- [Korean]
- Effect of Spray Angle the on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Y2O3 Coating Layer Manufactured by Atmospheric Plasma Spray Process
-
Yu-Jin Hwang, Kyoung-Wook Kim, Ho-Young Lee, Sik-Chol Kwon, Kee Ahn Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):310-316. Published online August 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.310
-
-
1,504
View
-
35
Download
-
5
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
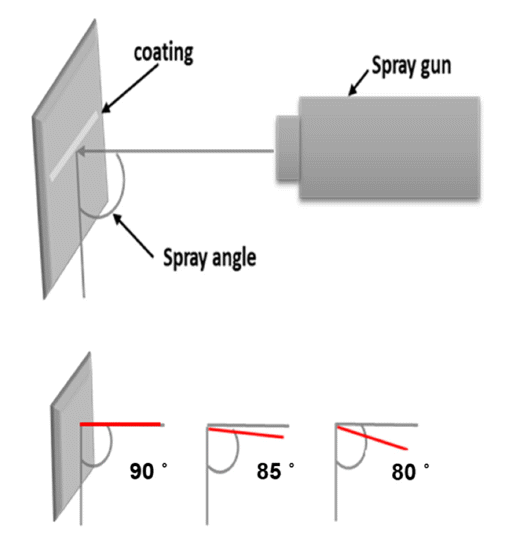
The effects of different spray angles (90°, 85°, 80°) on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a Y2O3 coating layer prepared using the atmospheric plasma spray (APS) process were studied. The powders employed in this study had a spherical shape and included a cubic Y2O3 phase. The APS coating layer exhibited the same phase as the powders. Thickness values of the coating layers were 90°: 203.7 ± 8.5 μm, 85°: 196.4 ± 9.6 μm, and 80°: 208.8 ± 10.2 μm, and it was confirmed that the effect of the spray angle on the thickness was insignificant. The porosities were measured as 90°: 3.9 ± 0.85%, 85°: 11.4 ± 2.3%, and 80°: 12.7 ± 0.5%, and the surface roughness values were 90°: 5.9 ± 0.3 μm, 85°: 8.5 ± 1.1 μm, and 80°: 8.5 ± 0.4 μm. As the spray angle decreased, the porosity increased, but the surface roughness did not show a significant difference. Vickers hardness measurements revealed values of 90°: 369.2 ± 22.3, 85°: 315.8 ± 31.4, and 80°: 267.1 ± 45.1 HV. It was found that under the condition of a 90° angle with the lowest porosity exhibited the best hardness value. Based on the aforementioned results, an improved method for the APS Y2O3 coating layer was also discussed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Effect of In Situ Laser-Assisted Plasma Spraying on the Plasma Etching Resistance of Yttrium Oxide Coating
Xutao Zhao, Tian Xie, Panpan Zhang, Zhehe Yao, Qunli Zhang, Jiake Deng, Yongfeng Sui, Jianhua Yao
Coatings.2024; 14(11): 1427. CrossRef - Investigation of contamination particles generation and surface chemical reactions on Al2O3, Y2O3, and YF3 coatings in F-based plasma
Jongho So, Minjoong Kim, Hyuksung Kwon, Seonjeong Maeng, Eunmi Choi, Chin-Wook Chung, Ju-Young Yun
Applied Surface Science.2023; 629: 157367. CrossRef - Cleaning Effect of Atmospheric-Plasma-Sprayed Y2O3 Coating Using Piranha Solution Based on Contamination Particle Measurement
Hyuksung Kwon, Minjoong Kim, Jongho So, Seonjeong Maeng, Jae-Soo Shin, Ju-Young Yun
Coatings.2023; 13(3): 653. CrossRef - The effect of powder particle size on the corrosion behavior of atmospheric plasma spray-Y2O3 coating: Unraveling the corrosion mechanism by fluorine-based plasma
Minjoong Kim, Eunmi Choi, Dongjin Lee, Jungpil Seo, Tae-Sun Back, Jongho So, Ju-Young Yun, Song-Moon Suh
Applied Surface Science.2022; 606: 154958. CrossRef - The Effect of Powder Particle Size on the Corrosion Behavior of Atmospheric Plasma Spray-Y2o3 Coating: Unraveling the Corrosion Mechanism by Fluorine-Based Plasma
Minjoong Kim, Eunmi Choi, Dongjin Lee, Jungpil Seo, Tae Sun Back, Jongho So, Ju-Young Yun, Song-Moon Suh
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Liquid Al Erosion Property of Tribaloy T-800 Coating Material Manufactured by Laser Cladding Process
-
Kyoung-Wook Kim, Gi-Su Ham, Sun-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):210-218. Published online June 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.210
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
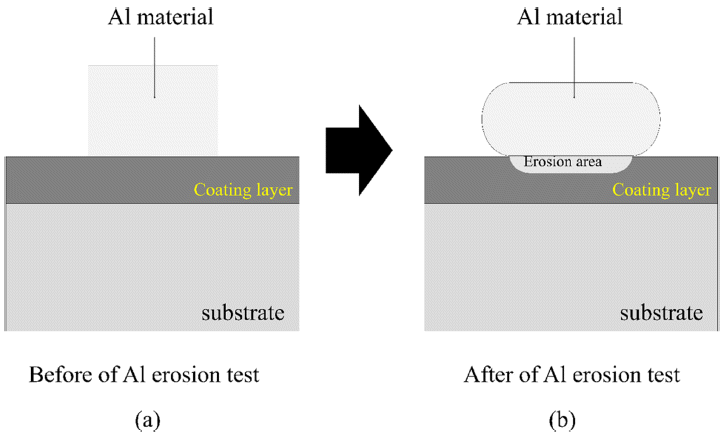
A T-800 (Co-Mo-Cr) coating material is fabricated using Co-Mo-Cr powder feedstock and laser cladding. The microstructure and melted Al erosion properties of the laser-cladded T-800 coating material are investigated. The Al erosion properties of the HVOF-sprayed MoB-CoCr and bulk T-800 material are also examined and compared with the laser-cladded T-800 coating material. Co and lave phases (Co2MoCr and Co3Mo2Si) are detected in both the lasercladded T-800 coating and the bulk T-800 materials. However, the sizes of the lave phases are measured as 7.9 μm and 60.6 μm for the laser-cladded and bulk T-800 materials, respectively. After the Al erosion tests, the erosion layer thicknesses of the three materials are measured as 91.50 μm (HVOF MoB-CoCr coating), 204.83 μm (laser cladded T-800), and 226.33 μm (bulk T-800). In the HVOF MoB-CoCr coating material, coarse cracks and delamination of the coating layer are observed. On the other hand, no cracks or local delamination of the coating layer are detected in the laser T-800 material even after the Al erosion test. Based on the above results, the authors discuss the appropriate material and process that could replace conventional bulk T-800 materials used as molten Al pots.
|