Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Powder Metall Inst > Volume 22(1); 2015 > Article
-
ARTICLE
분말야금 스테인리스 스틸의 산화특성에 미치는 조성 및 조직변화의 영향 - 이종필, 홍지현, 박동규, 안인섭*
- The Effects of Composition and Microstructure Variation on the Oxidation Characteristics of Stainless Steels Manufactured by Powder Metallurgy Method
- Jong-Pil Lee, Ji-Hyun Hong, Dong-Kyu Park, In-Shup Ahn*
-
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute 2015;22(1):52-59.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.52
Published online: January 31, 2015
경상대학교 나노·신소재융합공학부 및 LINC 사업단
School of Nano and Advanced Materials Science & Engineering, and LINC, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 660-701, Korea
- *Corresponding author : In-Shup Ahn, TEL: +82-55-772-1662, FAX: +82-55-772-1670, ais@gnu.ac.kr
© Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute All rights reserved
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,263 Views
- 11 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
- As well-known wrought stainless steel, sintered stainless steel (STS) has excellent high-temperature anticorrosion even at high temperature of 800°C, and exhibits good corrosion resistance in air. However, when temperature increases above 900°C, the corrosion resistance of STS begins to deteriorate and dramatically decreases. In this study, the effects of phase and composition of STS on high-temperature corrosion resistances are investigated for STS 316L, STS 304 and STS 434L above 800°C. The morphology of the oxide layers are observed. The oxides phase and composition are identified using X-ray diffractometer and energy dispersive spectroscopy. The results demonstrate that the best corrosion resistance of STS could be improved to that of 434L. The poor corrosion resistance of the austenitic stainless steels is due to the fact that NiFe2O4 oxides forming poor adhesion between the matrix and oxide film increase the oxidation susceptibility of the material at high temperature.
- 오스테나이트계 sintered stainless steel(STS)는 우수한 내식성, 내산화성 및 기계적 성질을 가지고 있어 일반 구 조용 재료, 저장용기, 화학공업용 재료 등에 널리 사용되 고 있으며[1, 2] 일반적으로 스테인리스 스틸의 사용온도 는 성분에 따라 다르나 대체로 600~1000℃ 범위이다. 대 표적인 오스테나이트계 STS 304 스테인리스 스틸에 황을 첨가하여 기계 가공성을 증진시킨 것이 STS 303이고, 탄 소함량을 낮추어 용접성을 증가시킨 것이 STS304L이며, Mo을 첨가하여 해수 또는 화학공업환경에서 부식저항성 을 증진시킨 STS316으로 발전되어 왔다. 특히 STS316 스 테인리스 스틸은 오스테나이트계 Cr-Ni-Mo합금으로서 핏 팅부식(Pitting Corrosion)을 방지하여 STS304 보다 더 우 수한 부식성을 부여하고, Mo에 의한 고용강화효과와 탄소 함량을 낮추어서 용접 시 탄화물 석출이 생성되지 않는 장점이 있다[3].
- Bitter등은 수증기와 일반 공기 중에서 STS 304L강의 고 온 산화에 대하여 연구하였는데, 이들의 연구결과에 의하 면 수증기 중에서는 초기에 FeO(Wustite)형성으로 인해 산화량이 시간에 따라 직선적으로 증가하다가, 내부에 (Fe-Cr)스피넬이 형성되어 산화속도가 점차 감소하지만, 반면에 공기중에서는 산화 초기에 (Cr,Fe)2O3의 보호성의 산화피막이 형성됨에 따라 포물선 형태로 빠르게 증가한 다고 하였다[4].
- S. C. Kuiry등은 고온에서 STS316L강의 표면상태에 따 른 산화특성을 연구하였는데 그 들의 연구 결과에 의하면 표면을 SiC연마지로 연마한 경우 산화 초기에 기계적 연 마에 의해 변형된 층을 통한 크롬의 빠른 외부확산에 의 해 표면에 Cr-rich 산화물을 형성함으로서 전해 에칭한 경 우보다 내산화성이 증가한다고 보고하였다[5]. 또한 스테 인리스 스틸에 Al, Si등의 원소를 첨가하거나[6] 표면에 이들 원소를 피복함으로서 고온에서 안정한 Al2O3, SiO2 와 같은 산화물을 표면에 형성시켜 내산화성을 증가시키 거나[7] 이들 합금에 활성화 원소인 Y, Ce, Hf을 소량 첨 가함에 의해 스케일 부착성을 증가시켜 내산화성을 향상 시킨다고 보고하였다[6]. 이와 같이 스테인리스 스틸의 표 면에 형성되는 산화피막의 성분은 산화 분위기나 표면 상 태 또는 첨가 원소에 의해 달라지게 되고 산화초기에 표 면에 형성된 산화피막이 전체적인 산화 속도를 지배하는 결과를 가져온다.
- 한편, Fe-Cr 합금의 페라이트계 스테인리스 스틸은 C 0.2%이하 Cr 11~27%의 성분범위를 가지며 경화성은 없 지만 마르텐사이트계에 비해 가공성이나 용접성도 좋고 대기 중의 산화뿐만 아니라 강산화성 용액에도 강하므로 질산계 화학공업용이나 건축재료, 주방용재료로서 사용된 다. 페라이트 계 스테인리스 스틸은 오스테나이트계보다 저렴하며 양호한 내식성, 내열성을 가지고 있으며 안정적 인 α 상을 형성함으로써 열팽창율이 낮고 열경화성이 없 다. 페라이트계 대표적 강종은 STS430(18Cr) 이며 여기에 Mo을 첨가하여 내식성을 향상시키고 C 함량을 낮추어 가 공성 및 용접성을 개량시킨 강종으로 STS434L 강이 있다 [8, 9]. 일반적으로 스테인리스 스틸은 대부분 종래의 주조 법으로 제조되고 있지만, 분말야금법(P/M) 복잡한 소형부 품을 낮은 생산가격으로 제조할 수 있는 이점이 있다. 그 러나 일반 스테인리스 스틸보다 더 부식을 잘 일으키는 기공구조를 갖는 P/M 스테인리스 스틸은 내부까지 개기 공을 통해 산화가 진행되므로 galvanic couple을 형성하여 활성표면을 증가시키는 역할을 한다[10, 11]. 따라서 소결 스테인리스 스틸의 고온 산화 거동이 일반적인 스테인리 스 스틸의 부식거동을 따르지 않는다고 알려져 있으며, [12-15] 고온에서의 P/M 스테인리스 스틸의 산화거동에 대한 자료는 많지 알려져 있지 않다.
- 따라서 본 연구에서는 Ni 함량이 다른 오스테나이트계 스 테인리스 스틸인 STS 316L과 오스테나이트상과 페라이트 상이 공존하는 STS 304L 강 그리고 페라이트계 스테인리스 스틸인 STS 434L을 택하여 상변화 및 조직변화에 대한 스 테인리스 스틸의 고온 산화거동을 연구하고자 하였다.
서 론
- 본 연구에서 사용된 STS; stainless steel(korea standard) 316L, 304L, 434L 분말은 Daido 사(일본)의 제품이며, 각 분말의 특성을 확인하기 위하여 전계방출형 주사현미경 (FE-SEM)으로 분말의 형상을 그림 1에 나타내었고, 각 분 말의 조성, 평균 입도와 밀도를 표 1에 나타내었다.
- Chemical composition, mean particle size and density of each stainless steel powders used in this study
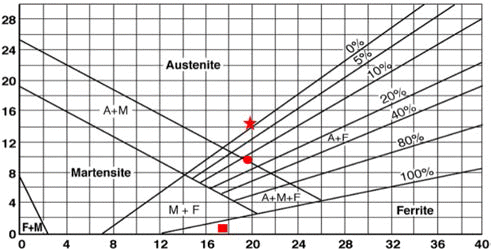
- 그림에서 보여주는 바와 같이 입자의 형태는 모두 수분 사된 불규칙한 형상의 250 μm의 평균입도를 갖는 분말이 었다. 또한 위의 세가지 종류의 스테인리스 스틸은 다음과 같은 당량계산식을 통해 [Cr eq(Cr당량) = Cr + 1.37 Mo + 1.5 Si + 2 Nb + 3 Ti, Ni eq(Ni당량) = Ni + 0.31 Mn + 22 C + 14.2 N + Cu] 그림 2의 Schaeffler diagram[16]을 이용하 여 분류하여 보면 18.1%Cr, 13.55%Ni의 조성을 가지는 STS 316L은 100% 오스테나이트계인 γ 상, 18.1%Cr, 9%Ni의 조성을 가지는 STS 304L은 오스테나이트계 α상 이 80%, 페라이트 γ상이 20% 존재이며, 16.73%Cr 조성 을 가지는 STS 434L은 100% 페라이트상의 스테인리스 스틸이다.
- 표 1과 같은 조성을 가지는 STS 316L, STS 304L, STS 434L 분말에 유압식 성형장비를 이용하여 성형을 하였다. 성형체의 소결은 푸셔로(Pusher furnace)에서 1270℃로 모 든 시편을 일괄 소결하였고 분해암모니아가스(H2 가스량: 10 Nm3/Hr, N2 가스량: 12 Nm3/Hr) 분위기 하에서 진행하 였다. 오스테나이트계 스테인리스 스틸의 고온산화 거동 을 알아보기 위하여 STS 316L(γ ), STS 304L(γ +α) 소결체 를 800℃, 900℃, 1000℃ 온도에서 210시간 동안 산화 시 켜 각각 시간에 따른 산화 거동을 조사하여 비교해 보았 으며, 비교적 내산화성이 우수한 페라이트계 스테인리스 스틸인 STS 434L 소결체 역시 800℃, 900℃, 1000℃에서 210시간 동안 산화 시켜 오스테나이트계 스테인리스 스틸 과 비교하였다. 산화실험은 대기 중에서 실시하였으며, 승 온시간을 30℃/min으로 300° 까지 가열하여 10분동안 예열 을 한 다음, 승온시간은 15℃/min으로 목표 온도까지 가 열하여 목표온도에 도달 했을 때 시편을 장입하였다. 산화 는 최대 210시간까지 하였으며 로에서 꺼내어 공냉후, 각 각의 시편의 단위면적당 무게 증가량을 측정하였다. 고온 산화 시간의 영향과 산화층의 특성을 조사하기 위하여 생 성된 각 산화층의 미세조직을 SEM(Scanning Electron Microscopy)과 OM(Optical Microscopy)을 사용하여 관찰 하였다. 또한, XRD(X-Ray Diffractometer), EDS(Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy)를 이용해 산화층 생성상의 상 분 석과 성분분석을 실시하였다.
실험방법
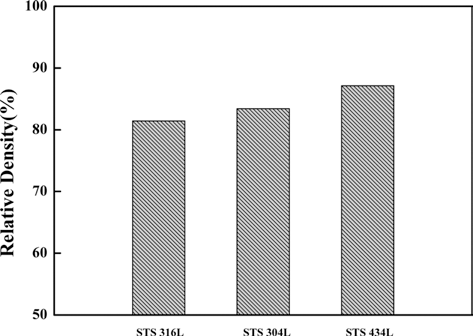
- 본 실험을 위하여 준비된 STS316L, STS 304L 및 STS 434L 소결체들의 밀도를 측정하여 그림 3각 시편의 상대 밀도값을 나타내었다. 분말소결체의 산화거동은 특히 밀 도에 따라 민감하게 변하기 때문에 상대밀도를 비슷한 값 을 갖는 시편을 제조하고자 하였다. 그림 3에서 보여주듯 이 γ 상의 STS 316L의 상대밀도는 82% 이며 γ +α 상의 STS 304L은 83%, 상의 STS 434L은 84%의 상대밀도를 보였다. 이들 시편의 상대밀도가 거의 비슷한 값을 갖고 있으므로 이들 시편으로 고온산화 실험을 진행하였다.
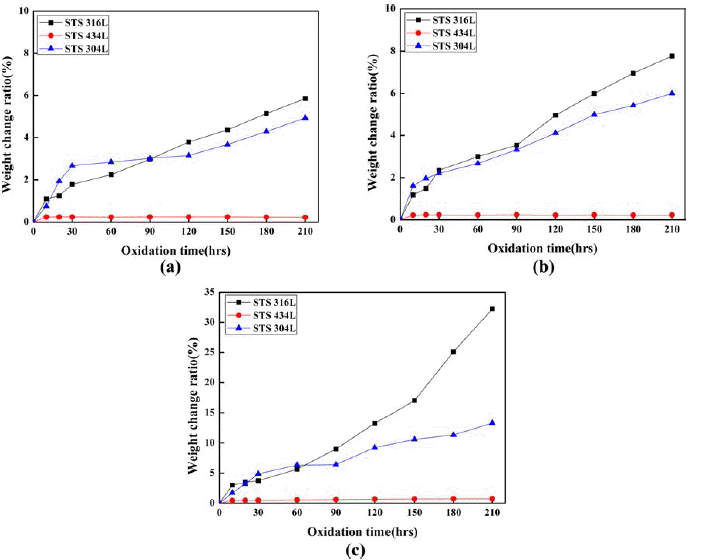
- 산화실험은 800℃에서 1000℃까지 210시간 노출시킨 소결체의 단위면적당 무게증가율을 측정하였다. 그림 4는 각 온도에서 산화 시간에 따른 시편의 단위 면적당 무게 변화를 나타낸 그림이다. 그림에서 보여주는 바와 같이 STS 434L은 모든 온도에서 산화시간에 따라 무게변화가 거의 없었으나 STS 304L 및 316L의 경우는 산화시간이 길어질수록 산화량이 점차 증가하였다. 특히, 그림 4(c)에 서 보여주는 바와 같이 1000℃에서는 γ상을 가지는 오스 테나이트계 STS 316L은 다른 소결체에 비해 더 빠른 무 게증가를 보였다. 그림 4의 STS 304L과 STS 316L의 산 화특성을 비교해 보면 각 온도에서 STS 316L은 산화시간 초기부터 거의 직선적으로 증가하는 양상을 보이는데 온 도가 증가할수록 기울기는 더 커지는 것을 알 수 있다. 반 면에 STS 304L의 경우는 초기산화는 STS 316L보다 빠르 게 일어나지만 시간이 지남에 따라 다소 산화속도가 STS 316L보다 느려지는 경향을 보이고 있다. 일반적으로 Mo 의 첨가는 부식성 및 내산화성 향상을 일으키지만 고온으 로 올라갈수록 Mo가 기화하면서 산화속도가 빨라진다고 보고되었다[17]. Fe-Mo 합금의 경우 Mo 함량이 20%까지 는 MoO2 또는 MoO상태로 산화됨에 따라 급격한 산화를 수반하지 않지만 Cr이나 Ni을 첨가하면 스케일에 균열 또 는 기공을 형성하여 액상의 MoO3를 형성하며, 액상의 MoO3는 Fe또는 Cr과 반응하여 계면에 Fe2O3 또는 Cr2O3 를 석출시켜 보호 피막으로서 기능을 상실시켜 직선적인 산화속도의 증가를 수반한다고 보고된 바 있다[18-20]. 따 라서 316L의 경우 산화층의 결합력이 약한 NiFe2O4 산화 물의 형성으로 인한 박리현상과 Mo 첨가로 인한 Mo의 기화가 산화속도를 증가시킨 것으로 사료된다.
- Weight gain of respective specimens according to the oxidation time at different temperature after 210 hrs oxidation in air: (a) 800°C, (b) 900°C, (c) 1000°C.
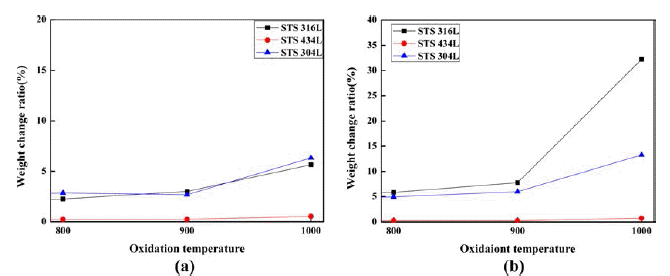
- 그림 5에서 보여주듯이 무게증가율은 온도에 따라 달라 지며, 온도가 올라갈수록 소결체들의 산화가 증가하였다.
- 산화는 900도까지는 STS 304와 STS 316L의 산화정도차 이가 크게 심하지는 않지만 1000도가 되면서 STS 304의 산화는 급격히 증가하였다. 또한 STS 434L의 산화는 온 도에 큰 영향을 받지 않았다. 페라이트계 P/M 스테인리스 스틸은 오스테나이트계 P/M 스테인리스 스틸 보다 산화 저항성이 더 우수하다고 알려져 있으므로, Ni이 P/M 스테 인리스 스틸의 산화 거동에 중대한 역할을 한 것으로 생 각된다.
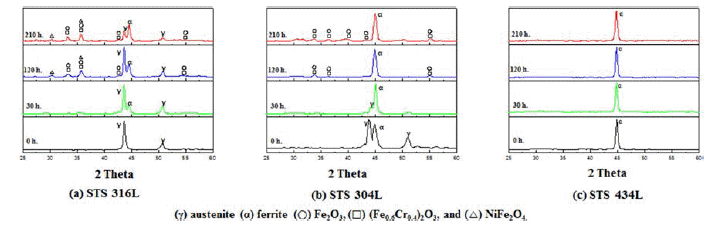
- 대기중에서 고온산화실험을 행한 시편의 온도증가에 따 른 산화거동을 조사하기 위하여 800℃에서 산화시험 후 분석한 X선 회절 패턴을 그림 6에 나타내었다.
- Weight gain of respective specimens related with oxidation temperature: (a) 60 hrs, (b) 210 hrs.
- X-ray diffractograms corresponding to respective specimens after different periods of exposure at 800°C in air: (a) STS 316L, (b) STS 304L, (c) STS 434L.
- STS 316L은 산화시키기 전에는 Fe-상으로 구성되어 있 는 것을 알 수 있었고, STS 304L은 Fe-(+)상으로 STS 434L은 페라이트 상으로 구성됨을 알 수 있었으며, 이는 그림 2의 Schaeffler diagram과 일치하는 것을 알 수 있었 다[16].
- 그리고 그림 6의 (a)와 같이 Fe-γ상의 STS 316L 소결 체는 30시간 이후부터 Fe-α 상이 나타났으며, 시간이 지 남에 따라 Fe-γ피크가 감소하고 Fe-α피크가 증가하는 것 을 확인 할 수 있었으며, 또한 산화물 피크가 120시간부 터 생성되는 것을 알 수 있었다. 산화물 피크의 종류로는 Fe2O3, (Fe0.6Cr0.4)2O3, NiFe2O4인 것을 확인 할 수 있었 다[9]. STS 304L소결체는 시간이 지남에 따라 STS 316L 과 같이 Fe-γ 피크가 감소하고 Fe-α피크가 증가 하였는데, 생성된 산화물들은 Fe2O3, (Fe0.6Cr0.4)2O3 두 가지 였으며, NiFe2O4는 생성되지 않은 것을 알 수 있었다[4]. 즉, 온도 가 올라갈수록 γ상은 소멸되고 α상의 분율이 증가되는 것으로 사료된다. 한편 STS 434L은 α상을 제외하고 어떠 한 피크도 존재하지 않았으며, 산화가 거의 진행되지 않은 것으로 사료된다[21].
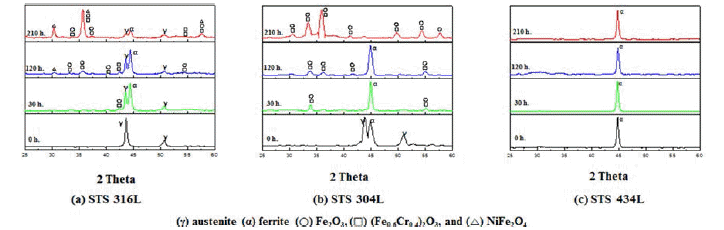
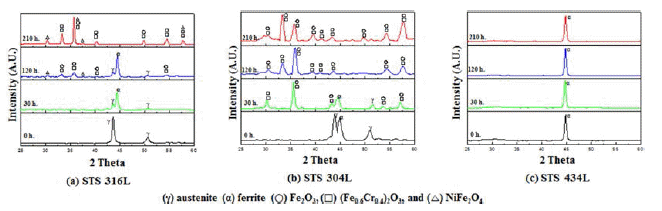
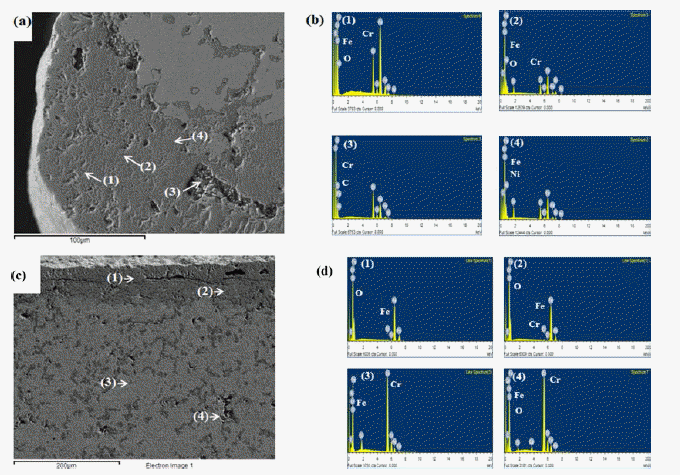
- 이러한 현상은 그림 7에서 보여주는 바와 같이 900도의 산화온도에서도 800℃의 경우와 거의 같은 X-ray 회절 패 턴경향을 보였다. 단지 산화물의 회절피이크의 대부분이 약간 증가하고 좀더 예리하여 졌으며, 316L의 경우 120시 간이후에는 페라이트 상의 강도가 더 증가하였고 STS 304L의 경우는 30시간부터는 γ피크가 나타나지 않았다. 1000℃의 대기중에서 210시간까지 산화시험 후 각 소결체 의 시간에 따른 X선 회절 패턴을 그림 8에 나타내었다. 그림 8(c)에서 보아서 알 수 있듯이 STS 434L은 Fe-α상 만 가지고 산화물 피크는 발견되지 않았다. (a) STS 316L 은 120시간까지 Fe-γ 피크와 Fe-α피크가 존재하였지만 210 시간이 되면서 사라지는 것을 확인 할 수 있었다. 반면에 산화물 피크는 더욱 샤프해지는 것을 알 수 있었으며, 그림 7, 8에서 언급한 바와 같이 산화물종류로는 Fe2O3, FeCr2O3, NiFe2O4산화물이 존재하였다. 이와같이 고온에서 Fe-γ 피 크가 감소하고 Fe-α 상이 나타난 이유는 문헌에 따르면 Fe에 고용되어 있던 첨가원소가 산화시간이 경과함에 따 라 산소와 반응하여 Ni산화물과 Cr산화물로 소비되어 감 소한 첨가원소로 인해 FCC에서 BCC구조로 동소변태가 가능하게 되어 페라이트인 Fe-α상이 나타난 것으로 사료 된다[3, 6, 9]. 또한 210시간이 되면서 대부분의 페라이트 상들도 합금원소와 함께 산화 반응하면서 소멸된 것으로 사료된다. 또한 STS 304L의 경우는 상대적으로 Ni 함량 이 적어서 NiFe2O4산화물이 생성되지 않은 것으로 예측되 며 이것으로 인하여 고온에서 산화가 느리게 진행되는 것 으로 생각된다. 그 이유로는 NiFe2O4산화막은 부착력이 떨어지기 때문에 STS 316L에서는 쉽게 기지조직과 박리 현상이 일어났지만 NiFe2O4산화막이 관찰되지 않은 STS 304L 및 434L에서는 NiFe2O4가 생성되지 않은 관계로 박 리현상이 일어나지 않은 것으로 생각된다. STS 316L(a)과 304L(b)의 산화물상을 좀더 비교 분석해 보고자 EDS 분 석을 하였다. 그림 9은 STS 316L과 STS 304L 시편을 대 기 중 900℃ 210시간 산화시킨 후의 EDS분석 결과이다. 그림 9(c)를 보면 외부 산화물인 점 (1)은 Cr과 Ni이 소량 고용되어 있는 Fe2O3이고, 내부 산화막인 점 (2)는 Ni이 고용되어 있는 (Fe0.6Cr0.4)2O3 산화물이며, 내부 산화막 내 옅은 회색인 점 (3)은 Cr이 고용되어 있는 NiFe2O3 산화물 이고 마지막 점 (4)는 기공 주위의 산화물 부분으로써 주 로 Cr2O3로 이루어진 부분이다. 이와 같이 Fe-γ 상을 가지 는 STS 316L 시편의 경우 Fe는 산화층 전체에 걸쳐 나타 나며 그 아래에는 (Fe0.6Cr0.4)2O3 산화물 생성에서 추측할 수 있는 바와 같이 Fe와 Cr은 비슷한 분포 형태를 가진다. Ni은 산화층과 기지와의 계면에서 발견할 수 있었으며, 문 헌에 의하면 기지 내에서는 spinel 산화물을 형성하여 산 화 속도를 감소시키는 것으로 알려져 있다[18,19].
- X-ray diffractograms corresponding to respective specimens after different periods of exposure at 900°C in air: (a) STS 316L, (b) STS 304L, (c) STS 434L.
- X-ray diffractograms corresponding to respective specimens after different periods of exposure at 1000°C in air: (a) STS 316L, (b) STS 304L, (c) STS 434L.
- The oxide layer formed on sintered (a,b)STS 316L, (c,d)STS 304L stainless steel after 210hr exposure at 900°C in air: (a,c) SEM cross-sectional image, (b,d) EDS spectra of spot (1), (2), (3) and (4).
- STS 316L 및 STS 304L에 합금원소로 첨가된 Si의 경 우 900℃ 이상의 고온에서도 안정한 산화층을 유지하는 원소이며, 산화초기에는 Si의 산화물은 모재 표면에서 Cr 의 핵 생성 site로 작용하면서 Cr산화물의 성장을 촉진시키 므로 표면 Cr2O3층 형성에 필요한 Cr 임계 농도를 줄이는 역 할을 하는 것으로 알려져 있`고, Cr2O3산화피막 아래에 얇은 산화막 SiO2를 형성하여 각종 원소의 확산을 저지하여 내산 화성을 크게 향상되는 것으로 보고된 바 있다[6].
- 한편 기지 내에서도 석출물의 형상이 관찰되었는데 이 러한 석출물은 대기 중의 산소는 표면에서 먼저 반응하여 표면 산화물을 형성하는 반면에, 대기 중의 질소(N)은 기 지 내부의 Cr과 반응하여 CrN으로 석출된 것으로 생각된 다. 이 현상은 900℃에서 스테인레스 스틸기지내에 질화 물이 많이 석출된다는 연구결과와 유사하게 많은 석출상 이 관찰 되었으며, 이러한 Cr질화물의 석출은 국부적인 Cr농도차를 야기하고 이러한 Cr농도 차는 산화속도를 증 가시킨 것으로 알려져 있다[9].
- 그러나 STS 304L 시편의 경우는 산화층에서의 생성상 도 점 (1)은 Cr이 소량 고용되어 있는 Fe2O3 산화물이며, 내 부 산화막인 점 (2)는 Ni이 소량 고용되어있는 (Fe0.6Cr0.4)2O3 산화물이며, 기지내의 점 (3)은 Fe와 Ni, Cr의 복합 탄화 물이며 기공주위의 점 (4)는 Cr2O3로 이루어진, STS 316L 과 비슷한 경향을 보였다. 단, STS 316L 과 비교하여 보 았을 때 STS 316L은 산화층 및 기지와의 계면에 Ni함량 이 높은 반면 STS 304L의 경우 산화층의 Ni함량이 거의 없고 기지금속에 상당량의 Ni이 분포하고 있음을 알 수 있었다.
- STS 304과 같은 저 Cr 스테인리스 스틸은 표면에 (Fe0.6Cr0.4)2O3산화물이나 FeCr2O3와 같은 스피넬 산화물이 형성되기도 하며, 조건에 따라서는 이러한 스피넬 산화물 도 비교적 보호성이 있다. 그러나 Cr2O3 가 형성되고 유지 될 때 가장 보호성이 높은 것으로 알려져 있다. 한편 Ni은 Cr2O3 산화물의 기계적 특성을 향상시키고 금속 이온의 확산을 방해하여 내산화성을 강화시키며 또한, Cr2O3가 Fe2O3와 FeCr2O4로 변하면서 산화속도가 급증하는 현상을 억제하는 것으로 알려져 있다[12, 13]. 그러나, 이미 발표 된 문헌에 의하면[22-25] Ni이 비교적 저온에서 우수한 내 식성과 내산화성을 유지하는 반면 고온에서는 Ni이 부착 력이 약한 NiFe2O4로 산화되는 것으로 알려진 바, 본 연 구에서도 STS 316L에서는 산화층에 생성된 Ni-Fe복합산 화물이 기지와의 결합력을 약화시켜서 박리현상이 일어나 며 STS 304L 및 434L보다도 더 빠르게 산화가 진행된 것 이라 사료된다.
실험결과 및 고찰
- P/M 법으로 제조된 조성별 Fe-γ 계, Fe-(γ +α)계, Fe-α계 소결체의 고온산화거동에 대한 실험 결과, 다음과 같은 결 론을 얻을 수 있었다.
P/M 법으로 제조된 Fe-α계 스테인리스 스틸은 Fe-γ계 스테인리스 스틸 보다 주기적인 산화와 thermal shock 가 있는 곳에서 고온 산화특성이 더 우수 하고 국부부식 에 대한 저항성이 높으며 Crack이 발생할 경향이 더 낮기 때문에 고온 산화에 덜 민감한 것으로 판단된다.
Fe-γ 계의 경우 Ni이 함유되어 고온에서 부착력이 약 한 NiFe2O4로 산화되어 기지금속과 산화층과의 박리를 가 속화 시킨 것으로 판단된다.
같은 조건에서 STS434L의 산화 진행 정도가 가장 느렸 으며, 그 다음으로 STS 304L, STS 316L 순으로 나타났다.
결 론
-
Acknowledgements
- 본 논문은 한국연구재단 (No. NRF-2013R1A1A2063036 호)에 의해 지원받아 수행하였으며 이에 감사드립니다.
감사의 글
- 1. D. B Lee: Korean J. Met. Mater., (2010) 49 153.
- 2. Y. Y Lee, Y. H Kim and Y. D Lee: Korean J. Met. Mater., (1994) 32 123(Korean).
- 3. R. K Wild: Corros. Sci., (1977) 17 87.Article
- 4. J. T Bittel, L. H Sjodahl and J. F White: Corros. Sci., (1969) 25 7.ArticlePDF
- 5. S. C Kuiry, S Seal, S. K Bose and S. K Roy: ISIJ. Int., (1994) 34 599.Article
- 6. F. H Stott, G. C Wood and J Stringer: Oxid. Met., (1995) 44 113.ArticlePDF
- 7. B Weiss and R Stickler: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., (1972) 3 851–0-0.ArticlePDF
- 8. J. H Ryu and K. S Lee: Journal of the Corrosion Science Society of Korea., (1992) 21 69(Korean).
- 9. H-S.J Kim: Korean Powder Metall. Inst., (2013) 20 432.Article
- 10. A Tiziani, A Molinari, L Fedrizzi, A Tomasi and P. L Bronora: Corrosion Sci., (1990) 45 672.
- 11. A Sharon and D Itzhak: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., (1997) 224 177.Article
- 12. S. Y Chen, S. L Kuan and W. T Tsai: Corrosion Sci., (2006) 48 634.
- 13. A. V. C Sobral, M. P Hierro, F. J Prez, W Ristow Jr and C. V Franco: Mater. Corros., (2000) 51 791.Article
- 14. I. S Lee: Korean. J. Met. Mater., (2009) 47 716(Korean).
- 15. A Rahmel and M Schutz: Oxid. Met., (1992) 38 255.ArticlePDF
- 16. T Takalo, N Suutala and T Moisio: Metall. Mater. Trans. A., (1979) 10 1173.ArticlePDF
- 17. Y. Y Lee, Y. H Kim and Y. D Lee: Korean J. Met. Mater., (1994) 32 2(Korean).
- 18. O Vedat Akgun: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., (1995) 203 324.
- 19. G. C Wood: Corrosion Sci., (1962) 2 173.Article
- 20. D Caplan and M Cohen: Corros. Sci., (1959) 15 141.
- 21. T Tanabe and S. J Imoto: Jpn. Inst. Met. Mater., (1979) 9 507.
- 22. A Bautista, F Velasco and J Abenojar: Corrosion Sci., (2002) 45 1343.Article
- 23. H Asteman, J. E Svensson, L. G Johansson and M Norell: Oxid. Met., (1999) 52 95.Article
- 24. J Botella, C Merino and E Otero: Oxid. Met., (1998) 49 297.Article
- 25. F. J Perez, M. J Cristobal, G Arnau, M. P Hierro and J Saura: J. Oxid. Met., (2001) 55 105.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- The effect of different turbulent flow on failure behavior in secondary loop of the pressurized water reactor
Y. Hu, L. Zhao, Y.H. Lu, T. Shoji
Nuclear Engineering and Design.2020; 368: 110812. CrossRef
-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Effect of Laser Beam Diameter on the Microstructure and Hardness of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Additively Manufactured by Direct Energy Deposition
- Effect of Process Stopping and Restarting on the Microstructure and Local Property of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting Process

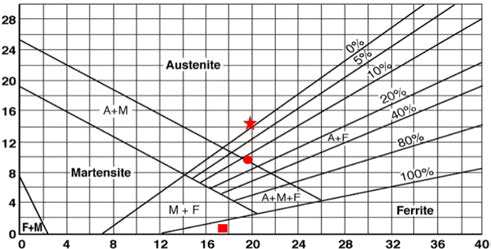
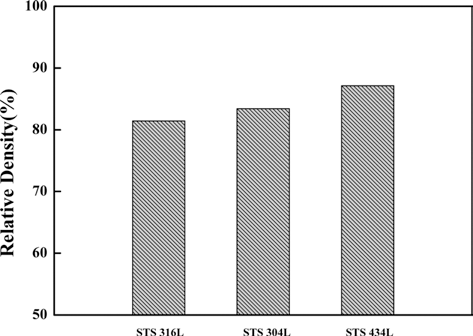
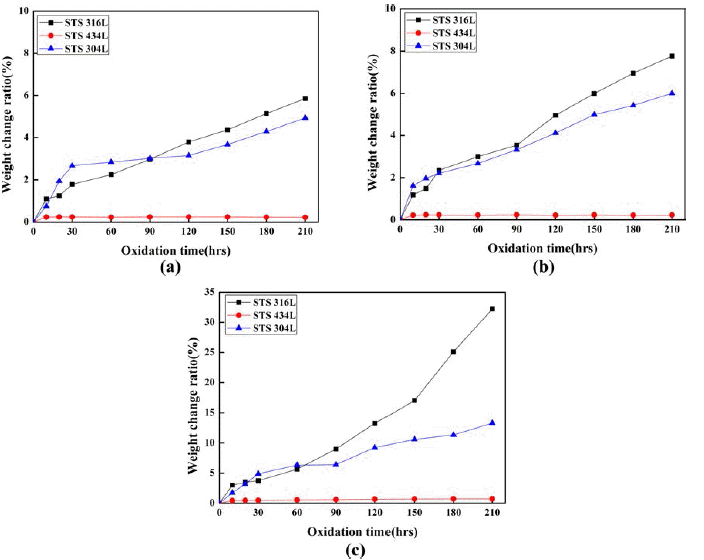
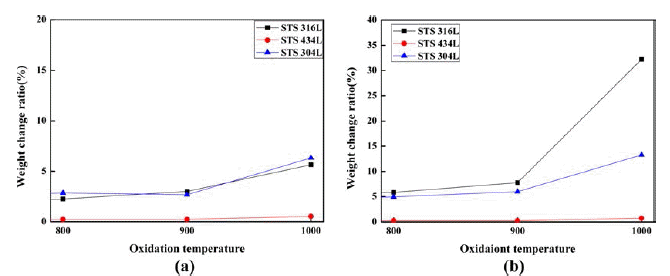
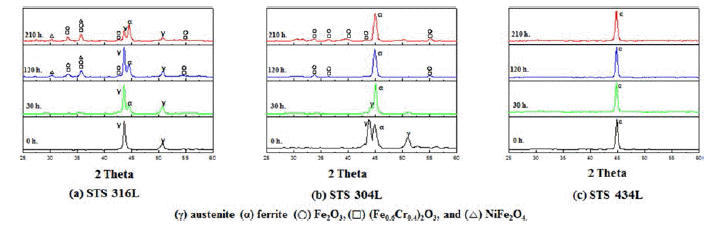
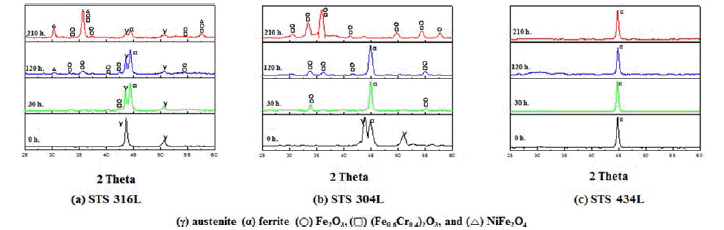
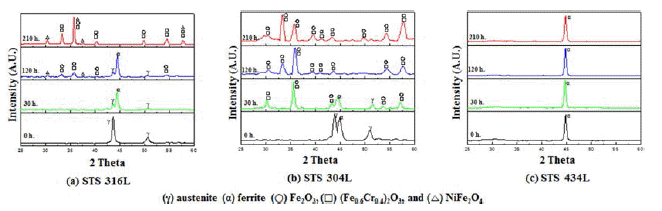

Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
Fig. 5.
Fig. 6.
Fig. 7.
Fig. 8.
Fig. 9.
| C | Cr | Ni | Mo | Si | Mn | Cu | Fe | Mean particle size | Density (g/cm3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||
| STS 316L | 0.02 | 16.1 | 13.55 | 2.24 | 0.87 | 0.1 | 0.2 | Bal | 254 μm | 6.4 |
| STS 304L | 0.02 | 18.1 | 9 | 0.01 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.02 | Bal | 254 μm | 6.3 |
| STS 343L | 0.01 | 16.73 | - | 1.09 | 0.8 | 0.17 | - | Bal | 250 μm | 6.1 |
Table 1.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI