Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
- Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):299-308. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00234
- 931 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of high-performance metal filters is essential for maintaining ultra-clean environments in semiconductor manufacturing. In this study, cross-sealed honeycomb filters were fabricated using STS316L powder via material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) for semiconductor gas filtration. The effects of filter geometry (4 or 9 channels) and sintering temperature (850°C, 950°C, or 1,050°C) on performance were examined. First, 4-channel and 9-channel filters sintered at the same temperature (950°C) exhibited similar porosities of 50.08% and 50.57%, but the 9-channel filter showed a higher pressure-drop (0.26 bar) and better filtration-efficiency (3.55 LRV) than the 4-channel filter (0.19 bar and 3.25 LRV, respectively). Second, for filters with the same geometry (4-channel) increasing the sintering temperature reduced porosity from 64.52% to 40.33%, while the pressure-drop increased from 0.13 bar to 0.22 bar and filtration-efficiency improved from 2.53 LRV to 3.51 LRV. These findings demonstrate that filter geometry and sintering temperature are key factors governing the trade-off between air permeability, pressure-drop, and filtration efficiency. This work provides insights and data for optimizing MEAM-based high-performance metal powder filter design.
- [Korean]
- Study on Microstructures and Hardness of STS316L Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting
- Gi Hun Shin, Joon Phil Choi, Kyung Tae Kim, Byoung Kee Kim, Ji Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;24(3):210-215. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.210

- 925 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, STS316L powders prepared by gas atomization are used to manufacture bulk structures with dimensions of 10 × 10 × 10 mm3 using selective laser melting (SLM). The microstructures and hardness of the fabricated 316L stainless steel has been investigated with the laser beam overlap varied from 10% to 70%. The microstructures of the fabricated STS316L samples show a decrease in the balling and satellite of powders introducing defect in the bulk samples and the porosity caused by the gap between the molten metal pools disappearing as the overlap ratio increases, whereas a low overlap ratio results in significant balling and a large amount of isolated powders due to the increased gap between the melt pools. Furthermore, the highest value in Vickers hardness is obtained for the sample fabricated by 30% overlapped laser beams. These results show that the overlap ratio of laser beams in the SLM process should be considered as an important process parameter.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al–Si-based alloys by selective laser melting process
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Dong Won Kim, Soo ho Jung, Jung Woo Nam, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Ji Hun Yu, Injoon Son
Powder Metallurgy.2021; 64(3): 198. CrossRef - Effect of laser remelting on the surface characteristics of 316L stainless steel fabricated via directed energy deposition
Seung Yeong Cho, Gwang Yong Shin, Do Sik Shim
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2021; 15: 5814. CrossRef - Investigation on Interfacial Microstructures of Stainless Steel/Inconel Bonded by Directed Energy Deposition of alloy Powders
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Soo-Ho Jung, Jihun Yu, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Chul Yong Sim, Seung Jun An
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 219. CrossRef - Influence of Powder Size on Properties of Selectively Laser-Melted- AlSi10Mg Alloys
Yeong Seong Eom, Dong Won Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Sang Sun Yang, Jungho Choe, Injoon Son, Ji Hun Yu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(2): 103. CrossRef - Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef - Microstructures and Characterization of Al-Si-Mg Alloy Processed by Selective Laser Melting with Post-Heat-treatment
Gi Seung Lee, Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Byoung Kee Kim, Ji Hun Yu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(2): 138. CrossRef - Correlation between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Additive Manufactured H13 Tool Steel
Woojin An, Junhyeok Park, Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Im Doo Jung, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Hyokyung Sung
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(11): 663. CrossRef
- Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al–Si-based alloys by selective laser melting process
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of STS316L Porous Metal for Vacuum Injection Mold
- Se Hoon Kim, Sang Min Kim, Sang Ho Noh, Jin Pyeong Kim, Jae Hyuck Shin, Si-Young Sung, Jin Kwang Jin, Taean Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):197-202. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.197
- 788 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
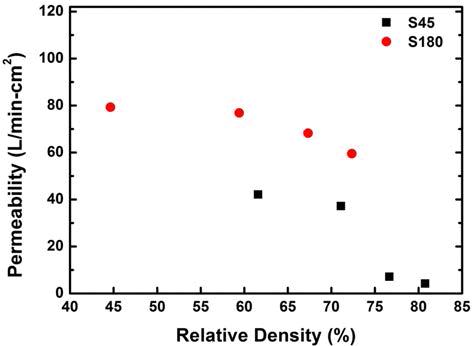
PDF In this study, porous stainless steel (STS316L) sintered body was fabricated by powder metallurgy method and its properties such as porosity, compressive yield strength, hardness, and permeability were evaluated. 67.5Fe-17Cr- 13Ni-2.5Mo (wt%) powder was produced by a water atomization. The atomized powder was classified into size with under 45 μm and over 180 μm, and then they were compacted with various pressures and sintered at 1210°C for 1 h in a vacuum atmosphere. The porosities of sintered bodies could be obtained in range of 20~53% by controlling the compaction pressure. Compressive yield strength and hardness were achieved up to 268 MPa and 94 Shore D, respectively. Air permeability was obtained up to 79 l/min·cm2. As a result, mechanical properties and air permeability of the optimized porous body having a porosity of 25~40% were very superior to that of Al alloy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Printability and physical properties of iron slag powder composites using material extrusion-based 3D printing
Hyungjin Kim, Sangkyu Lee
Journal of Iron and Steel Research International.2021; 28(1): 111. CrossRef - Study on Effects of Mold Temperature on the Injection Molded Article
J.-H. Han, Y.-C. Kim
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1271. CrossRef
- Printability and physical properties of iron slag powder composites using material extrusion-based 3D printing
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


