Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Review on Characterization Method and Recent Research Trend about Metal Powder for Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) Process
- Bin Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Yong Son, Kyoung-Tae Park, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):509-519. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.509
- 1,393 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
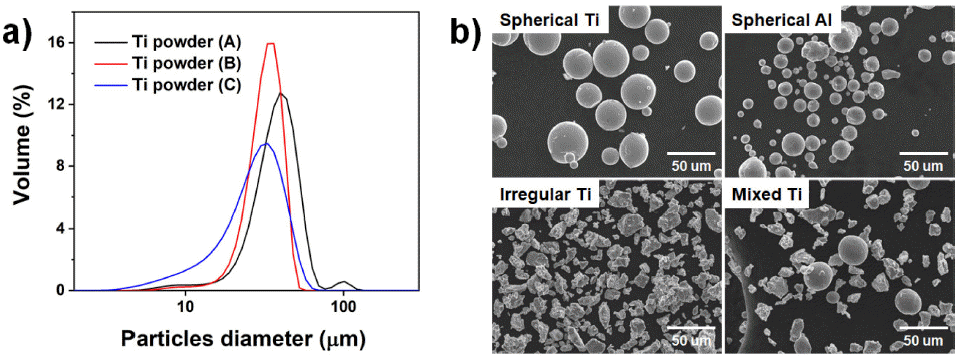
PDF A well-established characterization method is required in powder bed fusion (PBF) metal additive manufacturing, where metal powder is used. The characterization methods from the traditional powder metallurgy process are still being used. However, it is necessary to develop advanced methods of property evaluation with the advances in additive manufacturing technology. In this article, the characterization methods of powders for metal PBF are reviewed, and the recent research trends are introduced. Standardization status and specifications for metal powder for the PBF process which published by the ISO, ASTM, and MPIF are also covered. The establishment of powder characterization methods are expected to contribute to the metal powder industry and the advancement of additive manufacturing technology through the creation of related databases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
Yu Cao, Xiaohui Dong, Yulong Zhu, Tao Huang, Bin Jiang, Chenghang Zhang
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2026; 263: 140. CrossRef -
Enhanced flow properties of SiO
2
nanoparticles coated low-cost hydrogenation-dehydrogenation Ti-6Al-4V powder for powder bed fusion process
Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Tae hu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(2): 95. CrossRef -
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
Jongik Lee, Taehoo Kang, Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Sanghee Jung, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 333. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - A Study on Fabrication of PCD Endmill Holder using PBF Additive Manufacturing Technology
Min-Woo Sa, Ho-Min Son, Kyung-Hwan Park, Sang-Geun Lee, Dae-Ho Shin, Dong-Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2024; 23(6): 124. CrossRef - Rheological Characteristic Analysis Methods and Tests of Metal Powders for PBF Additive Manufacturing
Wan-Sik Woo, Ho-Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2023; 22(10): 1. CrossRef - Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef - Enhancing spreadability of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation titanium powder and novel method to characterize powder spreadability for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, InYeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Dongju Lee, Bin Lee
Materials & Design.2022; 223: 111247. CrossRef
- Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
- [Korean]
- A study about sculpture characteristic of SKD61 tool steel fabricated by selective laser melting(SLM) process
- Jaecheol Yun, Jungho Choe, Ki-Bong Kim, Sangsun Yang, Dong-Yeol Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Chang-Woo Lee, Chang-Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):137-143. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.137
- 1,028 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
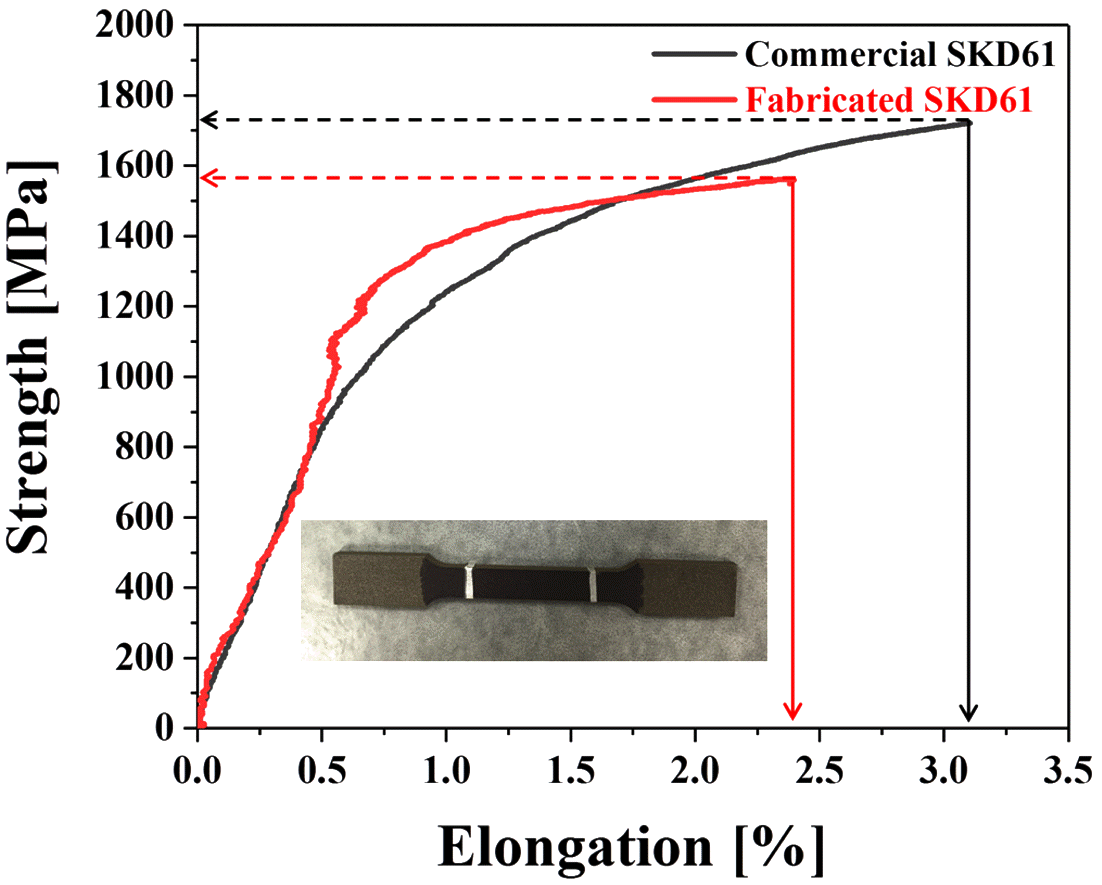
PDF In this study, two types of SKD61 tool-steel samples are built by a selective laser melting (SLM) process using the different laser scan speeds. The characteristics of two kinds of SKD61 tool-steel powders used in the SLM process are evaluated. Commercial SKD61 tool-steel power has a flowability of 16.68 sec/50 g and its Hausner ratio is calculated to be 1.25 by apparent and tapped density. Also, the fabricated SKD61 tool steel powder fabricated by a gas atomization process has a flowability of 21.3 sec/50 g and its Hausner ratio is calculated to be 1.18. Therefore, we confirmed that the two powders used in this study have excellent flowability. Samples are fabricated to measure mechanical properties. The highest densities of the SKD61 tool-steel samples, fabricated under the same conditions, are 7.734 g/cm3 (using commercial SKD61 powder) and 7.652 g/cm3 (using fabricated SKD61 powder), measured with Archimedes method. Hardness is measured by Rockwell hardness testing equipment 5 times and the highest hardnesses of the samples are 54.56 HRC (commercial powder) and 52.62 HRC (fabricated powder). Also, the measured tensile strengths are approximately 1,721 MPa (commercial SKD61 powder) and 1,552 MPa (fabricated SKD61 powder), respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef
- Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Property Improvement of the H13 Tool Steel Sculptures Built by Metal 3D Printing Process via Optimum Conditions
- Jaecheol Yun, Jungho Choe, Haengna Lee, Ki-Bong Kim, Sangsun Yang, Dong-Yeol Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Chang-Woo Lee, Ji-Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;24(3):195-201. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.195
- 1,200 View
- 11 Download
- 8 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
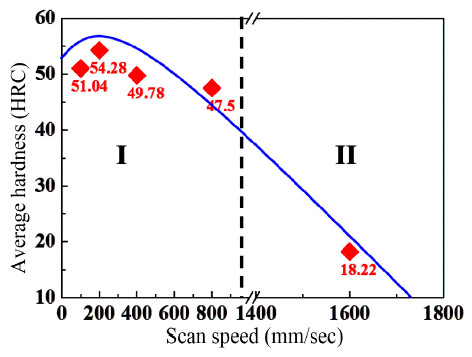
PDF In this study, H13 tool steel sculptures are built by a metal 3D printing process at various laser scan speeds. The properties of commercial H13 tool steel powders are confirmed for the metal 3D printing process used: powder bed fusion (PBF), which is a selective laser melting (SLM) process. Commercial H13 powder has an excellent flowability of 16.68 s/50 g with a Hausner ratio of 1.25 and a density of 7.68 g/cm3. The sculptures are built with dimensions of 10 × 10 × 10 mm3 in size using commercial H13 tool steel powder. The density measured by the Archimedes method is 7.64 g/cm3, similar to the powder density of 7.68 g/cm3. The hardness is measured by Rockwell hardness equipment 5 times to obtain a mean value of 54.28 HRC. The optimum process conditions in order to build the sculptures are a laser power of 90 W, a layer thickness of 25 μm, an overlap of 30%, and a laser scan speed of 200 mm/s.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancement of resistance to cracking under thermal cycling of EDM-treated H13 steel by shot peening with optimized intensity
Pengpeng Zuo, Zhiyang Dou, Huikai Yang, Haoyan Hou, Yafeng Zheng
Engineering Failure Analysis.2026; 187: 110622. CrossRef - Spheroidization of Enamel Powders by Radio Frequency Plasma Treatment and Application to Additive Manufacturing
Ki-Bong Kim, Dong-Yeol Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Jungho Choe, Ji-Na Kwak, Woo-Hyung Jung
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 388. CrossRef - Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef - Nano-mechanical Behavior of H13 Tool Steel Fabricated by a Selective Laser Melting Method
Van Luong Nguyen, Eun-ah Kim, Jaecheol Yun, Jungho Choe, Dong-yeol Yang, Hak-sung Lee, Chang-woo Lee, Ji-Hun Yu
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A.2019; 50(2): 523. CrossRef - Correlation between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Additive Manufactured H13 Tool Steel
Woojin An, Junhyeok Park, Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Im Doo Jung, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Hyokyung Sung
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(11): 663. CrossRef - Evaluation of Strain-Rate Sensitivity of Selective Laser Melted H13 Tool Steel Using Nanoindentation Tests
Van Luong Nguyen, Eun-ah Kim, Seok-Rok Lee, Jaecheol Yun, Jungho Choe, Dong-yeol Yang, Hak-sung Lee, Chang-woo Lee, Ji-Hun Yu
Metals.2018; 8(8): 589. CrossRef - Comparison of Nano-Mechanical Behavior between Selective Laser Melted SKD61 and H13 Tool Steels
Jaecheol Yun, Van Luong Nguyen, Jungho Choe, Dong-Yeol Yang, Hak-Sung Lee, Sangsun Yang, Ji-Hun Yu
Metals.2018; 8(12): 1032. CrossRef - A study about sculpture characteristic of SKD61 tool steel fabricated by selective laser melting(SLM) process
Jaecheol Yun, Jungho Choe, Ki-Bong Kim, Sangsun Yang, Dong-Yeol Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Chang-Woo Lee, Chang-Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(2): 137. CrossRef
- Enhancement of resistance to cracking under thermal cycling of EDM-treated H13 steel by shot peening with optimized intensity
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


