Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Microwave Absorbance of Polymer Composites Containing SiC Fibers Coated with Ni-Fe Thin Films
- Tian Liu, Sung-Soo Kim, Woo-cheal Choi, Byungil Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):375-378. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.375

- 1,027 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Conductive and dielectric SiC are fabricated using electroless plating of Ni–Fe films on SiC chopped fibers to obtain lightweight and high-strength microwave absorbers. The electroless plating of Ni–Fe films is achieved using a two-step process of surface sensitizing and metal plating. The complex permeability and permittivity are measured for the composite specimens with the metalized SiC chopped fibers dispersed in a silicone rubber matrix. The original noncoated SiC fibers exhibit considerable dielectric losses. The complex permeability spectrum does not change significantly with the Ni–Fe coating. Moreover, dielectric constant is sensitively increased with Ni–Fe coating, owing to the increase of the space charge polarization. The improvements in absorption capability (lower reflection loss and small matching thickness) are evident with Ni–Fe coating on SiC fibers. For the composite SiC fibers coated with Ni–Fe thin films, a -35 dB reflection loss is predicted at 7.6 GHz with a matching thickness of 4 mm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Magnetic sputtering of FeNi/C bilayer film on SiC fibers for effective microwave absorption in the low-frequency region
Tong Guo, Ben Huang, Changgeng Li, Yumin Lou, Xiu-Zhi Tang, Xiaozhong Huang, Jianling Yue
Ceramics International.2021; 47(4): 5221. CrossRef
- Magnetic sputtering of FeNi/C bilayer film on SiC fibers for effective microwave absorption in the low-frequency region
- [Korean]
- Influence of Sintering Temperature on Magnetic Properties of Ni-Zn-Cu Ferrites Used for Mangetic Shielding in NFC
- Yo-Han Ryu, Sung-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):132-135. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.132
- 481 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
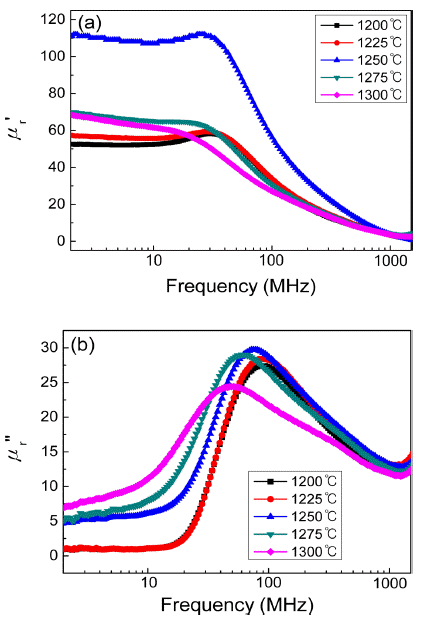
PDF This study investigates the influence of sintering temperature on the magnetic properties and frequency dispersion of the complex permeability of Ni–Zn–Cu ferrites used for magnetic shielding in near-field communication (NFC) systems. Sintered specimens of (Ni0.7Zn0.3)0.96Cu0.04Fe2O4 are prepared by conventional ceramic processing. The complex permeability is measured by an RF impedance analyzer in the range of 1 MHz to 1.8 GHz. The real and imaginary parts of the complex permeability depend sensitively on the sintering temperature, which is closely related to the microstructure, including grain size and pore distribution. In particular, internal pores within grains produced by rapid grain growth decrease the permeability and increase the magnetic loss at the operating frequency of NFC (13.56 MHz). At the optimized sintering temperature (1225-1250°C), the highest permeability and lowest magnetic loss can be obtained.
- [Korean]
- High-frequency Magnetic Properties of Ni-Zn-Co Ferrites Used for Mangetic Shielding in NFC
- Yo-Han Ryu, Sung-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):429-433. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.429
- 614 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
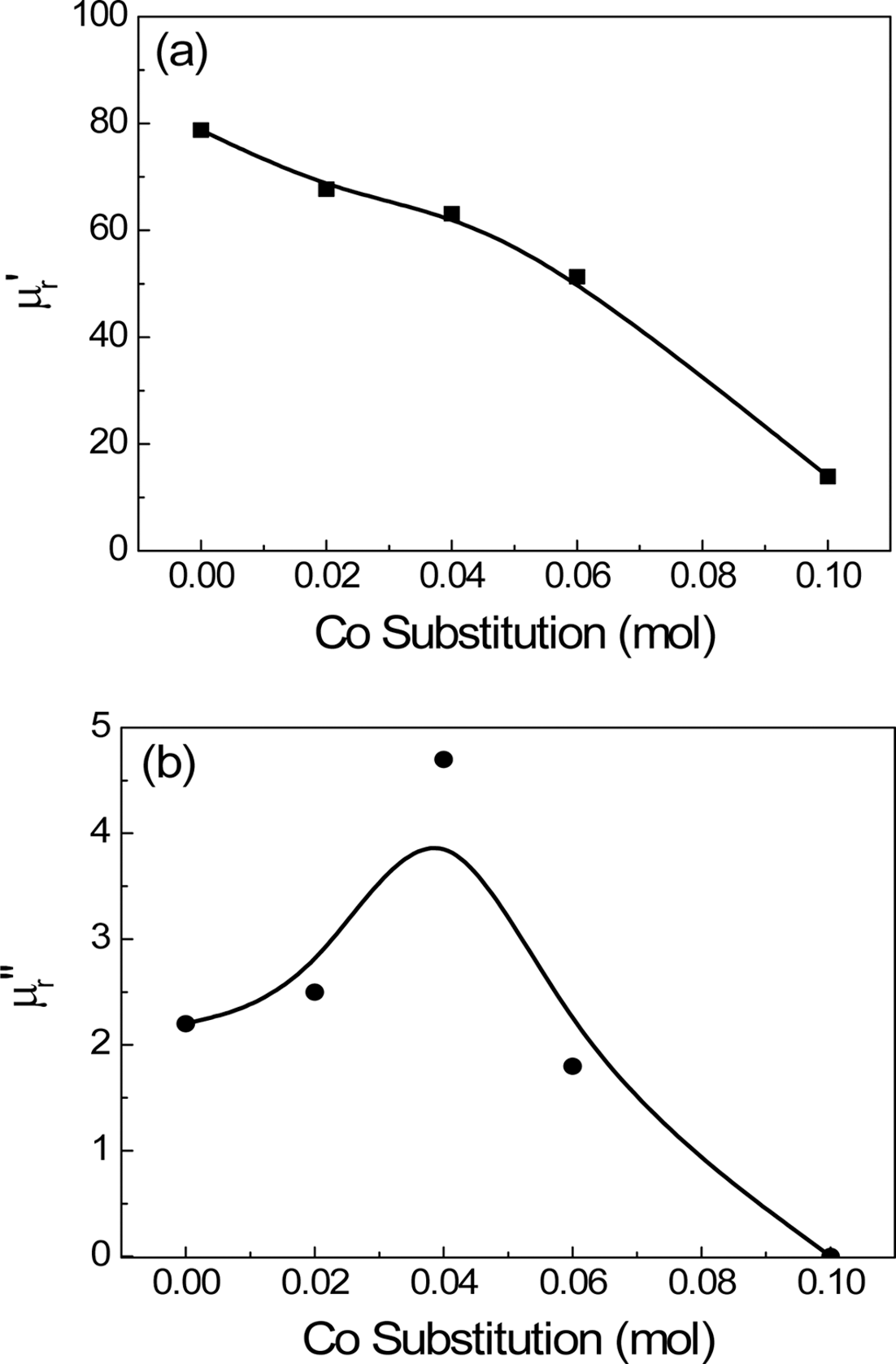
PDF This study investigated the magnetic properties and frequency dispersion of complex permeability of Ni-Zn-Co ferrites used for magnetic shielding in near field communication (NFC) system. The sintered specimens of (Ni0.7Zn0.3)1-xCoxFe2O4 composition were prepared by the conventional ceramic processing. The coercive force and saturation magnetization were measured by vibrating sample magnetometer. The complex permeability was measured by RF impedance analyzer in the range of 1 MHz~1.8 GHz. The coercive force increased and saturation magnetization decreased with increasing the Co substitution. The real and imaginary parts of complex permeability decreased and the resonance frequency increased with Co substitution, which was attributed to the increase in crystal anisotropy field and reduction in saturation magnetization. The effect of Co substitution could be found in reducing the magnetic loss to nearly zero at the operating frequency of NFC (13.56 MHz).
- [Korean]
- Microwave Absorbing Properties of Rubber Composites Containing Soft Magnetic Fe-Alloy Particles
- Han-Shin Cho, Sung-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(2):125-128.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.2.125

- 652 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magnetic and dielectric properties of rubber composites are controlled by using two kinds of high-permeability metal particles with different electrical conductivity (Sendust, Permalloy), and their effect on microwave absorbance has been investigated, focusing on the quasi-microwave frequency band (0.8-2 GHz). Noise absorbing sheets are composite materials of magnetic flake particles of high aspect ratio dispersed in polymer matrix with various filler amount of 80-90 wt.%. The frequency dispersion and magnitude of complex permeability is almost the same for Sendust and Permalloy composite specimens. However, the complex permittivity of the Permalloy composite (varepsilon_rprimesimeq250, varepsilon_rprimeprimesimeq50) is much greater than that of Sendust composite (varepsilon_rprimesimeq70, varepsilon_rprimeprimesimeq0). Due to the large dielectric permittivity of Permalloy composite, the absorbing band is shifted to lower frequency region. However, the investigation of impedance matching reveals that the magnetic permeability is still small to satisfy the zero-reflected condition at the quasi-microwave frequency band, resulting in a small microwave absorbance lower than 10 dB.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermo-oxidative stability of rubber magnetic composites cured with sulfur, peroxide and mixed curing systems
Ján Kruželák, Andrea Kvasničáková, Rastislav Dosoudil
Plastics, Rubber and Composites.2018; 47(7): 324. CrossRef - Electromagnetic Wave Shielding Effect of Nano-powder Dispersed Epoxy Resin Composite
Jun-Young Han, Chul-Hee Lee, Min-Gyu Choi, Soon-Jik Hong, Joong-Hark Park, Dong-Jin Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.1970; 22(4): 234. CrossRef
- Thermo-oxidative stability of rubber magnetic composites cured with sulfur, peroxide and mixed curing systems
- [Korean]
- Sintering and Microwave Dielectric Properties of Bi18(Ca0.725Zn0.275)8Nb12O65 [BCZN] Dielectrics with V2O5 Addition
- Young-Jong Lee, Sung-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(4):289-294.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.4.289

- 471 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - For the aim of low-temperature co-fired ceramic microwave components, sintering behavior and microwave properties (dielectric constant varepsilon_r, quality factor Q, and temperature coefficient of resonant frequency tau_f) are investigated in Bi_18O(Ca_0.725Zn_0.275)_8Nb_12O_65 [BCZN] ceramics with addition of V_2O_5. The specimens are prepared by conventional ceramic processing technique. As the main result, it is demonstrated that the additives (V_2O_5) show the effect of lowering of sintering temperature and improvement of microwave properties at the optimum additive content. The addition of 0.25 wt% V_2O_5 lowers the sintering temperature to 890°C utilizing liquidphase sintering and show the microwave dielectric properties (dielectric constant varepsilon_r = 75, quality factor Qtimesf = 572 GHz, temperature coefficient of resonance frequency tau_f;=;-10;ppm/°C). The estimated microwave dielectric properties with V_2O_5 addition (increase of varepsilon_r, decrease of Qtimesf, shift of tau_f to negative values) can be explained by the observed microstrucure (sintered density, abnormal grain structure) and possibly high-permittivity Bi_18Zn_8Nb_12O_65 (BZN) phase determined by X-ray diffraction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- V2O5-Assisted Low-Temperature Sintering and Microwave Dielectric Properties of (1 − x)Li2.08TiO3–xLi2ZnTi3O8 (x = 0.3−0.7) Ceramics for LTCC Applications
Yu-Seon Lee, Kyoung-Ho Lee
Materials.2025; 19(1): 94. CrossRef
- V2O5-Assisted Low-Temperature Sintering and Microwave Dielectric Properties of (1 − x)Li2.08TiO3–xLi2ZnTi3O8 (x = 0.3−0.7) Ceramics for LTCC Applications
- [Korean]
- Effects of the Sintering Variable on Impact Energy in MA 316L ODS and Wet 316L ODS Stainless Steels
- Sung-Soo Kim, Chang-Hee Han, Jin-Sung Jang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(2):113-122.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.2.113

- 432 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Two kinds of oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) 316L stainless steel were manufactured using a wet mixing process(wet) and a mechanical alloying method (MA). An MA 316L ODS was prepared by a mixing of metal powder and a mechanical alloying process. A wet 316L ODS was manufactured by a wet mixing with 316L stainless steel powder. A solution of yttrium nitrate was dried after being in the wet 316L ODS alloy. The results showed that carbon and oxygen were effectively reduced during the degassing process before the hydroisostatic process (HIP) in both alloys. It appeared that the effect of HIP treatment on increase in impact energy was pronounced in the MA 316L ODS alloy. The MA 316L ODS alloy showed a higher yield strength and a smaller elongation, when compared to the wet 316L ODS alloy. This seemed to be attributed to the enhancement of bonding between oxide and matrix particles from HIP and to the presence of a finer oxide of about 20 nm from the MA process in the MA 316L ODS alloy.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of ODS 316L Stainless Steels
- Min-Ho Kim, Ho-Jin Ryu, Sung-Soo Kim, Chang-Hee Han, Jin-Sung Jang, Oh-Jong Kwon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(2):122-130.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.2.122

- 670 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Austenitic oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) stainless steel was fabricated using a wet mixing process without a mechanical milling in order to reduce contaminations of impurities during their fabrication process. Solution of yttrium nitrate was dried after a wet mixing with 316L stainless steel powder. Carbon and oxygen contents were effectively reduced by this wet processing. Microstructural analysis showed that coarse yttrium silicates of about 150 nm were formed in austenitic ODS steels with a silicon content of about 0.8 wt%. Wet-processed austenitic ODS steel without silicon showed higher yield strength by the presence of finer oxide of about 20 nm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dispersion Behaviors of Y2O3Particles Into Aisi 316L Stainless Steel by Using Laser Cladding Technology
Eun-Kwang Park, Sung-Mo Hong, Jin-Ju Park, Min-Ku Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Kyeong-Won Seol, Yang-Kyu Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(4): 269. CrossRef - Effects of the Sintering Variable on Impact Energy in MA 316L ODS and Wet 316L ODS Stainless Steels
Sung-Soo Kim, Chang-Hee Han, Jin-Sung Jang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2010; 17(2): 113. CrossRef
- Dispersion Behaviors of Y2O3Particles Into Aisi 316L Stainless Steel by Using Laser Cladding Technology
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


