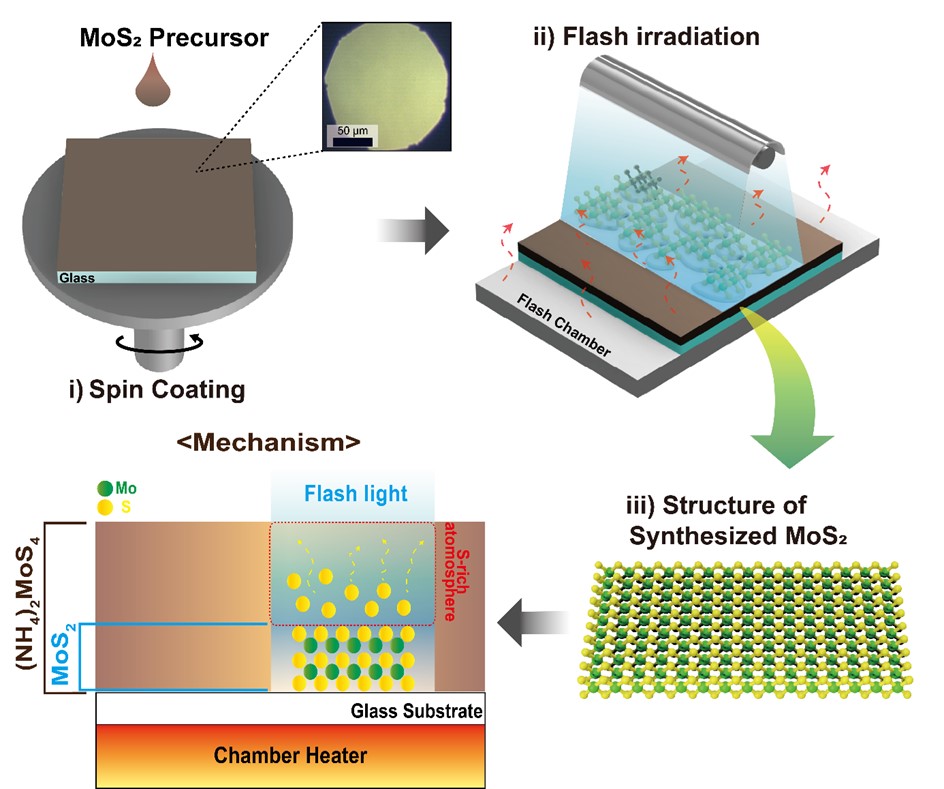
- This study presents the synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) using flashlamp annealing and provides a comprehensive investigation of its structural and physical properties. The proposed flash-induced approach enables rapid production of high-quality MoS₂, offering superior process efficiency compared to conventional synthesis techniques. The structural, electronic, and thermal characteristics of the synthesized MoS₂ were systematically examined using multiple analytical methods, with particular attention to how synthesis conditions influence layer structure, crystallinity, and defect density. The results indicate that MoS₂ produced through this method exhibits material properties suitable for high-performance electronic devices and energy storage applications. Moreover, this work demonstrates the potential of flash-induced synthesis for scalable and practical fabrication of MoS₂-based nanomaterials, thereby contributing to the broader advancement of transition metal dichalcogenide technologies across diverse nanotechnology applications.
|