Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of TiC powder by carburization of TiH2 powder
- Hun-Seok Lee, Hyang-Im Seo, Young-Seon Lee, Dong-Jun Lee, Jei-Pil Wang, Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):29-33. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.29

- 595 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Titanium carbide (TiC) powders are successfully synthesized by carburization of titanium hydride (TiH2) powders. The TiH2 powders with size lower than 45 μm (-325 Mesh) are optimally produced by the hydrogenation process, and are mixed with graphite powder by ball milling. The mixtures are then heat-treated in an Ar atmosphere at 800-1200oC for carburization to occur. It has been experimentally and thermodynamically determined that the dehydrogenation, “TiH2 = Ti + H2”, and carburization, “Ti + C = TiC”, occur simultaneously over the reaction temperature range. The unreacted graphite content (free carbon) in each product is precisely measured by acid dissolution and by the filtering method, and it is possible to conclude that the maximal carbon stoichiometry of TiC0.94 is accomplished at 1200°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 251. CrossRef
- Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
- [English]
- Fabrication of Sintered Compact of Fe-TiB2 Composites by Pressureless Sintering of (FeB+TiH2) Powder Mixture
- Xuan-Khoa Huynh, Ji Soon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):282-286. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.282
- 818 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
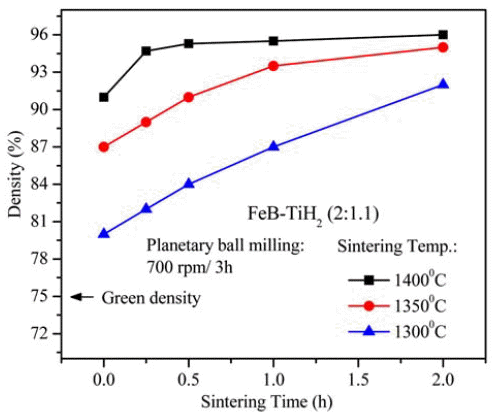
PDF A sintered body of TiB2-reinforced iron matrix composite (Fe-TiB2) is fabricated by pressureless-sintering of a mixture of titanium hydride (TiH2) and iron boride (FeB) powders. The powder mixture is prepared in a planetary ball-mill at 700 rpm for 3 h and then pressurelessly sintered at 1300, 1350 and 1400°C for 0-2 h. The optimal sintering temperature for high densities (above 95% relative density) is between 1350 and 1400°C, where the holding time can be varied from 0.25 to 2 h. A maximum relative density of 96.0% is obtained from the (FeB+TiH2) powder compacts sintered at 1400°C for 2 h. Sintered compacts have two main phases of Fe and TiB2 along with traces of TiB, which seems to be formed through the reaction of TiB2 formed at lower temperatures during the heating stage with the excess Ti that is intentionally added to complete the reaction for TiB2 formation. Nearly fully densified sintered compacts show a homogeneous microstructure composed of fine TiB2 particulates with submicron sizes and an Fe-matrix. A maximum hardness of 71.2 HRC is obtained from the specimen sintered at 1400°C for 0.5 h, which is nearly equivalent to the HRC of conventional WC-Co hardmetals containing 20 wt% Co.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimizing the Microstructure and Properties of Fe–Ni–Cu–Mo–C Sintered Steel by TiB2
Zenglin Liu, Yankang Wang, Weilong Lu, Feng Liu, Wei Han, Wuqiang He
Science of Advanced Materials.2024; 16(6): 707. CrossRef - Effect of Ce Addition on the As-Cast and As-Forged Microstructure of Fe-TiB2 Composites
Lin Zhang, Jianwen Gao, Minghao Huang, Engang Wang
JOM.2019; 71(11): 4144. CrossRef - Microstructure, mechanical, and tribological properties of pressureless sintered and spark plasma sintered Fe TiB2 nanocomposites
Hak-Rae Cho, Ji-Soon Kim, Koo-Hyun Chung
Tribology International.2019; 131: 83. CrossRef
- Optimizing the Microstructure and Properties of Fe–Ni–Cu–Mo–C Sintered Steel by TiB2
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


