Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Densification Behavior of Rhenium Alloy using Master Sintering Curve
- Dong Yong Park, Yong Jun Oh, Young Sam Kwon, Seong Taek Lim, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):7-15. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.7
- 1,177 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
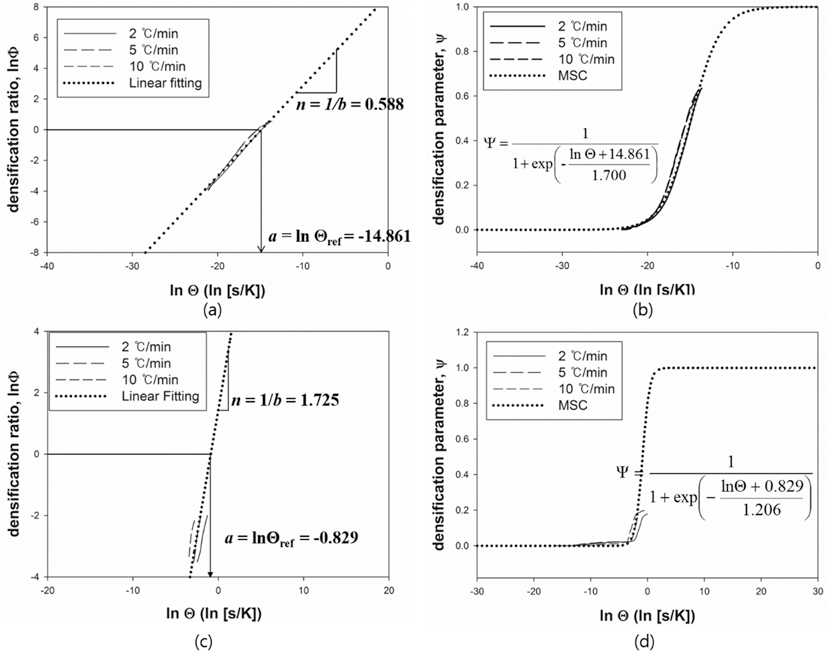
PDF This study investigated the densification behavior of rhenium alloys including W-25 wt.%Re and Re-2W- 1Ta (pure Re) during sintering. The dilatometry experiments were carried out to obtain the
in-situ shrinkage in H2 atmosphere. The measured data was analyzed through shrinkage, strain rate and relative density, and then symmetrically treated to construct the linearized form of master sintering curve (MSC) and MSC as a well-known and straightforward approach to describe the densification behavior during sintering. The densification behaviors for each material were analyzed in many respects including apparent activation energy, densification parameter, and densification ratio. MSC with a minimal set of preliminary experiments can make the densification behavior to be characterized and predicted as well as provide guideline to sinter cycle design. Considering the results of linearized form and MSC, it was confirmed that the W-25 wt.%Re compared to Pure Re is more easily densified at the relatively low temperature.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The influence of sintering time on the microstructural properties of chromium-rhenium matrix composites
Marcin Chmielewski, Szymon Nosewicz, Dorota Jakubowska, Małgorzata Lewandowska, Jarosław Mizera, Jerzy Rojek, Piotr Bazarnik
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2016; 59: 78. CrossRef
- The influence of sintering time on the microstructural properties of chromium-rhenium matrix composites
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


