- [Korean]
- 3D-Printed Stretchable Electrodes Enabled by a Titanium/Acrylamide-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposite
-
Se Jin Choi, Han Eol Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):67-72. Published online February 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00465
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
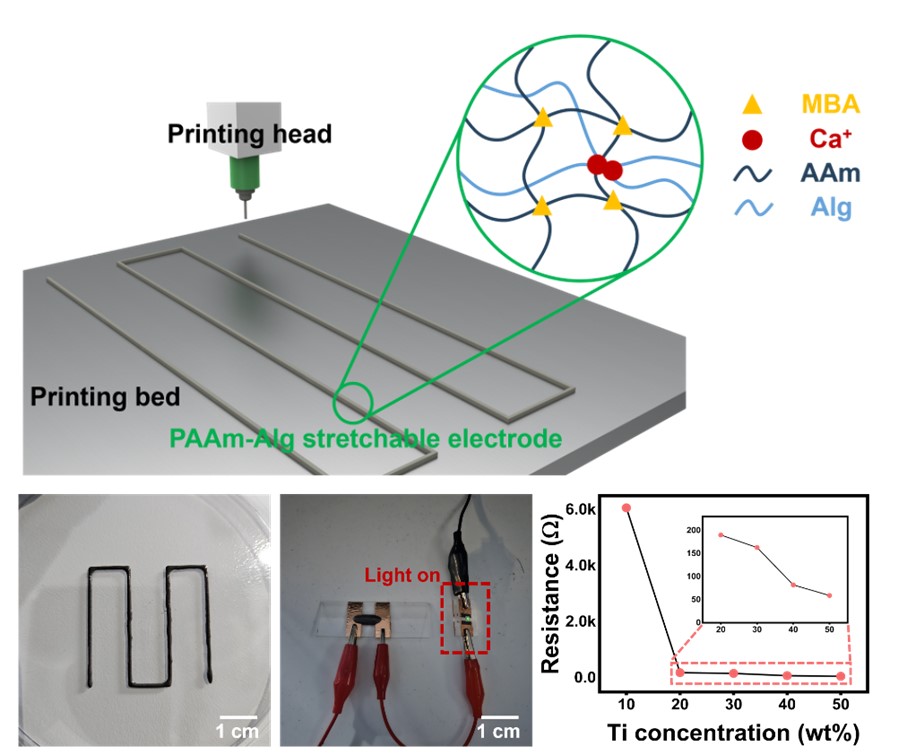
- Wearable electronics have been the focus of considerable interest in various fields, such as human-machine interfaces, soft robotics, and medical treatments, due to their flexibility, stretchability, and light weight. To address the shortcomings of existing metal thin film-based wearable devices, stretchable conductive polymers have been developed. In particular, double networking hydrogels are being actively studied as a polymer with a three-dimensional stereoscopic structure that can be patterned. Nonetheless, they have shortcomings such as poor electrical properties and cumbersome manufacturing processes, making it difficult to apply them in electronic devices. Herein, we report 3D-printed stretchable electrodes enabled by a titanium/polyacrylamide-alginate-based hydrogel nanocomposite. This research suggests the strategy for resolving the challenges of high costs and complex fabrication processes associated with stretchable electrode, providing a solution to accelerate the commercialization of wearable electronic devices.
|