Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- The Influence of a Single Melt Pool Morphology on Densification Behavior of Three-Dimensional Structure Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing
- Jungho Choe, Jaecheol Yun, Dong-Yeol Yang, Sangsun Yang, Ji-Hun Yu, Chang-Woo Lee, Yong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;24(3):187-194. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.187
- 937 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
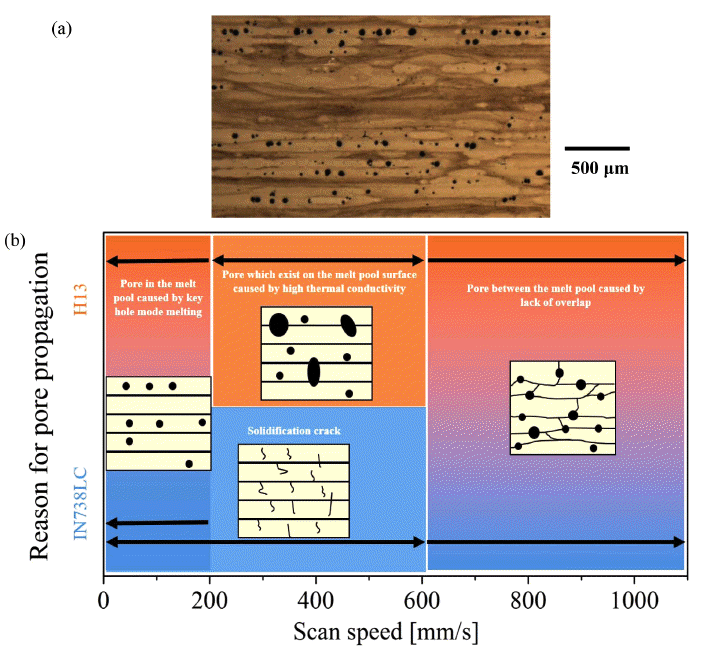
PDF Selective laser melting (SLM) can produce a layer of a metal powder and then fabricate a three-dimensional structure by a layer-by-layer method. Each layer consists of several lines of molten metal. Laser parameters and thermal properties of the materials affect the geometric characteristics of the melt pool such as its height, depth, and width. The geometrical characteristics of the melt pool are determined herein by optical microscopy and three-dimensional bulk structures are fabricated to investigate the relationship between them. Powders of the commercially available Fe-based tool steel AISI H13 and Ni-based superalloy Inconel 738LC are used to investigate the effect of material properties. Only the scan speed is controlled to change the laser parameters. The laser power and hatch space are maintained throughout the study. Laser of a higher energy density is seen to melt a wider and deeper range of powder and substrate; however, it does not correspond with the most highly densified three-dimensional structure. H13 shows the highest density at a laser scan speed of 200 mm/s whereas Inconel 738LC shows the highest density at 600 mm/s.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef - Correlation between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Additive Manufactured H13 Tool Steel
Woojin An, Junhyeok Park, Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Im Doo Jung, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Hyokyung Sung
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(11): 663. CrossRef - Effect of Porosity on Mechanical Anisotropy of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Additively Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting
Jeong Min Park, Jin Myoung Jeon, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(6): 475. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Accuracy of Dental Prostheses manufactured by Metal 3D Printer
Junho Hwang, Yun-Ho Kim, Hyun-Deok Kim, Kyu-Bok Lee
Journal of Welding and Joining.2018; 36(5): 70. CrossRef - A study about sculpture characteristic of SKD61 tool steel fabricated by selective laser melting(SLM) process
Jaecheol Yun, Jungho Choe, Ki-Bong Kim, Sangsun Yang, Dong-Yeol Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Chang-Woo Lee, Chang-Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(2): 137. CrossRef
- Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
- [Korean]
- Analyses of Densification and Consolidation of Copper Powders during High-Pressure Torsion Process Using Finite Element Method
- Dong Jun Lee, Eun Yoo Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):6-9. Published online February 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.6
- 869 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
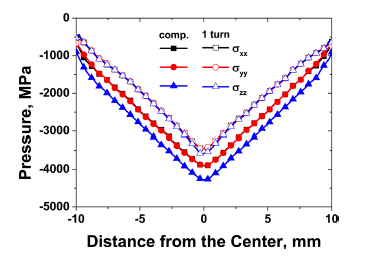
PDF In this study, the behavior of densification of copper powders during high-pressure torsion (HPT) at room temperature is investigated using the finite element method. The simulation results show that the center of the workpiece is the first to reach the true density of copper during the compressive stage because the pressure is higher at the center than the periphery. Subsequently, whole workpiece reaches true density after compression due to the high pressure. In addition, the effective strain is increased along the radius during torsional stage. After one rotation, the periphery shows that the effective strain is increased up to 25, which is extensive deformation. These high pressure and severe strain do not only play a key role in consolidation of copper powders but also make the matrix harder by grain refinement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
Soo-Hyun Joo, Dong-Hai Pi, Jing Guo, Hidemi Kato, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(3): 383. CrossRef
- Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
- [English]
- Densification Behavior of Rhenium Alloy using Master Sintering Curve
- Dong Yong Park, Yong Jun Oh, Young Sam Kwon, Seong Taek Lim, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):7-15. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.7
- 1,270 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
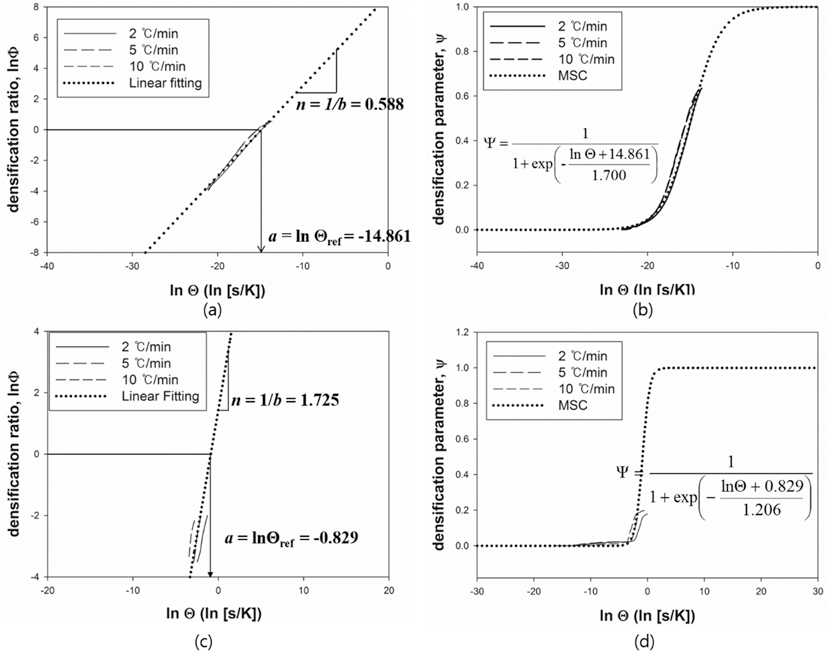
PDF This study investigated the densification behavior of rhenium alloys including W-25 wt.%Re and Re-2W- 1Ta (pure Re) during sintering. The dilatometry experiments were carried out to obtain the
in-situ shrinkage in H2 atmosphere. The measured data was analyzed through shrinkage, strain rate and relative density, and then symmetrically treated to construct the linearized form of master sintering curve (MSC) and MSC as a well-known and straightforward approach to describe the densification behavior during sintering. The densification behaviors for each material were analyzed in many respects including apparent activation energy, densification parameter, and densification ratio. MSC with a minimal set of preliminary experiments can make the densification behavior to be characterized and predicted as well as provide guideline to sinter cycle design. Considering the results of linearized form and MSC, it was confirmed that the W-25 wt.%Re compared to Pure Re is more easily densified at the relatively low temperature.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The influence of sintering time on the microstructural properties of chromium-rhenium matrix composites
Marcin Chmielewski, Szymon Nosewicz, Dorota Jakubowska, Małgorzata Lewandowska, Jarosław Mizera, Jerzy Rojek, Piotr Bazarnik
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2016; 59: 78. CrossRef
- The influence of sintering time on the microstructural properties of chromium-rhenium matrix composites
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


