Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Effect of the Cross-rolling Process on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of 9Cr-1W ODS Steel
- Bu-An Kim, Sanghoon Noh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):37-42. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00332
- 873 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
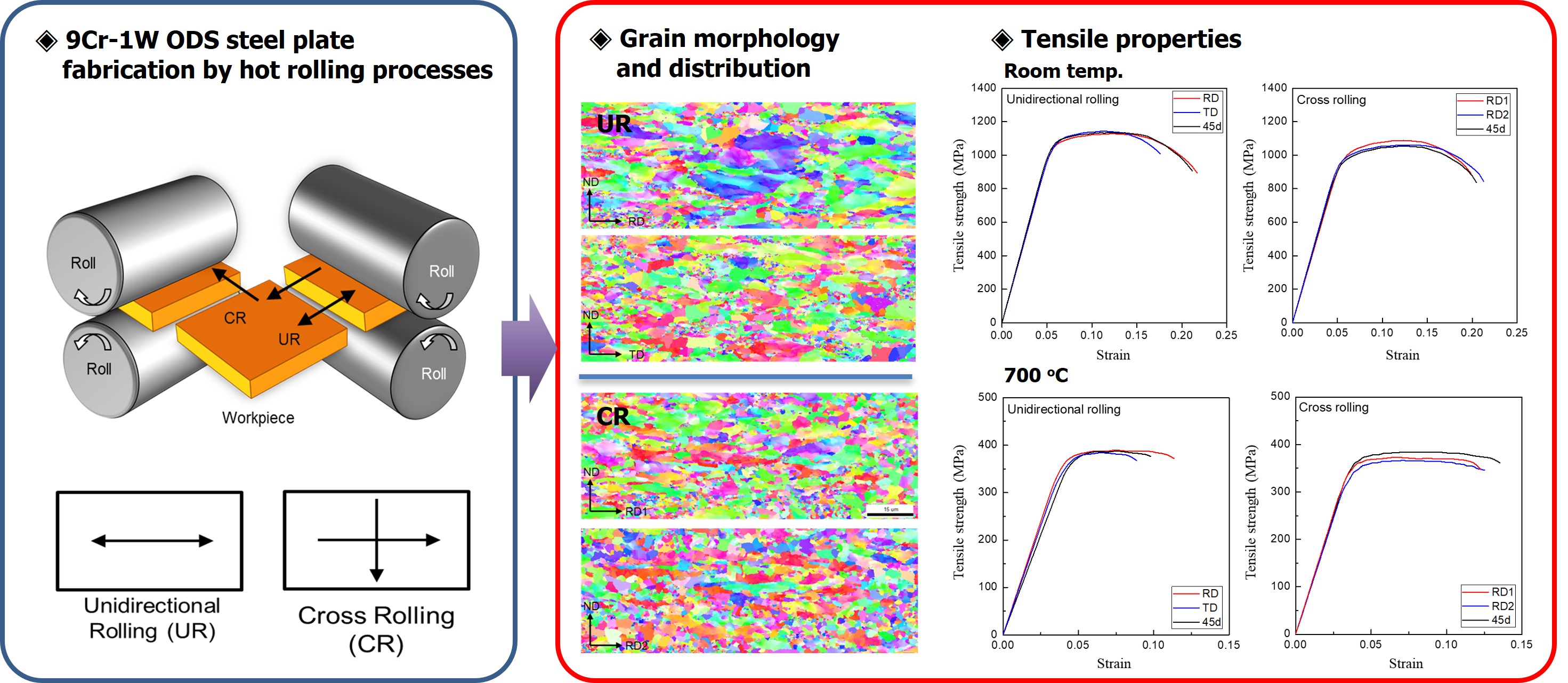
PDF - This study employed a cross-rolling process to fabricate oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel plates and investigated their microstructures and mechanical properties. The 9Cr-1W ODS ferritic steel was fabricated using mechanical alloying and hot isostatic pressing. The hot cross-rolling process produced thick ODS ferritic steel plates with a well-extended rectangular shape. The working direction greatly affected the grain structure and crystal texture of the ODS ferritic steel. Cross-rolled plates showed fine micro-grains with random crystal orientation, while unidirectionally rolled plates exhibited a strong orientation with larger, elongated grains. Transmission electron microscopy revealed a uniform distribution of nano-oxide particles in both rolling methods, with no major differences. Tensile tests of the ODS ferritic steel plates showed that the unidirectional rolled plates had anisotropic elongation, while cross-rolled plates exhibited isotropic behavior with uniform elongation. Cross-rolling produced finer, more uniform grains, reducing anisotropy and improving mechanical properties, making it ideal for manufacturing wide ODS steel components.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Anisotropy on the Wear Behavior of Age-Treated Maraging Steel Manufactured by LPBF
- Seung On Lim, Se-Eun Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):308-317. Published online August 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00171
- 1,904 View
- 36 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
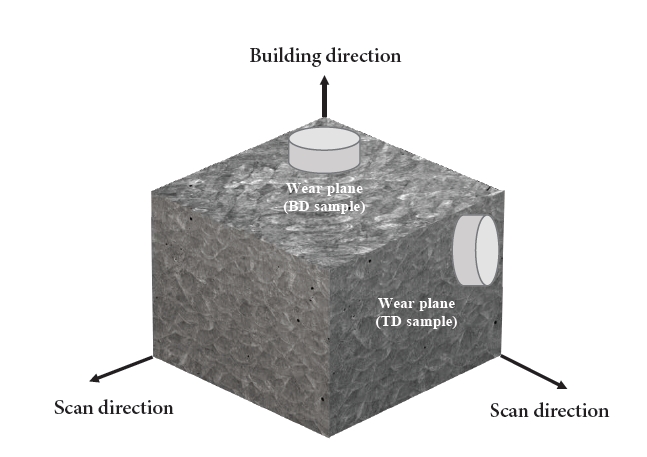
PDF - Maraging steel has excellent mechanical properties resulting from the formation of precipitates within the matrix through aging treatment. Maraging steel fabricated by the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process is suitable for applications including precise components and optimized design. The anisotropic characteristic, which depends on the stacking direction, affects the mechanical properties. This study aimed to analyze the influence of anisotropy on the wear behavior of maraging steel after aging treatment. The features of additive manufacturing tended to disappear after heat treatment. However, some residual cellular and dendrite structures were observed. In the wear tests, a high wear rate was observed on the building direction plane for all counter materials. This is believed to be because the oxides formed on the wear track positively affected the wear characteristics; meanwhile, the bead shape in the stacking direction surface was vulnerable to wear, leading to significant wear.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
Godwin Kwame Ahiale, Jin Woong Park, Raj Narayan Hajra, Yong-Jun Oh, Won Doo Choi, Tae-Wook Na, Gi Yong Kim, Hyun-Ju Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 949: 149397. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
- [Korean]
- Effect of Change in Open Porosity as a Function of Uniaxial Molding Pressure on Density Improvement After Impregnation
- Sang-Min Lee, Sang-Hye Lee, Jae-Seung Roh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):7-12. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.7

- 1,345 View
- 22 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The change in the open porosity of bulk graphite as a function of the uniaxial molding pressure during manufacturing is studied using artificial graphite powder. Subsequently, the graphite is impregnated to determine the effect of the open porosity on the impregnation efficiency and to improve the density of the final bulk graphite. Bulk graphite is manufactured with different uniaxial molding pressures after mixing graphite powder, which is the by-product of processing the final graphite products and phenolic resin. The bulk density and open porosity are measured using the Archimedes method. The bulk density and open porosity of bulk graphite increase as the molding pressure increases. The open porosity of molded bulk graphite is 25.35% at 30 MPa and 29.84% at 300 MPa. It is confirmed that the impregnation efficiency increases when the impregnation process is performed on a specimen with large open porosity. In this study, the bulk density of bulk graphite molded at 300 MPa is 11.06% higher than that before impregnation, which is the highest reported increase. Therefore, it is expected that the higher the uniaxial pressure, the higher the density of bulk graphite.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving the packing and mechanical properties of graphite blocks by controlling filler particle-size distribution
Hye in Hwang, Ji Hong Kim, Ji Sun Im
Advanced Composite Materials.2024; 33(5): 762. CrossRef - Effect of Pressure and Holding Time during Compression Molding on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Coke-Pitch Carbon Blocks
Sun-Ung Gwon, Sang-Hye Lee, U-Sang Youn, Jae-Seung Roh
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(2): 772. CrossRef - Correlation between Pitch Impregnation Pressure and Pore Sizes of Graphite Block
Changkyu Kim, Woong Kwon, Moon Hee Lee, Jong Seok Woo, Euigyung Jeong
Materials.2022; 15(2): 561. CrossRef
- Improving the packing and mechanical properties of graphite blocks by controlling filler particle-size distribution
- [Korean]
- Effect of Porosity on Mechanical Anisotropy of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Additively Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting
- Jeong Min Park, Jin Myoung Jeon, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):475-481. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.475
- 1,184 View
- 12 Download
- 12 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
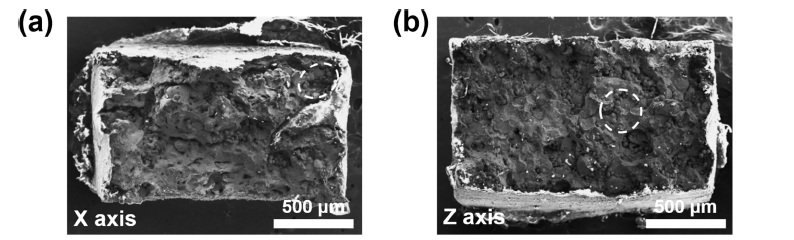
PDF Selective laser melting (SLM), a type of additive manufacturing (AM) technology, leads a global manufacturing trend by enabling the design of geometrically complex products with topology optimization for optimized performance. Using this method, three-dimensional (3D) computer-aided design (CAD) data components can be built up directly in a layer-by-layer fashion using a high-energy laser beam for the selective melting and rapid solidification of thin layers of metallic powders. Although there are considerable expectations that this novel process will overcome many traditional manufacturing process limits, some issues still exist in applying the SLM process to diverse metallic materials, particularly regarding the formation of porosity. This is a major processing-induced phenomenon, and frequently observed in almost all SLM-processed metallic components. In this study, we investigate the mechanical anisotropy of SLM-produced 316L stainless steel based on microstructural factors and highly-oriented porosity. Tensile tests are performed to investigate the microstructure and porosity effects on mechanical anisotropy in terms of both strength and ductility.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of temperature and impact loading condition on deformation behavior in 316L austenitic stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Tae Hyeong Kim, Haeum Park, Jun Seok Lee, Jeong Min Park, Jae Wung Bae
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 933: 148286. CrossRef - Selective laser melting additive manufactured H13 tool steel for aluminum extrusion die component construction
Evangelos Giarmas, Vasileios Tsakalos, Emmanuel Tzimtzimis, Nikolaos Kladovasilakis, Ioannis Kostavelis, Dimitrios Tzovaras, Dimitrios Tzetzis
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2024; 133(9-10): 4385. CrossRef - Nanoindentation Creep Behavior of Additively Manufactured H13 Steel by Utilizing Selective Laser Melting Technology
Evangelos Giarmas, Emmanouil K. Tzimtzimis, Nikolaos Kladovasilakis, Dimitrios Tzovaras, Dimitrios Tzetzis
Materials.2024; 17(15): 3756. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef - Development of multi-defect diagnosis algorithm for the directed energy deposition (DED) process with in situ melt-pool monitoring
Hyewon Shin, Jimin Lee, Seung-Kyum Choi, Sang Won Lee
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2023; 125(1-2): 357. CrossRef - Corrosion Resistance of Laser Powder Bed Fused AISI 316L Stainless Steel and Effect of Direct Annealing
Kichang Bae, Dongmin Shin, Jonghun Lee, Seohan Kim, Wookjin Lee, Ilguk Jo, Junghoon Lee
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6336. CrossRef - Experimental investigation on the effect of process parameters in additive/subtractive hybrid manufacturing 316L stainless steel
Chengming Tang, Jibin Zhao, Zhiguo Wang, Yuhui Zhao, Tianran Wang
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2022; 121(3-4): 2461. CrossRef - Interface characteristics and mechanical behavior of additively manufactured multi-material of stainless steel and Inconel
Man Jae Sagong, Eun Seong Kim, Jeong Min Park, Gangaraju Manogna Karthik, Byeong-Joo Lee, Jung-Wook Cho, Chong Soo Lee, Takayoshi Nakano, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2022; 847: 143318. CrossRef - Effect of heat treatment on microstructural heterogeneity and mechanical properties of 1%C-CoCrFeMnNi alloy fabricated by selective laser melting
Jeong Min Park, Eun Seong Kim, Hyeonseok Kwon, Praveen Sathiyamoorthi, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim
Additive Manufacturing.2021; 47: 102283. CrossRef - Manufacturing Aluminum/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composites via Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Eo Ryeong Lee, Se Eun Shin, Naoki Takata, Makoto Kobashi, Masaki Kato
Materials.2020; 13(18): 3927. CrossRef - Effects of microstructure and internal defects on mechanical anisotropy and asymmetry of selective laser-melted 316L austenitic stainless steel
Jin Myoung Jeon, Jeong Min Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2019; 763: 138152. CrossRef - Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef
- Effect of temperature and impact loading condition on deformation behavior in 316L austenitic stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


