- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of BaTiO3 Nanoparticles Using a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
-
Young Hwangbo, Young-In Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):326-331. Published online August 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.326
-
-
820
View
-
5
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The structural formation of inorganic nanoparticles dispersed in polymer matrices is a key technology for producing advanced nanocomposites with a unique combination of optical, electrical, and mechanical properties. Barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanoparticles are attractive for increasing the refractive index and dielectric constant of polymer nanocomposites. Current synthesis processes for BaTiO3 nanoparticles require expensive precursors or organic solvents, complicated steps, and long reaction times. In this study, we demonstrate a simple and continuous approach for synthesizing BaTiO3 nanoparticles based on a salt-assisted ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. This process allows the synthesis of BaTiO3 nanoparticles with diameters of 20-50 nm and a highly crystalline tetragonal structure. The optical properties and photocatalytic activities of the nanoparticles show that they are suitable for use as fillers in various nanocomposites. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Sr doping effects on La(1-x)SrxMnO3-BaTiO3 nanocomposites: A comprehensive analysis of structural, optical, magnetic, and dielectric properties
Milad Karamzadeh-Jahromi, Morteza Izadifard, Mohammad Ebrahim Ghazi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 1006: 176272. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Microstructure and Electrical Properties of Silver Conductive Features Using a Powder Composed of Silver
nanoparticles and Nanoplatelets
-
Yong-Sung Goo, Yong-Ho Choa, Young Hwangbo, Young-In Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):358-363. Published online October 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.358
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Noncontact direct-printed conductive silver patterns with an enhanced electrical resistivity are fabricated using a silver ink with a mixture of silver nanoparticles and nanoplates. The microstructure and electrical resistivity of the silver pattern are systematically investigated as a function of the mixing ratio of the nanoparticles and nanoplates. The pattern, which is fabricated using a mixture with a mixing ratio of 3(nanoparticles):7(nanoplates) and sintered at 200°C shows a highly dense and well-sintered microstructure and has a resistivity of 7.60 μΩ·cm. This originates a mutual synergistic effect through a combination of the sinterability of the nanoparticles and the packing ability of the nanoplates. This is a conductive material that can be used to fabricate noncontact direct-printed conductive patterns with excellent electrical conductivity for various flexible electronics applications, including solar cells, displays, RFIDs, and sensors.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of a TiOF2 Powder via an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
-
Young Hwangbo, Young-In Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):307-310. Published online August 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.307
-
-
585
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
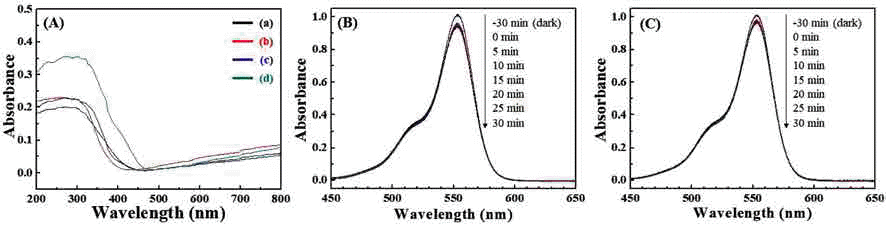
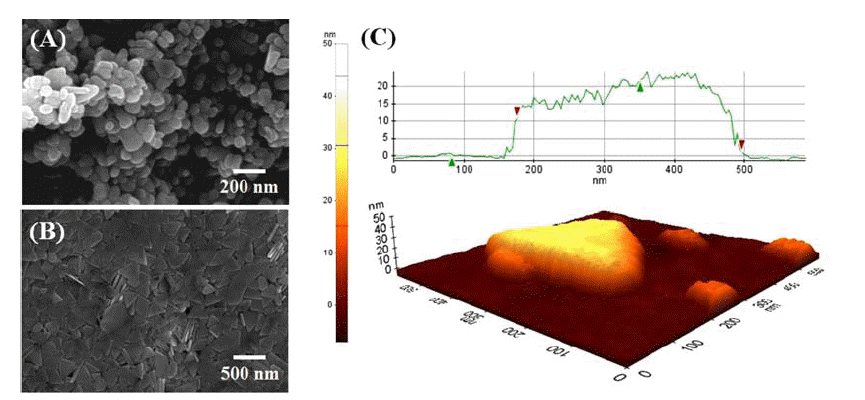
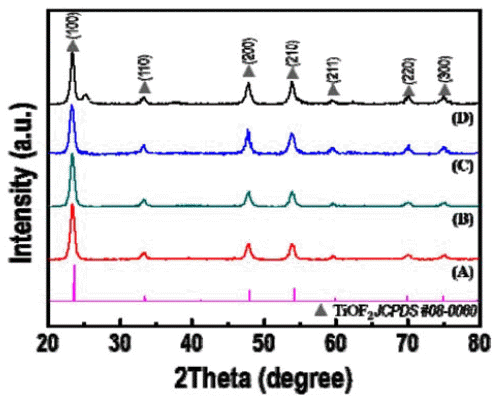
TiOF2, which has remarkable electrochemical and optical properties, is used in various applications such as Li-ion batteries, electrochemical displays, and photocatalysts. In addition, it is possible to utilize the template which is allowed to synthesize fluorine doped TiO2 powders with hollow or faceted structures. However, common synthesis methods of TiOF2 powders have some disadvantages such as the use of expensive and harmful precursors and batchtype processes with a limited production scale. In this study, we report a synthetic route for preparing TiOF2 powders by using an inexpensive and harmless precursor and a continuous ultrasonic spray pyrolysis process under a controlled atmosphere to address the aforementioned problems. The synthesized powder has an average size of 1 μm, a spherical shape, a pure TiOF2 phase, and exhibits a band-gap energy of 3.2 eV. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
Jong Min Byun, Chun Woong Park, Young In Kim, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 257. CrossRef
|