- [English]
- Enhancing the Dispersion Stability of Exfoliated MoS2 Nanoflakes for Na⁺ Intercalation
-
Jae Min Sung, Dong-Won Kyung, Ammad Ali, Kee-Ryung Park, Mi Hye Lee, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum Sung Kim, Haejin Hwang, Leeseung Kang, Yoseb Song
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00255
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
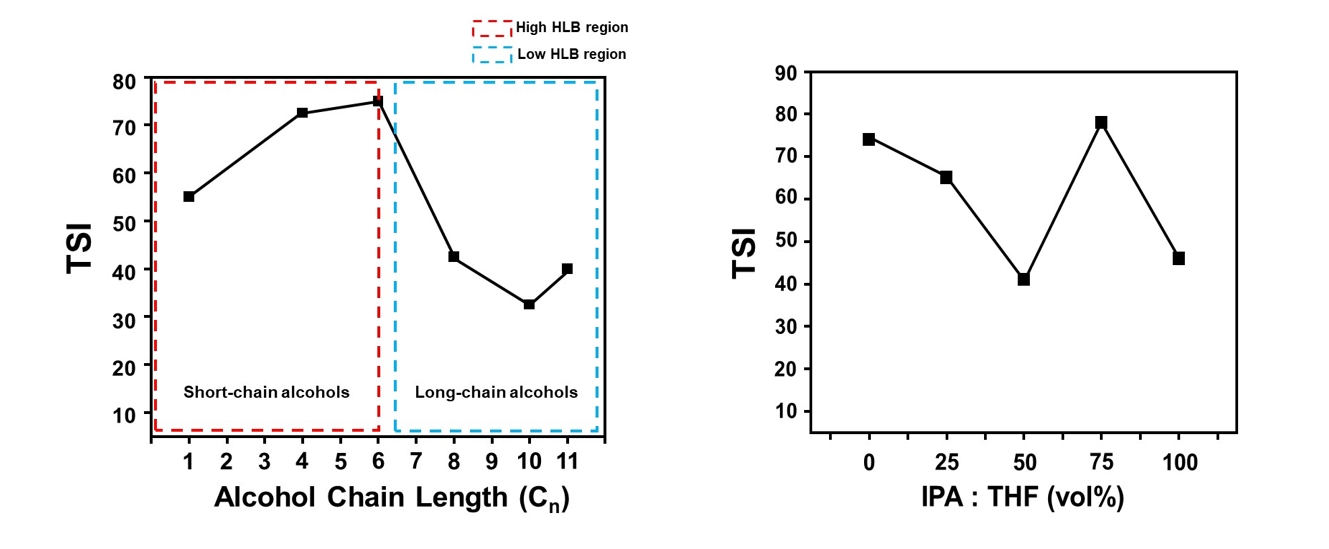
- This study investigated the dispersion stability of exfoliated MoS₂ nanoflakes in various organic solvents and binary mixtures using a Turbiscan optical analyzer. Sedimentation behavior was quantitatively evaluated via transmittance variation (ΔT), backscattering variation (ΔBS), and the Turbiscan stability index (TSI). Alcohol-based solvents were categorized by hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values. Long-chain alcohols, such as 1-undecanol, showed increased stability due to high viscosity and strong hydrophobic affinity with MoS2 basal planes, while short-chain alcohols exhibited poor stabilization. Binary mixtures of isopropanol (IPA) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were also assessed, with the 5:5 volume ratio showing the best stability profile, including the lowest TSI and minimal ΔT and ΔBS values. This improvement is attributed to synergistic interactions, as IPA stabilizes hydrophilic edge sites, while THF engages with hydrophobic basal surfaces. These findings highlight the importance of balancing physicochemical properties when selecting solvents to improve MoS2 dispersion for structural modification and electrocatalytic applications.
- [Korean]
- Optimization of Mechanical Properties in WC–Mo₂C–Co Cemented Carbides via Dual Hard-Phase Based Heterogeneous Microstructure Design
-
Jinwoo Seok, Jong Tae Kim, Juree Jung, SongYi Kim, Bin Lee, Junhee Han, Leeseung Kang
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):428-436. Published online October 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00297
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
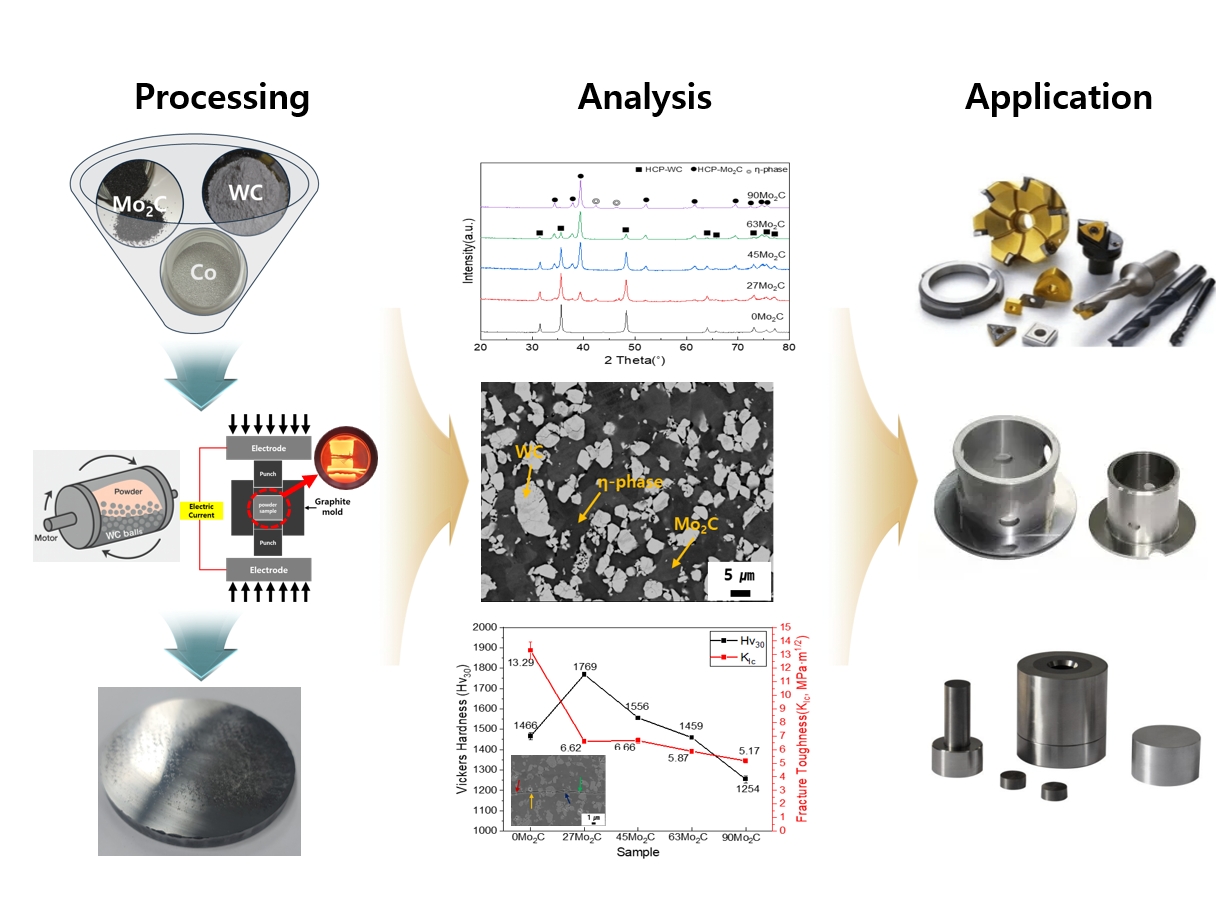
- WC–Mo₂C–Co cemented carbides were fabricated to investigate the effects of Mo₂C addition on microstructure and mechanical properties. Dual hard-phase design using WC and Mo₂C was employed to optimize the balance between hardness and toughness. Spark plasma sintering (SPS) was conducted at various temperatures after ball milling, and 1300 °C for 5 min was identified as the optimized sintering condition, achieving complete densification and phase stability. The addition of Mo₂C refined the microstructure by suppressing abnormal WC grain growth through preferential dissolution of Mo₂C into the Co binder. Hardness increased up to 1769 Hv30 due to grain refinement and solid-solution strengthening, while promoted η-phase formation and reduced fracture toughness.The 27Mo₂C composition exhibited the most balanced combination of hardness and toughness. These results demonstrate that controlled Mo₂C addition enables dual hard-phase strengthening and microstructure optimization in WC–Mo₂C–Co carbides for advanced cutting and forming applications.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Properties of InP/ZnS core/shell Nanoparticles with One-pot process
-
So Yeong Joo, Myung Hwan Hong, Leeseung Kang, Tae Hyung Kim, Chan Gi Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):11-16. Published online February 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.11
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
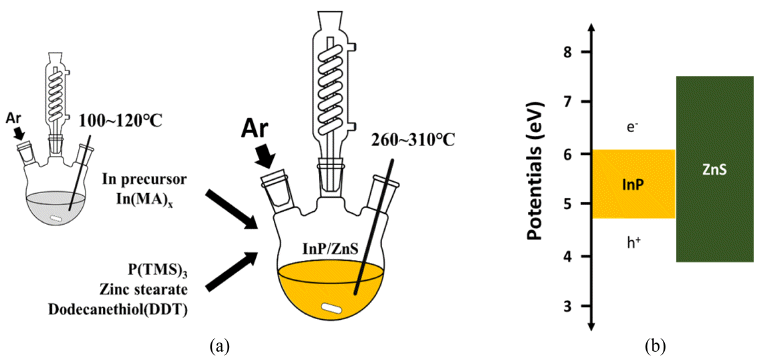
In this study, simple chemical synthesis of green emitting Cd-free InP/ZnS QDs is accomplished by reacting In, P, Zn, and S precursors by one-pot process. The particle size and the optical properties were tailored, by controlling various experimental conditions, including [In]/[MA] (MA: myristic acid) mole ratio, reaction temperature and reaction time. The results of ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV-vis), and of photoluminescence (PL), reveal that the exciton emission of InP was improved by surface coating, with a layer of ZnS. We report the correlation between each experimental condition and the luminescent properties of InP/ZnS core/shell QDs. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) techniques were used to characterize the as-synthesized QDs. In contrast to core nanoparticles, InP/ZnS core/shell treated with surface coating shows a clear ultraviolet peak. Besides this work, we need to study what clearly determines the shell kinetic growth mechanism of InP/ZnS core shell QDs.
- [Korean]
- Current Technology Trends Analysis on the Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Fluorescent Substance in the Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps of Waste Flat Panel Displays
-
Leeseung Kang, Dongyoon Shin, Jieun Lee, Joong Woo Ahn, Hyun-Seon Hong
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):27-31. Published online February 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.27
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Flat panel display devices are mainly used as information display devices in the 21st century. The worldwide waste flat panel displays are expected at 2-3 million units but most of them are land-filled for want of a proper recycling technology More specifically, rare earth metals of La and Eu are used as fluorescent materials of Cold Cathode Flourscent Lamp(CCFL)s in the waste flat panel displays and they are critically vulnerable and irreplaceable strategic mineral resources. At present, most of the waste CCFLs are disposed of by land-filling and incineration and proper recovery of 80-plus tons per annum of the rare earth fluorescent materials will significantly contribute to steady supply of them. A dearth of Korean domestic research results on recovery and recycling of rare earth elements in the CCFLs prompts to initiate this status report on overseas research trends and noteworthy research results in related fields.
- [English]
- Effect of Bimodal WC Particle Size Distribution on the Mechanical Properties of WC–Mo2C–Co Cemented Carbides
-
Jinwoo Seok, Jong Tae Kim, Juree Jung, Bin Lee, Junhee Han, Leeseung Kang
-
Received December 16, 2025 Accepted February 27, 2026 Published online February 27, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00500
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
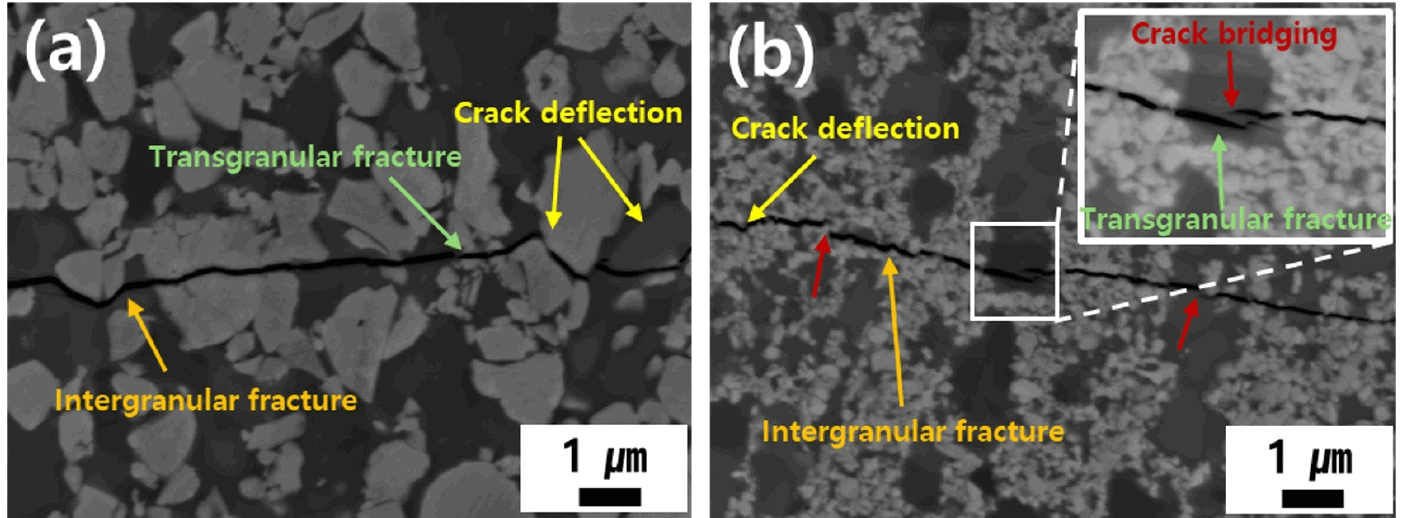
- In this study, the influence of bimodal WC particle size design on the microstructure and mechanical properties of WC–27 wt.% Mo₂C–10 wt.% Co cemented carbides was systematically investigated. Bimodal hard-phase designs were realized by combining ultrafine WC (300 nm) and coarse WC (1.8 μm) at various ratios, followed by consolidation via spark plasma sintering (SPS). During sintering, Mo₂C preferentially dissolved into the Co-rich liquid phase due to its higher solubility than WC, forming a Co–Mo–C liquid. During sintering progresses, ultrafine WC selectively dissolved owing to its high interfacial energy, gradually transforming the liquid composition into a Co–Mo–W–C system. Owing to the short holding time and rapid cooling rate of SPS, the η-phase (M₆C) formed during sintering remained metastable. Meanwhile, selective dissolution–reprecipitation resulted in the formation of Mo₂C-based core–rim structures with W enrichment in the rim region as (Mo, W)₂C. As the fraction of ultrafine WC increased, the hardness increased from 1769 to 1997 kgf/mm2, whereas the fracture toughness exhibited an insignificant difference from 6.56 to 6.65 MPa•m¹ᐟ². Fracture behavior analysis revealed that crack deflection and crack bridging occurred at the Mo₂C core–rim interfaces, effectively suppressing straight crack propagation. These results demonstrate that the introduction of ultrafine WC plays a dominant role in enhancing mechanical performance, and that bimodal WC design combined with Mo₂C addition is a highly effective strategy for developing high-performance cemented carbides for machining
|