Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- The Synthesis Method of Tin Dioxide Nanoparticles by Plasma-Assisted Electrolysis Process and Gas Sensing Property
- Tae Hyung Kim, Yoseb Song, Chan-Gi Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):351-356. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.351
- 1,439 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
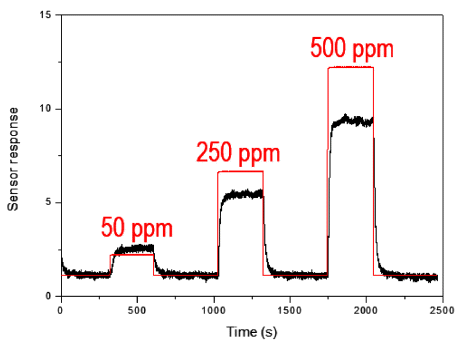
PDF Tin dioxide nanoparticles are prepared using a newly developed synthesis method of plasma-assisted electrolysis. A high voltage is applied to the tin metal plate to apply a high pressure and temperature to the synthesized oxide layer on the metal surface, producing nanoparticles in a low concentration of sulfuric acid. The particle size, morphology, and size distribution is controlled by the concentration of electrolytes and frequency of the power supply. The as-prepared powder of tin dioxide nanoparticles is used to fabricate a gas sensor to investigate the potential application. The particle-based gas sensor exhibits a short response and recovery time. There is sensitivity to the reduction gas for the gas flowing at rates of 50, 250, and 500 ppm of H2S gas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
Min Ah Han, Hyun-Jong Kim, Hee Chul Lee, Jin-Seong Park, Ho-Nyun Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 133. CrossRef
- Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Properties of InP/ZnS core/shell Nanoparticles with One-pot process
- So Yeong Joo, Myung Hwan Hong, Leeseung Kang, Tae Hyung Kim, Chan Gi Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):11-16. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.11
- 1,001 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
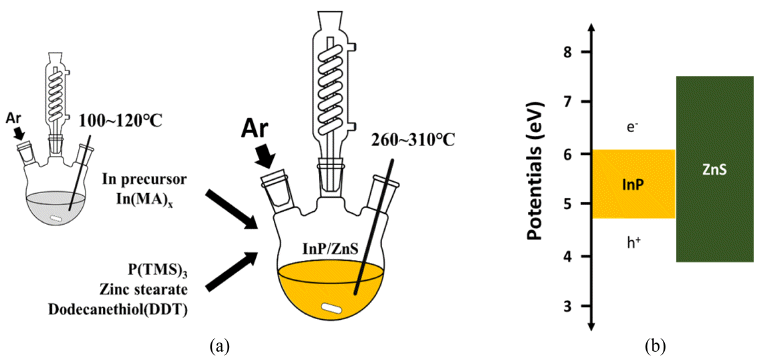
PDF In this study, simple chemical synthesis of green emitting Cd-free InP/ZnS QDs is accomplished by reacting In, P, Zn, and S precursors by one-pot process. The particle size and the optical properties were tailored, by controlling various experimental conditions, including [In]/[MA] (MA: myristic acid) mole ratio, reaction temperature and reaction time. The results of ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV-vis), and of photoluminescence (PL), reveal that the exciton emission of InP was improved by surface coating, with a layer of ZnS. We report the correlation between each experimental condition and the luminescent properties of InP/ZnS core/shell QDs. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) techniques were used to characterize the as-synthesized QDs. In contrast to core nanoparticles, InP/ZnS core/shell treated with surface coating shows a clear ultraviolet peak. Besides this work, we need to study what clearly determines the shell kinetic growth mechanism of InP/ZnS core shell QDs.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


