Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Additive Manufacturing for Sensor Integrated Components
- Im Doo Jung, Min Sik Lee, Young Jin Woo, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):111-118. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.111

- 1,315 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The convergence of artificial intelligence with smart factories or smart mechanical systems has been actively studied to maximize the efficiency and safety. Despite the high improvement of artificial neural networks, their application in the manufacturing industry has been difficult due to limitations in obtaining meaningful data from factories or mechanical systems. Accordingly, there have been active studies on manufacturing components with sensor integration allowing them to generate important data from themselves. Additive manufacturing enables the fabrication of a net shaped product with various materials including plastic, metal, or ceramic parts. With the principle of layer-bylayer adhesion of material, there has been active research to utilize this multi-step manufacturing process, such as changing the material at a certain step of adhesion or adding sensor components in the middle of the additive manufacturing process. Particularly for smart parts manufacturing, researchers have attempted to embed sensors or integrated circuit boards within a three-dimensional component during the additive manufacturing process. While most of the sensor embedding additive manufacturing was based on polymer material, there have also been studies on sensor integration within metal or ceramic materials. This study reviews the additive manufacturing technology for sensor integration into plastic, ceramic, and metal materials.
- [English]
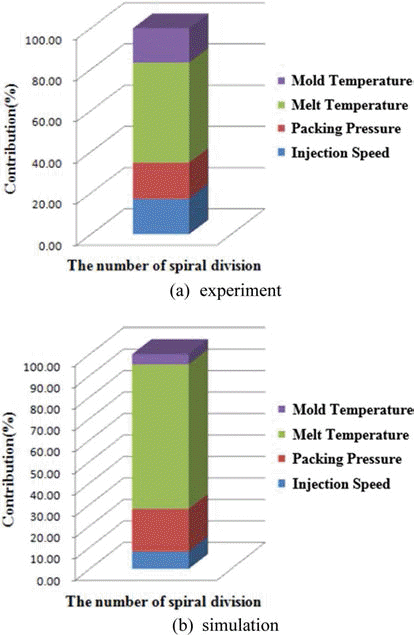
- Simulation and Experiment of Injection Molding Process for Superalloy Feedstock
- Im Doo Jung, Youngmoo Kim, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):1-5. Published online February 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.1
- 1,239 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder injection molding is an important manufacturing technology to mass produce superalloy components with complex shape. Injection molding step is particularly important for realizing a desired shape, which requires much time and efforts finding the optimum process condition. Therefore computer aided engineering can be very useful to find proper injection molding conditions. In this study, we have conducted a finite element method based simulation for the spiral mold test of superalloy feedstock and compared the results with experimental ones. Sensitivity analysis with both of simulation and experiment reveals that the melt temperature of superalloy feedstock is the most important factor for the full filling of mold cavity. The FEM based simulation matches well the experimental results. This study contributes to the optimization of superalloy powder injection molding process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
Joo Won OH, Chang Woo GAL, Daseul SHIN, Jae Man PARK, Woo Seok YANG, Seong Jin PARK
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2018; 65(9): 539. CrossRef - Effect of Diamond Particle Size on the Thermal Shock Property of High Pressure High Temperature Sintered Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
Ji-Won Kim, Min-Seok Baek, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(5): 364. CrossRef
- Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering Behaviors of M-type Barium Hexaferrite Nano Powders
- Im Doo Jung, Youngmoo Kim, Yang-Ki Hong, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):256-259. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.256

- 1,042 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A magnetic powder, M-type barium hexaferrite (BaFe12O19), was consolidated with the spark plasma sintering process. Three different holding temperatures, 850°C, 875°C and 900°C were applied to the spark plasma sintering process with the same holding times, heating rates and compaction pressure of 30 MPa. The relative density was measured simultaneously with spark plasma sintering and the convergent relative density after cooling was found to be proportional to the holding temperature. The full relative density was obtained at 900°C and the total sintering time was only 33.3 min, which was much less than the conventional furnace sintering method. The higher holding temperature also led to the higher saturation magnetic moment (σs) and the higher coercivity (Hc) in the vibrating sample magnetometer measurement. The saturation magnetic moment (σs) and the coercivity (Hc) obtained at 900°C were 56.3 emu/g and 541.5 Oe for each.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of microwave sintering on density, microstructural and magnetic properties of pure strontium hexaferrite at low temperatures and heating rate
Wail M. Matran, Mazli Mustapha, Mohd Faizairi Nor, Faizal Mustapha, Fahd Saeed Alakbari, Gamal Al-shawesh, Mohammed Bawahab
Heliyon.2024; 10(20): e38766. CrossRef - A study of crystalline – texture and anisotropic properties of hexagonal BaFe12O19 sintered by in-situ magnetic-anisotropy spark plasma sintering (MASPS)
Haetham G. Mohammed, Thar Mohammed Badri Albarody, Husam Kareem Mohsin Al-Jothery, Mazli Mustapha, N.M Sultan
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials.2022; 553: 169268. CrossRef - Process Optimization of In Situ Magnetic-Anisotropy Spark Plasma Sintering of M-Type-Based Barium Hexaferrite BaFe12O19
Haetham Mohammed, Thar Albarody, Susilawati Susilawati, Scott Gohery, Aris Doyan, Saiful Prayogi, Muhammad Bilad, Reza Alebrahim, Anwar Saeed
Materials.2021; 14(10): 2650. CrossRef - Self-Consolidation and Surface Modification of Mechanical Alloyed Ti-25.0 at.% Al Powder Mixture by Using an Electro-Discharge Technique
S.Y. Chang, H.S. Jang, Y.H. Yoon, Y.H. Kim, J.Y. Kim, Y.K. Lee, W.H. Lee
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1293. CrossRef - Plastic deformation and microstructural evolution during the shock consolidation of ultrafine copper powders
Dong-Hyun Ahn, Wooyeol Kim, Minju Kang, Lee Ju Park, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2015; 625: 230. CrossRef
- Effect of microwave sintering on density, microstructural and magnetic properties of pure strontium hexaferrite at low temperatures and heating rate
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


