Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Perforated Polygonal Cobalt Oxides using a Carbon Nanofiber Template
- Dong-Yo Sin, Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):350-355. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.350
- 826 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
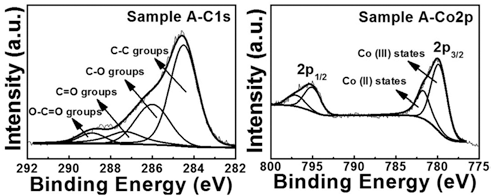
PDF Perforated polygonal cobalt oxide (CO3O4) is synthesized using electrospinning and a hydrothermal method followed by the removal of a carbon nanofiber (CNF) template. To investigate their formation mechanism, thermogravimetric analysis, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Xray photoelectron spectroscopy are examined. To obtain the optimum condition of perforated polygonal CO3O4, we prepare three different weight ratios of the Co precursor and the CNF template: sample A (Co precursor:CNF template- 10:1), sample B (Co precursor:CNF template-3.2:1), and sample C (Co precursor:CNF template-2:1). Among them, sample A exhibits the perforated polygonal CO3O4 with a thin carbon layer (5.7-6.2 nm) owing to the removal of CNF template. However, sample B and sample C synthesized perforated round CO3O4 and destroyed CO3O4 powders, respectively, due to a decreased amount of Co precursor. The increased amount of the CNF template prevents the formation of polygonal CO3O4. For sample A, the optimized weight ratio of the Co precursor and CNF template may be related to the successful formation of perforated polygonal CO3O4. Thus, perforated polygonal CO3O4 can be applied to electrode materials of energy storage devices such as lithium ion batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Nitrogen Doped Protein Based Carbon as Pt Catalysts Supports for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Young-geun Lee, Geon-hyeong An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(3): 182. CrossRef - Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 96. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Nitrogen Doped Protein Based Carbon as Pt Catalysts Supports for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


