Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of STS316L Porous Metal for Vacuum Injection Mold
- Se Hoon Kim, Sang Min Kim, Sang Ho Noh, Jin Pyeong Kim, Jae Hyuck Shin, Si-Young Sung, Jin Kwang Jin, Taean Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):197-202. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.197
- 721 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
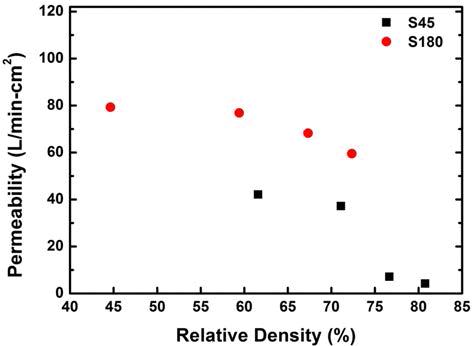
PDF In this study, porous stainless steel (STS316L) sintered body was fabricated by powder metallurgy method and its properties such as porosity, compressive yield strength, hardness, and permeability were evaluated. 67.5Fe-17Cr- 13Ni-2.5Mo (wt%) powder was produced by a water atomization. The atomized powder was classified into size with under 45 μm and over 180 μm, and then they were compacted with various pressures and sintered at 1210°C for 1 h in a vacuum atmosphere. The porosities of sintered bodies could be obtained in range of 20~53% by controlling the compaction pressure. Compressive yield strength and hardness were achieved up to 268 MPa and 94 Shore D, respectively. Air permeability was obtained up to 79 l/min·cm2. As a result, mechanical properties and air permeability of the optimized porous body having a porosity of 25~40% were very superior to that of Al alloy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Printability and physical properties of iron slag powder composites using material extrusion-based 3D printing
Hyungjin Kim, Sangkyu Lee
Journal of Iron and Steel Research International.2021; 28(1): 111. CrossRef - Study on Effects of Mold Temperature on the Injection Molded Article
J.-H. Han, Y.-C. Kim
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1271. CrossRef
- Printability and physical properties of iron slag powder composites using material extrusion-based 3D printing
- [English]
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Cu Foam by Slurry Coating Process
- Dahee Park, Eun-Mi Jung, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):87-92. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.87

- 873 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metallic porous materials have many interesting combinations of physical and geometrical properties with very low specific weight or high gas permeability. In this study, highly porous Cu foam is successfully fabricated by a slurry coating process. The Cu foam is fabricated specifically by changing the coating amount and the type of polyurethane foam used as a template. The processing parameters and pore characteristics are observed to identify the key parameters of the slurry coating process and the optimized morphological properties of the Cu foam. The pore characteristics of Cu foam are investigated by scanning electron micrographs and micro-CT analyzer, and air permeability of the Cu foam is measured by capillary flow porometer. We confirmed that the characteristics of Cu foam can be easily controlled in the slurry coating process by changing the microstructure, porosity, pore size, strut thickness, and the cell size. It can be considered that the fabricated Cu foams show tremendous promise for industrial application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation and comparative evolution of mechanical behavior of Fe and Fe2O3 foams and their polymer composites
Vemoori Raju, Roy Johnson, Asit Kumar Khanra
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2018; 750: 71. CrossRef
- Preparation and comparative evolution of mechanical behavior of Fe and Fe2O3 foams and their polymer composites
- [English]
- Processing Methods for the Preparation of Porous Ceramics
- Rizwan Ahmad, Jang-Hoon Ha, In-Hyuck Song
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):389-398. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.389
- 3,377 View
- 104 Download
- 22 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Macroporous ceramics with tailored pore size and shape could be used for well-established and emerging applications, such as molten metal filtration, biomaterial, catalysis, thermal insulation, hot gas filtration and diesel particulate filters. In these applications, unique properties of porous materials were required which could be achieved through the incorporation of macro-pores into ceramics. In this article, we reviewed the main processing techniques which can be used for the fabrication of macroporous ceramics with tailored microstructure. Partial sintering, replica templates, sacrificial fugutives, and direct foaming techniques was described here and compared in terms of micro-structures and mechanical properties that could be achieved. The main focus was given to the direct foaming technique which was simple and versatile approach that allowed the fabrication of macro-porous ceramics with tailored features and properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Contribution of microscale stochastic truss models to investigate the macroscale elasticity constants of porous ceramics
Thierry Canet, Gilles Dusserre, Thierry Cutard
European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids.2025; 111: 105561. CrossRef - Synthesis and properties of high alumina cement-based porous composites in the ZrO2-CaO-Al2O3 system
Yesica L. Bruni, María F. Hernández, Susana Conconi, Gustavo Suárez
Ceramics International.2025; 51(23): 39794. CrossRef - Morphology and phase analysis of cordierite ceramic foams with Ag nanoparticles
J. Kupková, G. Kratošová, K. Čech Barabaszová, G. Simha Martynková
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2025; 1337(1): 012004. CrossRef - Organic waste-derived pore formers for macroporous ceramics fabrication: A review on synthesis, durability properties and potential applications
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Azmah Hanim, A.A. Oyekanmi, M.N.M. Ansari, Surajudeen Sikiru, O.J. Ojo-Kupoluyi
Materials Today Sustainability.2024; 27: 100824. CrossRef - Chemistry and Physics of Wet Foam Stability for Porous Ceramics: A Review
Kamrun Nahar Fatema, Md Rokon Ud Dowla Biswas, Jung Gyu Park, Ik Jin Kim
Micro.2024; 4(4): 552. CrossRef - Investigating mass transfer coefficients in lean methane combustion reaction through the morphological and geometric analysis of structured open cell foam catalysts
Carmen W. Moncada Quintero, Hernan G. Mazzei, Marion Servel, Frédéric Augier, Yacine Haroun, Jean-François Joly, Stefania Specchia
Chemical Engineering Science.2023; 281: 119138. CrossRef - Composite PLGA–Nanobioceramic Coating on Moxifloxacin-Loaded Akermanite 3D Porous Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Regeneration
Georgia K. Pouroutzidou, Lambrini Papadopoulou, Maria Lazaridou, Konstantinos Tsachouridis, Chrysanthi Papoulia, Dimitra Patsiaoura, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Konstantinos Chrissafis, George Vourlias, Konstantinos M. Paraskevopoulos, Antonios D. Anastasiou, Dim
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(3): 819. CrossRef - Development of high strength large open porosity alumina ceramics using the sacrificial phase route: The role of the sacrificial phase fineness
Julian Alzukaimi, Rafi Jabrah
Ceramics International.2023; 49(2): 2923. CrossRef - Sustainable nanocomposite porous absorbent and membrane sieves: Definition, classification, history, properties, synthesis, applications, and future prospects
Sameer Ahmad, Weqar Ahmad Siddiqi, Sharif Ahmad
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2023; 11(2): 109367. CrossRef - Processing and characterization of porous composites based on CaAl4O7/CaZrO3
Yesica L. Bruni, María S. Conconi, María F. Hernández, Gustavo Suárez
Ceramics International.2023; 49(23): 37630. CrossRef - Trace addition of cellulose nanofiber in gel-casting system for structurally controlled porous ceramics towards superior thermal-insulating property
Yunzi Xin, Takashi Shirai
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan.2022; 130(5): 355. CrossRef - State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
Ismail Barbaros, Yongmin Yang, Babak Safaei, Zhicheng Yang, Zhaoye Qin, Mohammed Asmael
Nanotechnology Reviews.2022; 11(1): 321. CrossRef - A review of petroleum emulsification types, formation factors, and demulsification methods
Ahmed Abdulrazzaq Hadi, Ali Abdulkhabeer Ali
Materials Today: Proceedings.2022; 53: 273. CrossRef - SLURRY OPTIMISATION FOR FAST FREEZE-DRYING OF POROUS ALUMINA
Kritkaew Somton
Ceramics - Silikaty.2021; : 368. CrossRef - Recycling food, agricultural, and industrial wastes as pore-forming agents for sustainable porous ceramic production: A review
Siti Zuliana Salleh, Afiqah Awang Kechik, Abdul Hafidz Yusoff, Mustaffa Ali Azhar Taib, Maryana Mohamad Nor, Mardawani Mohamad, Tse Guan Tan, Arlina Ali, Mohamad Najmi Masri, Julie Juliewatty Mohamed, Siti Koriah Zakaria, Jia Geng Boon, Faisal Budiman, Pa
Journal of Cleaner Production.2021; 306: 127264. CrossRef - Novel noble-metal-free ceramic filter with controlled pore structure for environmental cleaning
Yunzi Xin, Sohei Nakagawa, Harumitsu Nishikawa, Takashi Shirai
Ceramics International.2021; 47(8): 11819. CrossRef - Fabrication of porous titania sheet via tape casting: Microstructure and water permeability study
Saber Ghannadi, Hossein Abdizadeh, Alireza Babaei
Ceramics International.2020; 46(7): 8689. CrossRef - Farklı Bağlayıcı ve Sinterleme Katkılarının SiC Seramik Prefom Mikroyapısı Üzerine Etkisi
Ebru Yılmaz, Fatih Çalışkan
Academic Perspective Procedia.2019; 2(3): 1309. CrossRef - The preparation and characterization of porous alumina ceramics using an eco‐friendly pore‐forming agent
Julian Alzukaimi, Rafi Jabrah
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2019; 16(2): 820. CrossRef - Wet Foam Stability from Colloidal Suspension to Porous Ceramics: A Review
Ik Jin Kim, Jung Gyu Park, Young Han Han, Suk Young Kim, James F. Shackelford
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2019; 56(3): 211. CrossRef - Processing of porous alumina by foaming method-effect of foaming agent, solid loading and binder
Soumya Devavarapu, Paritosh Chaudhuri, Aroh Shrivastava, Santanu Bhattacharyya
Ceramics International.2019; 45(9): 12264. CrossRef - Macroporous flexible polyvinyl alcohol lithium adsorbent foam composite prepared via surfactant blending and cryo-desiccation
Grace M. Nisola, Lawrence A. Limjuco, Eleazer L. Vivas, Chosel P. Lawagon, Myoung Jun Park, Ho Kyong Shon, Neha Mittal, In Wook Nah, Hern Kim, Wook-Jin Chung
Chemical Engineering Journal.2015; 280: 536. CrossRef
- Contribution of microscale stochastic truss models to investigate the macroscale elasticity constants of porous ceramics
- [Korean]
- Characterization of the Silica Coated Diatomite Based Ceramic Filter for Water Treatment
- Byung-Seo Bae, Jang-Hoon Ha, In-Hyuck Song, Yoo-Dong Hahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):21-27. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.21

- 471 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, diatomite based materials were investigated as a support filter for silica particle coating. The silica sol for coating was synthesized by a stöber process. The diatomite support was dry-pressed at 10 MPa and sintered at 1200°C for 1 hour. The coating sol was prepared as a mixture of EtOH and silica sol. The diatomite support was coated by a dip-coating process. Silica coated diatomite filter was sintered at 1000~1200°C for 1 hour. The largest pore size was decreased with increasing concentration ratio of coating sol. The gas and water permeability of silica coated diatomite decreased with increasing of concentration ratio of the coating sol.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


