Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
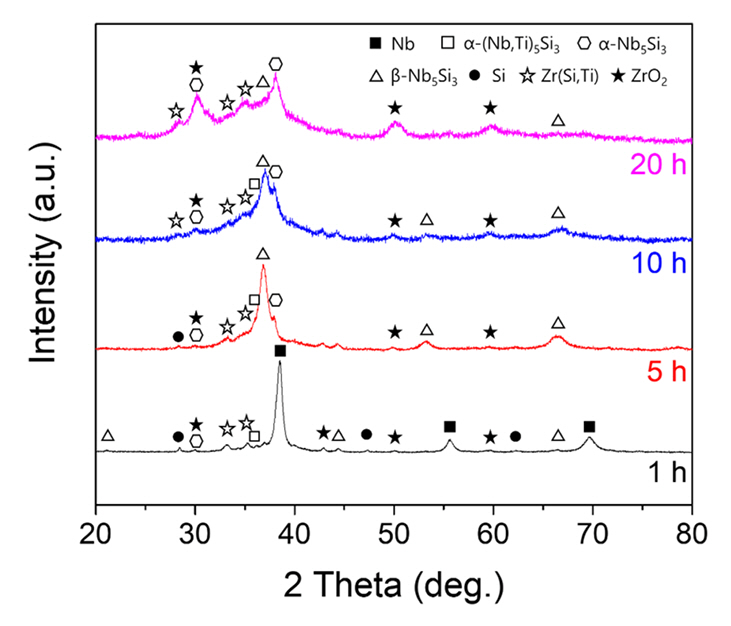
- Development of High-strength, High-temperature Nb-Si-Ti Alloys through Mechanical Alloying
- Jung-Joon Kim, Sang-Min Yoon, Deok-Hyun Han, Jongmin Byun, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.30
- 2,035 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [Korean]
- Effect of Iron Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Mo-Fe P/M Alloys
- HyoWoon Hwang, YongJae Lee, JiHwan Park, Dong-Geun Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):325-331. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.325
- 1,123 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Beta-titanium alloys are used in many industries due to their increased elongation resulting from their BCC structure and low modulus of elasticity. However, there are many limitations to their use due to the high cost of betastabilizer elements. In this study, biocompatible Ti-Mo-Fe beta titanium alloys are designed by replacing costly betastabilizer elements (e.g., Nb, Zr, or Ta) with inexpensive Mo and Fe elements. Additionally, Ti-Mo-Fe alloys designed with different Fe contents are fabricated using powder metallurgy. Fe is a strong, biocompatible beta-stabilizer element and a low-cost alloying element. The mechanical properties of the Ti-Mo-Fe metastable beta titanium alloys are analyzed in relation to the microstructural changes. When the Fe content increases, the tensile strength and elongation decrease due to brittle fracture despite a decreasing pore fraction. It is confirmed that the hardness and tensile strength of Ti-5Mo-2Fe P/M improve to more than 360 Hv and 900 MPa, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - Fabrication of Ti-Mo Core-shell Powder and Sintering Properties for Application as a Sputtering Target
Won Hee Lee, Chun Woong Park, Heeyeon Kim, Yuncheol Ha, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 43. CrossRef - Effect of Strain Rate on Deformation Behaviors of Ti-12.1Mo -1Fe Metastable Beta Alloy
In Kyeong Jin, Dong-Geun Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(10): 741. CrossRef
- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
- [Korean]
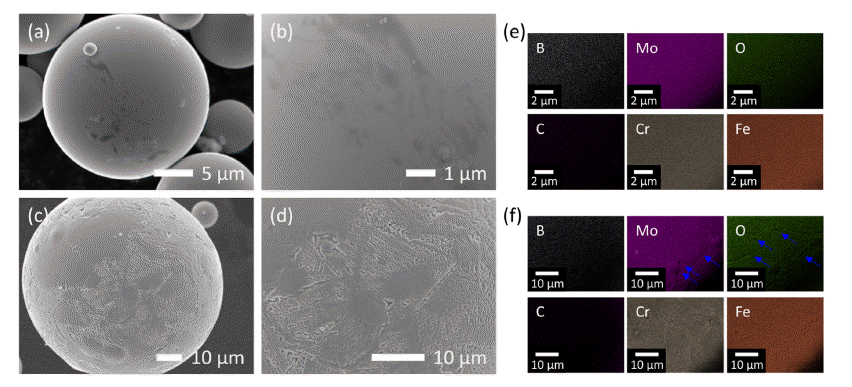
- Development of Amorphous Iron Based Coating Layer using High-velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Spraying
- Jungjoon Kim, Song-Yi Kim, Jong-Jae Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Hyunkyu Lim, Min-Ha Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):483-490. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.483
- 681 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A new Fe-Cr-Mo-B-C amorphous alloy is designed, which offers high mechanical strength, corrosion resistance as well as high glass-forming ability and its gas-atomized amorphous powder is deposited on an ASTM A213-T91 steel substrate using the high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) process. The hybrid coating layer, consisting of nanocrystalline and amorphous phases, exhibits strong bonding features with the substrate, without revealing significant pore formation. By the coating process, it is possible to obtain a dense structure in which pores are hardly observed not only inside the coating layer but also at the interface between the coating layer and the substrate. The coating layer exhibits good adhesive strength as well as good wear resistance, making it suitable for coating layers for biomass applications.
- [Korean]
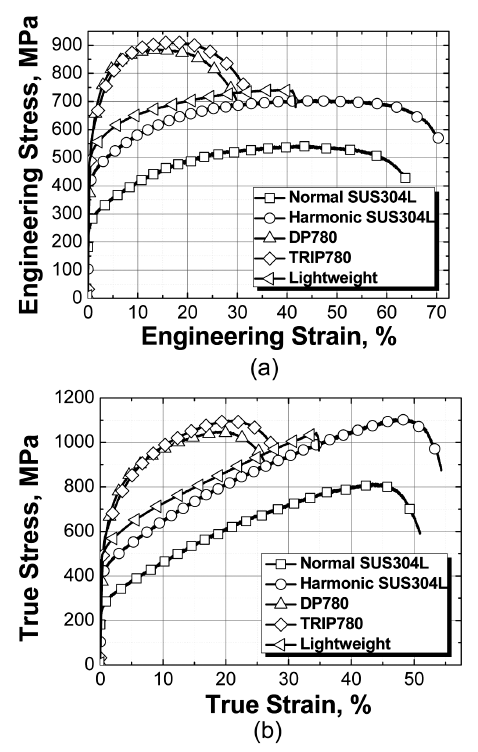
- Stretch-Flangeability of Harmonic Structure Material Manufactured by Powder Metallurgy Method
- Jae Ik Yoon, Hak Hyeon Lee, Hyung Keun Park, Kei Ameyama, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):128-132. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.128
- 829 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Harmonic structure materials are materials with a core–shell structure having a shell with a small grain size and a core with a relatively large grain size. They are in the spotlight because their mechanical properties reportedly feature strength similar to that of a sintered powder with a fine grain size and elongation similar to that of a sintered powder with a coarse grain size at the same time. In this study, the tensile properties, microstructure, and stretchflangeability of harmonic structure SUS304L made using powder metallurgy are investigated to check its suitability for automotive applications. The harmonic powders are made by mechanical milling and sintered using a spark plasma sintering method at 1173 K and a pressure of 50 MPa in a cylindrical die. The sintered powders of SUS304L having harmonic structure (harmonic SUS304L) exhibit excellent tensile properties compared with sintered powders of SUS304L having homogeneous microstructure. In addition, the harmonic SUS304L has excellent stretch-flangeability compared with commercial advanced high-strength steels (AHSSs) at a similar strength grade. Thus, the harmonic SUS304L is more suitable for automotive applications than conventional AHSSs because it exhibits both excellent tensile properties and stretch-flangeability.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


