- [Korean]
- Effect of Iron Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Mo-Fe P/M Alloys
-
HyoWoon Hwang, YongJae Lee, JiHwan Park, Dong-Geun Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):325-331. Published online August 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.325
-
-
322
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
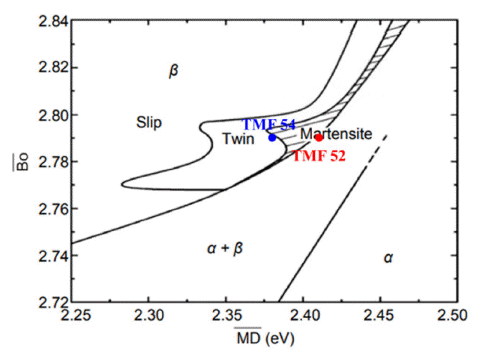
Beta-titanium alloys are used in many industries due to their increased elongation resulting from their BCC structure and low modulus of elasticity. However, there are many limitations to their use due to the high cost of betastabilizer elements. In this study, biocompatible Ti-Mo-Fe beta titanium alloys are designed by replacing costly betastabilizer elements (e.g., Nb, Zr, or Ta) with inexpensive Mo and Fe elements. Additionally, Ti-Mo-Fe alloys designed with different Fe contents are fabricated using powder metallurgy. Fe is a strong, biocompatible beta-stabilizer element and a low-cost alloying element. The mechanical properties of the Ti-Mo-Fe metastable beta titanium alloys are analyzed in relation to the microstructural changes. When the Fe content increases, the tensile strength and elongation decrease due to brittle fracture despite a decreasing pore fraction. It is confirmed that the hardness and tensile strength of Ti-5Mo-2Fe P/M improve to more than 360 Hv and 900 MPa, respectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication of Ti-Mo Core-shell Powder and Sintering Properties for Application as a Sputtering Target
Won Hee Lee, Chun Woong Park, Heeyeon Kim, Yuncheol Ha, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 43. CrossRef - Effect of Strain Rate on Deformation Behaviors of Ti-12.1Mo -1Fe Metastable Beta Alloy
In Kyeong Jin, Dong-Geun Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(10): 741. CrossRef
|