Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Microstructural Analysis of STS316L Samples Manufactured by Powder Bed Fusion and Post-heat Treatments
- S. Y. Song, D. W. Lee, D. V. Cong, J. W. Kim, S. M. Lee, S. H. Joo, J. C. Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):14-21. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.14
- 1,040 View
- 10 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
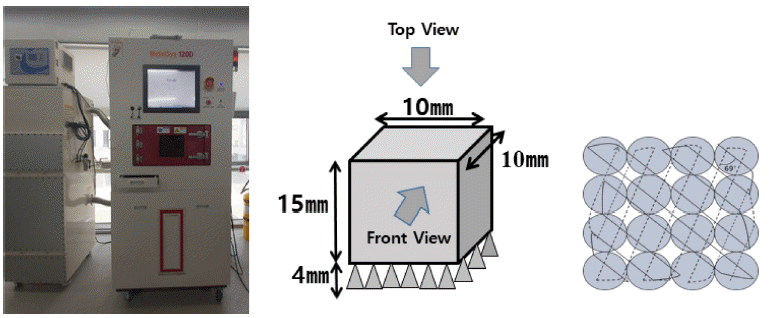
PDF In the powder bed fusion (PBF) process, a 3D shape is formed by the continuous stacking of very fine powder layers using computer-aided design (CAD) modeling data, following which laser irradiation can be used to fuse the layers forming the desired product. In this method, the main process parameters for manufacturing the desired 3D products are laser power, laser speed, powder form, powder size, laminated thickness, and laser diameter. Stainless steel (STS) 316L exhibits excellent strength at high temperatures, and is also corrosion resistant. Due to this, it is widely used in various additive manufacturing processes, and in the production of corrosion-resistant components with complicated shapes. In this study, rectangular specimens have been manufactured using STS 316L powder via the PBF process. Further, the effect of heat treatment at 800 °C on the microstructure and hardness has been investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Phase Composition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Biomedical Ti-15Nb-5Sn Alloy Prepared by Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
Jin-hwan Lim, Gyeong-ho Kang, Shuanglei Li, Tae-hyun Nam
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of thermal debinding conditions on microstructure and mechanical properties of a biomedical Ti-15Nb-5Sn alloy prepared by material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) process
Jin-hwan Lim, Soo-yeong Kim, Tae-gyun Gu, Shuanglei Li, Tae-hyun Nam
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1044: 184366. CrossRef - In vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Cell Viability of Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene for 3D-printed Artificial Joint Manufacturing
Seung-Lim Yoo, Da-Been Lee, Min-Gyu Park, Junyeong Lim, Chanwoo Sim, Taeho Yoon, Youngmin Seo, Dae-Wui Yoon
Biomedical Science Letters.2024; 30(4): 291. CrossRef
- Effect of Phase Composition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Biomedical Ti-15Nb-5Sn Alloy Prepared by Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
- Yu-Jin Hwang, Dong-Yeol Wi, Kyu-Sik Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):110-119. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.110
- 1,139 View
- 26 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
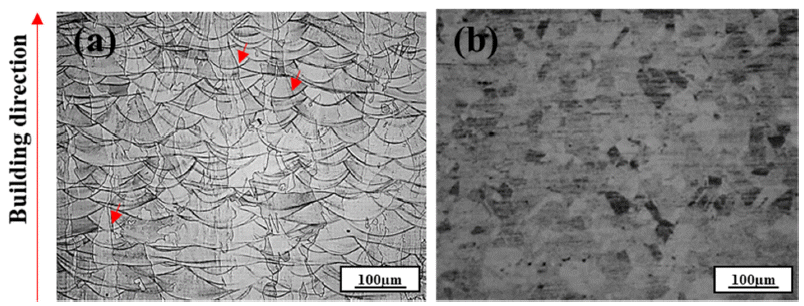
PDF In this study, the high-temperature oxidation properties of austenitic 316L stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is investigated and compared with conventional 316L manufactured by hot rolling (HR). The initial microstructure of LPBF-SS316L exhibits a molten pool ~100 μm in size and grains grown along the building direction. Isotropic grains (~35 μm) are detected in the HR-SS316L. In high-temperature oxidation tests performed at 700°C and 900°C, LPBF-SS316L demonstrates slightly superior high-temperature oxidation resistance compared to HR-SS316L. After the initial oxidation at 700°C, shown as an increase in weight, almost no further oxidation is observed for both materials. At 900°C, the oxidation weight displays a parabolic trend and both materials exhibit similar behavior. However, at 1100°C, LPBF-SS316L oxidizes in a parabolic manner, but HR-SS316L shows a breakaway oxidation behavior. The oxide layers of LPBF-SS316L and HR-SS316L are mainly composed of Cr2O3, Febased oxides, and spinel phases. In LPBF-SS316L, a uniform Cr depletion region is observed, whereas a Cr depletion region appears at the grain boundary in HR-SS316L. It is evident from the results that the microstructure and the hightemperature oxidation characteristics and behavior are related.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retention factor-based constitutive model of high-strength austenitic A4–80 bolts after fire exposure
Hui Wang, Bo Yang, Tao Sun, Weilai Yao, Wei Jiang
Journal of Constructional Steel Research.2025; 235: 109930. CrossRef - Study of structural stability at high temperature of pseudo-single tube with double layer as an alternative method for accident-tolerant fuel cladding
Jong Woo Kim, Hyeong Woo Min, Jaehwan Ko, Yonghee Kim, Young Soo Yoon
Journal of Nuclear Materials.2022; 566: 153800. CrossRef
- Retention factor-based constitutive model of high-strength austenitic A4–80 bolts after fire exposure
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


