Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Powder Injection Molding of Translucent Alumina using Supercritical Fluid Debinding
- Hyung Soo Kim, Jong Min Byun, Myung Jin Suk, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):407-414. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.407
- 1,032 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
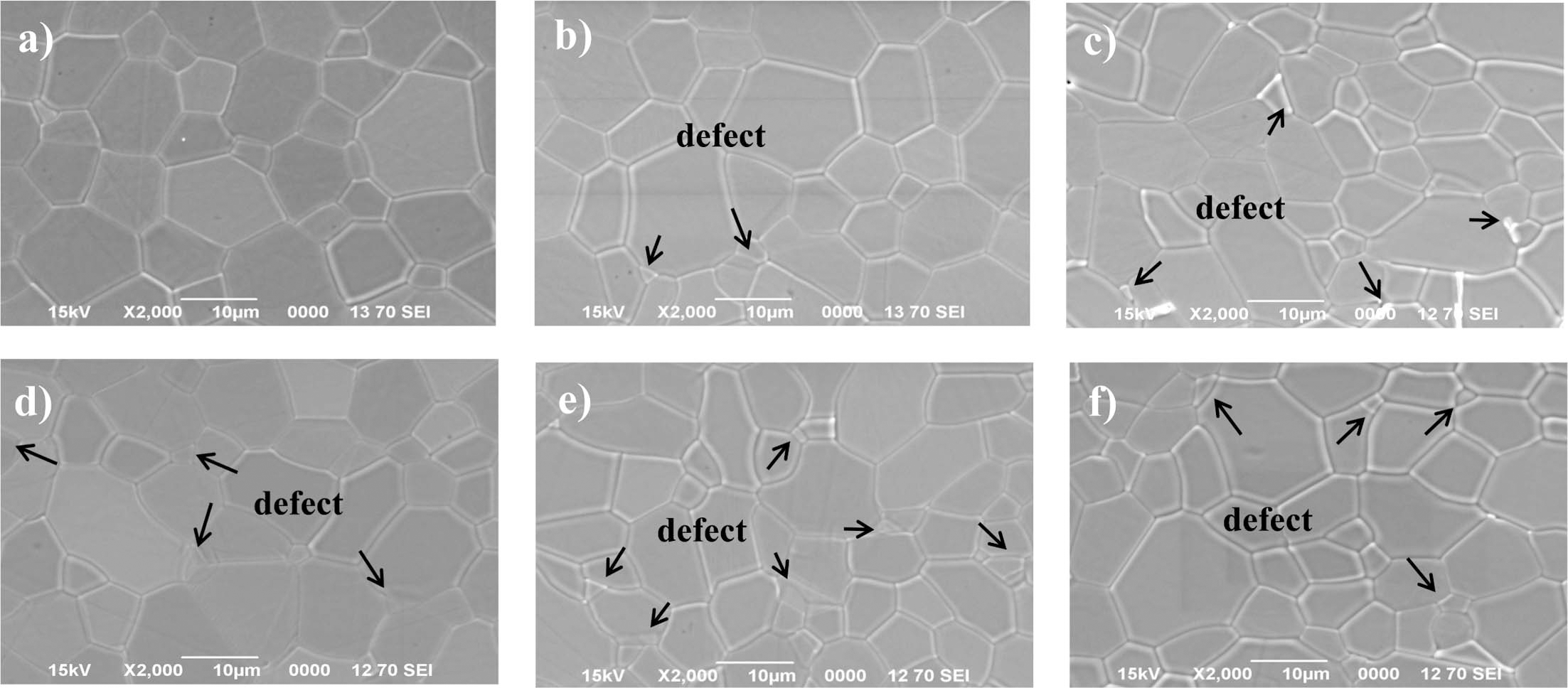
PDF The powder injection molding process having advantages in manufacturing three-dimensional precision parts essentially requires a debinding process before sintering to remove the binders used for preparing feedstock. In this study, powder injection molding of translucent alumina was performed, and carbon dioxide (CO2) is used as a supercritical fluid that makes it possible to remove a large amount of binder, which is paraffin wax. The relationship between the optical property of translucent alumina and the debinding condition (temperature and pressure) of supercritical CO2 was investigated. As temperature and pressure increased, extraction rate of the binder showed rising tendency and average grain size after sintering process was relatively fine. On the other hand, optical transmittance was reduced. As a result, the debinding condition at 50° and 20 MPa that represents the lowest extraction rate, 8.19 × 10−3 m2/sec, corresponds to the largest grain size of 14.7 μm and the highest optical transmittance of 45.2%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Supercritical CO₂ debinding: A promising method for binder removal in ceramic fabrication with potential applications in additive manufacturing – A review
Adolor David Aiyeki
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2026; 46(5): 117998. CrossRef - Experimental and numerical analysis of effects of supercritical carbon dioxide debinding on Inconel 718 MIM components
Dugauguez Olivier, Agne Aboubabky, Jimenez-Morales Antonia, Torralba José Manuel, Barriere Thierry
Powder Technology.2019; 355: 57. CrossRef
- Supercritical CO₂ debinding: A promising method for binder removal in ceramic fabrication with potential applications in additive manufacturing – A review
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


