Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Recent Research Progress on the Atomic Layer Deposition of Noble Metal Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell
- Jeong Hwan Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):63-71. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.63
- 618 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
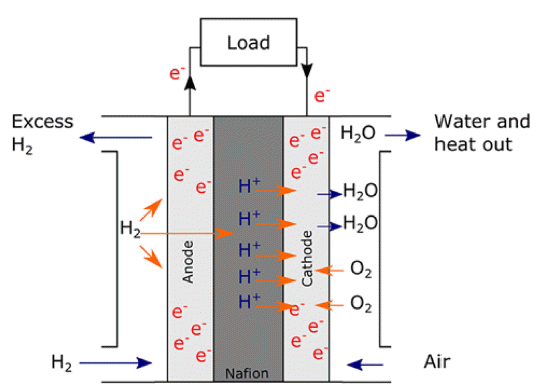
PDF It is necessary to fabricate uniformly dispersed nanoscale catalyst materials with high activity and long-term stability for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with excellent electrochemical characteristics of the oxygen reduction reaction and hydrogen oxidation reaction. Platinum is known as the best noble metal catalyst for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells because of its excellent catalytic activity. However, given that Pt is expensive, considerable efforts have been made to reduce the amount of Pt loading for both anode and cathode catalysts. Meanwhile, the atomic layer deposition (ALD) method shows excellent uniformity and precise particle size controllability over the three-dimensional structure. The research progress on noble metal ALD, such as Pt, Ru, Pd, and various metal alloys, is presented in this review. ALD technology enables the development of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with excellent reactivity and durability.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of a Ceria Based Composite Electrolyte for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Young-In Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):222-228. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.222
- 887 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
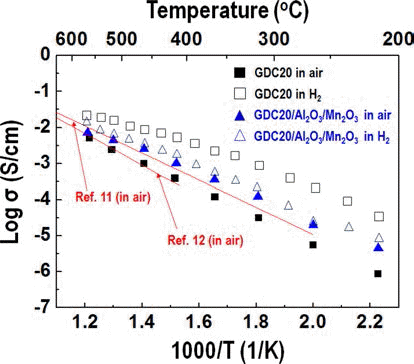
PDF Much research into fuel cells operating at a temperature below 800°C. is being performed. There are significant efforts to replace the yttria-stabilized zirconia electrolyte with a doped ceria electrolyte that has high ionic conductivity even at a lower temperature. Even if the doped ceria electrolyte has high ionic conductivity, it also shows high electronic conductivity in a reducing environment, therefore, when used as a solid electrolyte of a fuel cell, the powergeneration efficiency and mechanical properties of the fuel cell may be degraded. In this study, gadolinium-doped ceria nanopowder with Al2O3 and Mn2O3 as a reinforcing and electron trapping agents were synthesized by ultrasonic pyrolysis process. After firing, their microstructure and mechanical and electrical properties were investigated and compared with those of pure gadolinium-doped ceria specimen.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High growth-rate atomic layer deposition process of cerium oxide thin film for solid oxide fuel cell
Jin-Geun Yu, Byung Chan Yang, Jeong Woo Shin, Sungje Lee, Seongkook Oh, Jae-Ho Choi, Jaehack Jeong, Wontae Noh, Jihwan An
Ceramics International.2019; 45(3): 3811. CrossRef - Atomic-layer-deposited ZrO2-doped CeO2 thin film for facilitating oxygen reduction reaction in solid oxide fuel cell
Byung Chan Yang, Dohyun Go, Seongkook Oh, Jeong Woo Shin, Hyong June Kim, Jihwan An
Applied Surface Science.2019; 473: 102. CrossRef
- High growth-rate atomic layer deposition process of cerium oxide thin film for solid oxide fuel cell
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


