Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
- YongKwan Lee, Hyun-chul Kim, Myungsuk Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kyoungtae Park, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):330-343. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00136
- 1,053 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
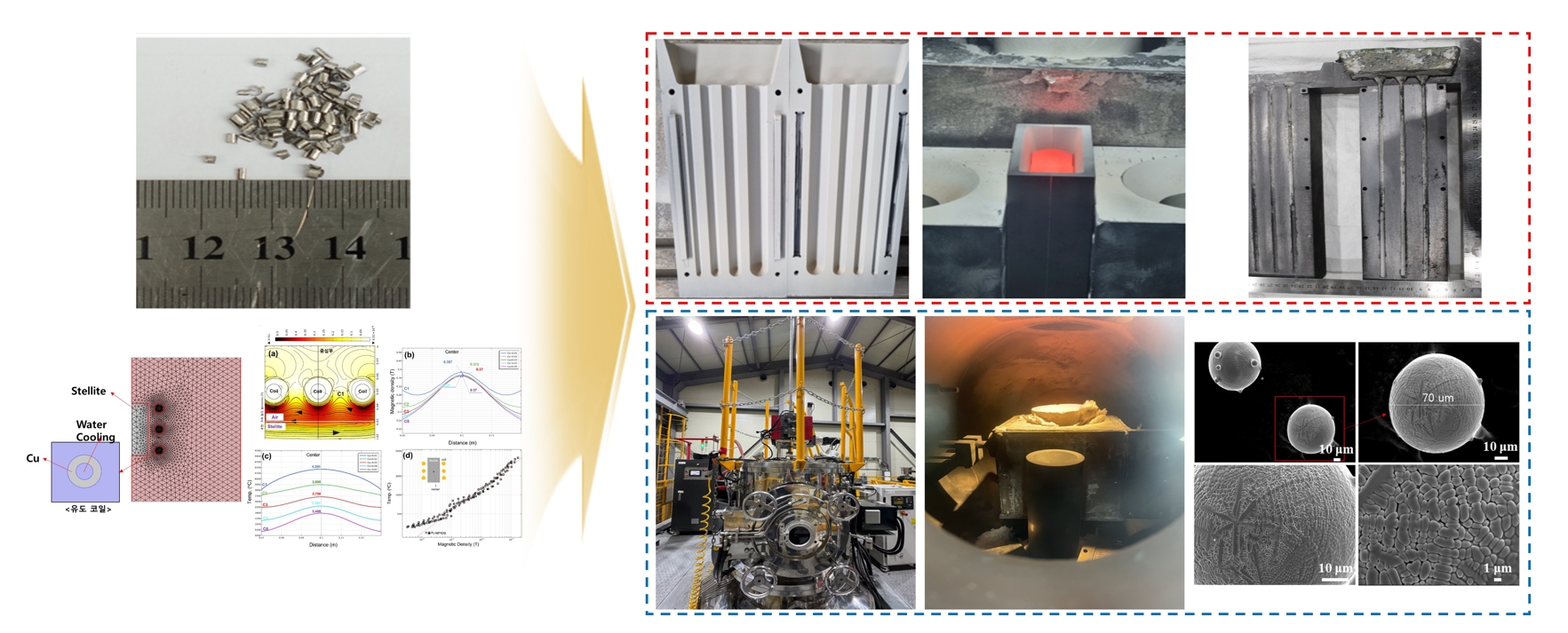
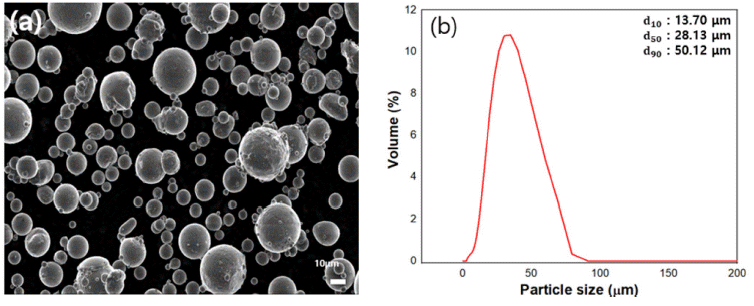
PDF - Co-Cr alloys are widely used in cutting tools and turbine components due to their high strength and resistance against wear and corrosion. However, scrap generated during hardfacing is often discarded due to impurities and oxidation, and research on its recycling remains limited. This study aimed to optimize the recycling process of Stellite 6 scrap to reduce waste and minimize costs while maintaining material quality. Melting, casting, and powdering processes were designed using HSC Chemistry, FactSage, and COMSOL Multiphysics, with optimization of key parameters such as the crucible material and temperature control. The recycled alloy and powder were analyzed using X-ray fluorescence analysis, inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy, and X-ray diffractometry, showing mechanical and chemical properties comparable to commercial Stellite 6. The Co and Cr contents were maintained, with a slight increase in Fe. These findings demonstrate the potential for producing high-quality recycled Stellite 6 materials, contributing to the sustainable utilization of metal resources in high-performance applications.
- [Korean]
- Improving Flow Property of AlSi10Mg Powder for Additive Manufacturing via Surface Treatment using Methyltrichlorosilane
- Sang Cheol Park, In Yeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee, Soong Ju Oh, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):363-369. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.363
- 895 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF AlSi10Mg alloys are being actively studied through additive manufacturing for application in the automobile and aerospace industries because of their excellent mechanical properties. To obtain a consistently high quality product through additive manufacturing, studying the flowability and spreadability of the metal powder is necessary. AlSi10Mg powder easily forms an oxide film on the powder surface and has hydrophilic properties, making it vulnerable to moisture. Therefore, in this study, AlSi10Mg powder was hydrophobically modified through silane surface treatment to improve the flowability and spreadability by reducing the effects of moisture. The improved flowability according to the number of silane surface treatments was confirmed using a Carney flowmeter. In addition, to confirm the effects of improved spreadability, the powder prior to surface treatment and that subjected to surface treatment four times were measured and compared using s self-designed recoating tester. The results of this study confirmed the improved flowability and spreadability based on the modified metal powder from hydrophilic to hydrophobic for obtaining a highquality additive manufacturing product.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef
- Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


