Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Alloy Design and Powder Manufacturing of Al-Cu-Si alloy for Low-Temperature Aluminum Brazing
- Heeyeon Kim, Chun Woong Park, Won Hee Lee, Young Do Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):339-345. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.339
- 1,448 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
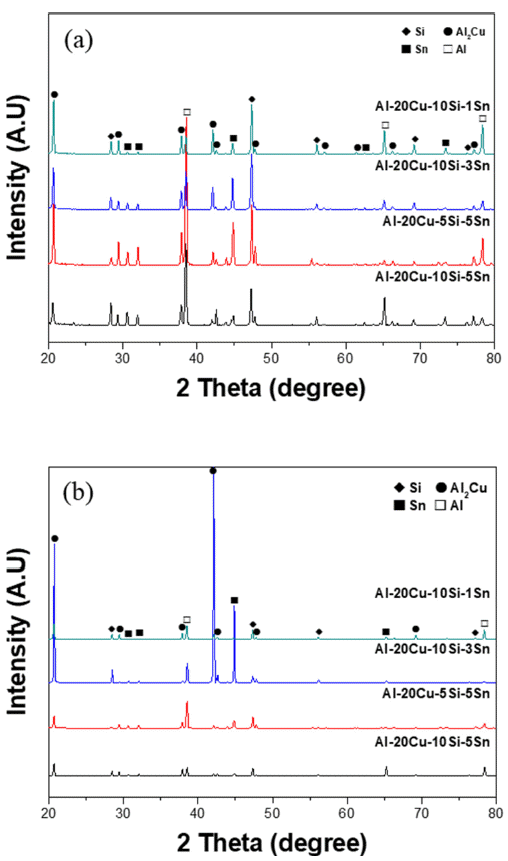
PDF This study investigates the melting point and brazing properties of the aluminum (Al)-copper (Cu)-silicon (Si)-tin (Sn) alloy fabricated for low-temperature brazing based on the alloy design. Specifically, the Al-20Cu-10Si-Sn alloy is examined and confirmed to possess a melting point of approximately 520°C. Analysis of the melting point of the alloy based on composition reveals that the melting temperature tends to decrease with increasing Cu and Si content, along with a corresponding decrease as the Sn content rises. This study verifies that the Al-20Cu-10Si-5Sn alloy exhibits high liquidity and favorable mechanical properties for brazing through the joint gap filling test and Vickers hardness measurements. Additionally, a powder fabricated using the Al-20Cu-10Si-5Sn alloy demonstrates a melting point of around 515°C following melting point analysis. Consequently, it is deemed highly suitable for use as a low-temperature Al brazing material.
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Properties of Bulk Graphite using Artificial Graphite Scrap as a Function of Particle Size
- Sang Hye Lee, Sang Min Lee, Won Pyo Jang, Jae Seung Roh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):13-19. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.13
- 1,893 View
- 17 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
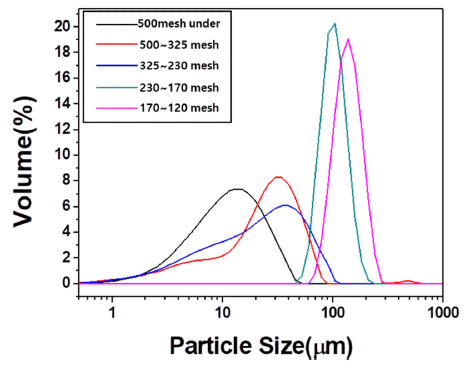
PDF Bulk graphite is manufactured using graphite scrap as the filler and phenolic resin as the binder. Graphite scrap, which is the by-product of processing the final graphite product, is pulverized and sieved by particle size. The relationship between the density and porosity is analyzed by measuring the mechanical properties of bulk graphite. The filler materials are sieved into mean particle sizes of 10.62, 23.38, 54.09, 84.29, and 126.64 μm. The bulk graphite density using the filler powder with a particle size of 54.09 μm is 1.38 g/cm3, which is the highest value in this study. The compressive strength tends to increase as the bulk graphite density increases. The highest compressive strength of 43.14 MPa is achieved with the 54.09 μm powder. The highest flexural strength of 23.08 MPa is achieved using the 10.62 μm powder, having the smallest average particle size. The compressive strength is affected by the density of bulk graphite, and the flexural strength is affected by the filler particle size of bulk graphite.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Microstructural Change under Pressure during Isostatic Pressing on Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Isotropic Carbon Blocks
Tae-Sub Byun, Sang-Hye Lee, Suk-Hwan Kim, Jae-Seung Roh
Materials.2024; 17(2): 387. CrossRef - Feasibility assessment of manufacturing carbonized blocks from rice husk charcoal
Young-Min Hwang, Jae-Seung Roh, Gibeop Nam
Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery.2024; 14(20): 26409. CrossRef - Improving the packing and mechanical properties of graphite blocks by controlling filler particle-size distribution
Hye in Hwang, Ji Hong Kim, Ji Sun Im
Advanced Composite Materials.2024; 33(5): 762. CrossRef - Effect of Impregnation and Graphitization on EDM Performance of Graphite Blocks Using Recycled Graphite Scrap
Sang-Hye Lee, Dong-Pyo Jeon, Hyun-Yong Lee, Dong-Gu Lee, Jae-Seung Roh
Processes.2023; 11(12): 3368. CrossRef - Ultrafine Graphite Scrap and Carbon Blocks Prepared by High-Solid-Loading Bead Milling and Conventional Ball Milling: A Comparative Assessment
Chonradee Amnatsin, Waroot Kanlayakan, Siraprapa Lhosupasirirat, Nattarut Verojpipath, Boonsueb Pragobjinda, Tanakorn Osotchan, Chakrit Sirisinha, Toemsak Srikhirin
ACS Omega.2023; 8(50): 47919. CrossRef - The Effect of the Heating Rate during Carbonization on the Porosity, Strength, and Electrical Resistivity of Graphite Blocks Using Phenolic Resin as a Binder
Sang-Hye Lee, Jae-Hyun Kim, Woo-Seok Kim, Jae-Seung Roh
Materials.2022; 15(9): 3259. CrossRef - Rheological Behaviour of Hard-Metal Carbide Powder Suspensions at High Shear Rates
B. Hausnerová, P. Sáha, J. Kubát, T. Kitano, J. Becker
Journal of Polymer Engineering.2000;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of Microstructural Change under Pressure during Isostatic Pressing on Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Isotropic Carbon Blocks
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Electromagnetic Shielding Characteristics of Crash Pad Using Electrically Conductive Powders and Al-coated Glass Fiber as Filler in Automotive
- Hong Cho, Sun-kyoung Jeoung, Byeong-woo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):124-130. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.124
- 741 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
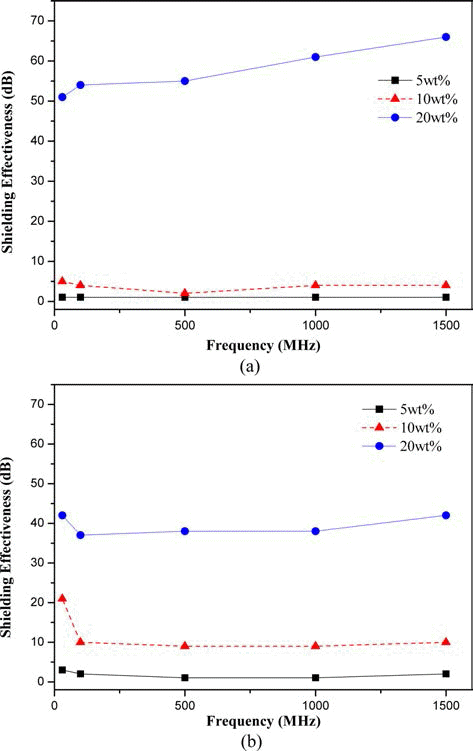
PDF The automotive industry is moving from the internal combustion engine to electric drive motors. Electric motors uses a high voltage system requiring the development of resources and components to shield the system. Therefore, in this study, we analyze electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding effectiveness (SE) characteristics of an auto crash pad according to the ratio of electrically conductive materials and propylene. In order to combine good mechanical characteristics and electromagnetic shielding of the automotive crash pad, metal-coated glass fiber (MGF) manufacturing methods are introduced and compared with powder-type methods. Through this study, among MGF methods, we suggest that the chopping method is the most effective shielding method.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


