Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Articles
- [Korean]
- Effect of Fe and Cr on ω Phase Formation in Metastable β-Ti Alloy
- Sun-Young Park, Young-Bum Chun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):354-360. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00220

- 970 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the effects of Fe and Cr contents on ω phase formation and transformation during solution treatment and the subsequent aging process, for which four model alloys with varying Fe and Cr contents but keeping Mo equivalent of ~ 12.6 were prepared by plasma arc melting and fabricated into plates by hot forging followed by hot-rolling. The atherrmal ω phase was observed in all Ti alloys after solution treatment followed by water quenching through XRD and TEM analysis. The largest volume fraction of athermal ω phase is formed in Ti alloy with only Fe 4 wt.% among all Ti alloys, leading to the highest Vickers value due to hardening effect ω phase. It was found that not only Mo equivalent but also each characteristic of β stabilizing elements should be considered to understand a microstructure evolution and mechanical properties.
- [Korean]
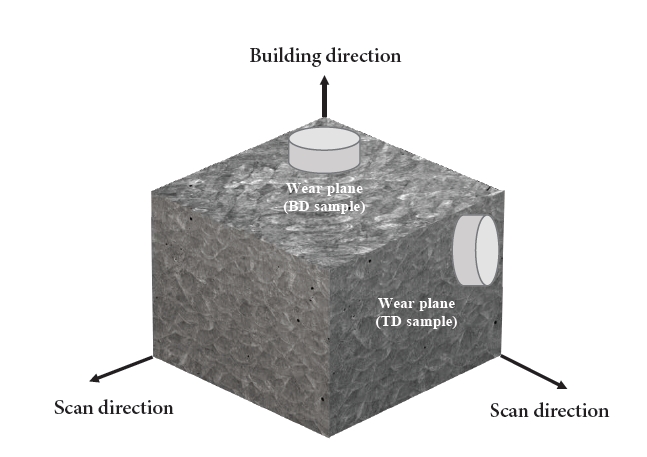
- Effect of Anisotropy on the Wear Behavior of Age-Treated Maraging Steel Manufactured by LPBF
- Seung On Lim, Se-Eun Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):308-317. Published online August 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00171
- 2,017 View
- 37 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Maraging steel has excellent mechanical properties resulting from the formation of precipitates within the matrix through aging treatment. Maraging steel fabricated by the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process is suitable for applications including precise components and optimized design. The anisotropic characteristic, which depends on the stacking direction, affects the mechanical properties. This study aimed to analyze the influence of anisotropy on the wear behavior of maraging steel after aging treatment. The features of additive manufacturing tended to disappear after heat treatment. However, some residual cellular and dendrite structures were observed. In the wear tests, a high wear rate was observed on the building direction plane for all counter materials. This is believed to be because the oxides formed on the wear track positively affected the wear characteristics; meanwhile, the bead shape in the stacking direction surface was vulnerable to wear, leading to significant wear.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
Godwin Kwame Ahiale, Jin Woong Park, Raj Narayan Hajra, Yong-Jun Oh, Won Doo Choi, Tae-Wook Na, Gi Yong Kim, Hyun-Ju Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 949: 149397. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


