Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
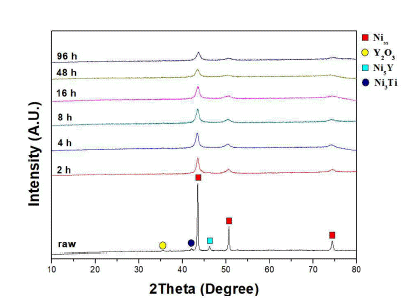
- Analysis on Milling Behavior of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Ni-based Atomizing Powder with Ni5Y Intermetallic Phase
- Chun Woong Park, Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):101-106. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.101
- 990 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ni-based oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) alloys have a higher usable temperature and better hightemperature mechanical properties than conventional superalloys. They are therefore being explored for applications in various fields such as those of aerospace and gas turbines. In general, ODS alloys are manufactured from alloy powders by mechanical alloying of element powders. However, our research team produces alloy powders in which the Ni5Y intermetallic phase is formed by an atomizing process. In this study, mechanical alloying was performed using a planetary mill to analyze the milling behavior of Ni-based oxide dispersions strengthened alloy powder in which the Ni5Y is the intermetallic phase. As the milling time increased, the Ni5Y intermetallic phase was refined. These results are confirmed by SEM and EPMA analysis on microstructure. In addition, it is confirmed that as the milling increased, the mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloy powder improve due to grain refinement by plastic deformation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
Xuelian Xiao, Keke Chang, Kai Xu, Ming Lou, Liping Wang, Qunji Xue
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2023; 167: 94. CrossRef - Effect of high-energy ball milling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloys fabricated using gas-atomized powder
Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2022; 57(38): 18195. CrossRef
- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
- [Korean]
- New Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 high-entropy alloy Fabricated by Powder Metallurgy
- Dami Yim, Hyung Keun Park, Antonio Joao Seco Ferreira Tapia, Byeong-Joo Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):208-212. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.208

- 1,037 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this paper, a new Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 high entropy alloy (HEA) is identified as a strong candidate for the single face-centered cubic (FCC) structure screened using the upgraded TCFE2000 thermodynamic CALPHAD database. The Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 HEA is fabricated using the mechanical (MA) procedure and pressure-less sintering method. The Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 HEA, which consists of elements with a large difference in melting point and atomic size, is successfully fabricated using powder metallurgy techniques. The MA behavior, microstructure, and mechanical properties of the Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 HEA are systematically studied to understand the MA behavior and develop advanced techniques for fabricating HEA products. After MA, a single FCC phase is found. After sintering at 900°C, the microstructure has an FCC single phase with an average grain size of 18 μm. Finally, the Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 HEA has a compressive yield strength of 302 MPa.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Composites of equiatomic Y, La, Ce, Nd, and Gd rare earth oxides: Chemical-shift effects and valence spectra
Jungsu Bin, Hyunbae Gee, Taesung Park, UiJun Go, Jeoung Han Kim, Youn-Seoung Lee
Current Applied Physics.2024; 59: 85. CrossRef - Fabrication, microstructure and mechanical property of a novel Nb-rich refractory high-entropy alloy strengthened by in-situ formation of dispersoids
Byungchul Kang, Taeyeong Kong, Ahmad Raza, Ho Jin Ryu, Soon Hyung Hong
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2019; 81: 15. CrossRef
- Composites of equiatomic Y, La, Ce, Nd, and Gd rare earth oxides: Chemical-shift effects and valence spectra
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


