Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Powder Mater > Volume 32(4); 2025 > Article
-
Research Article
- Enhanced Compressive Strength of Fired Iron Ore Pellets: Effects of Blending Fine and Coarse Particle Concentrates
- Ngo Quoc Dung1, Tran Xuan Hai1, Nguyen Minh Thuyet1, Nguyen Quang Tung2, Arvind Barsiwal1, Nguyen Hoang Viet1,*
-
Journal of Powder Materials 2025;32(4):315-329.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00129
Published online: August 29, 2025
1Faculty of Materials Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hanoi University of Science and Technology, Hanoi 100000, Vietnam
2Hoa Phat Dung Quat Steel Joint Stock Company, Binh Son, Quang Ngai 570000, Vietnam
- *Corresponding author: Nguyen Hoang Viet E-mail: viet.nguyenhoang@hust.edu.vn
© The Korean Powder Metallurgy & Materials Institute
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,760 Views
- 69 Download
Abstract
- This study investigated the effects of oxidative firing parameters and raw material characteristics on the pelletization of Australian and Minh Son (Vietnam) iron ore concentrates. The influence of firing temperature (1050°C–1150°C) and holding time (15–120 min) on pellet compressive strength was examined, focusing on microstructural changes during consolidation. Green pellets were prepared using controlled particle size distributions and bentonite as a binder. Scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analyses revealed that grain boundary diffusion, liquid phase formation, and densification significantly improved mechanical strength. X-ray diffraction confirmed the complete oxidation of magnetite to hematite at elevated temperatures, a critical transformation for metallurgical performance. Optimal firing conditions for both single and blended ore compositions yielded compressive strengths above 250 kgf/pellet, satisfying the requirements for blast furnace applications. These results provide valuable guidance for improving pellet production, promoting the efficient utilization of diverse ore types, and enhancing the overall performance of ironmaking operations.
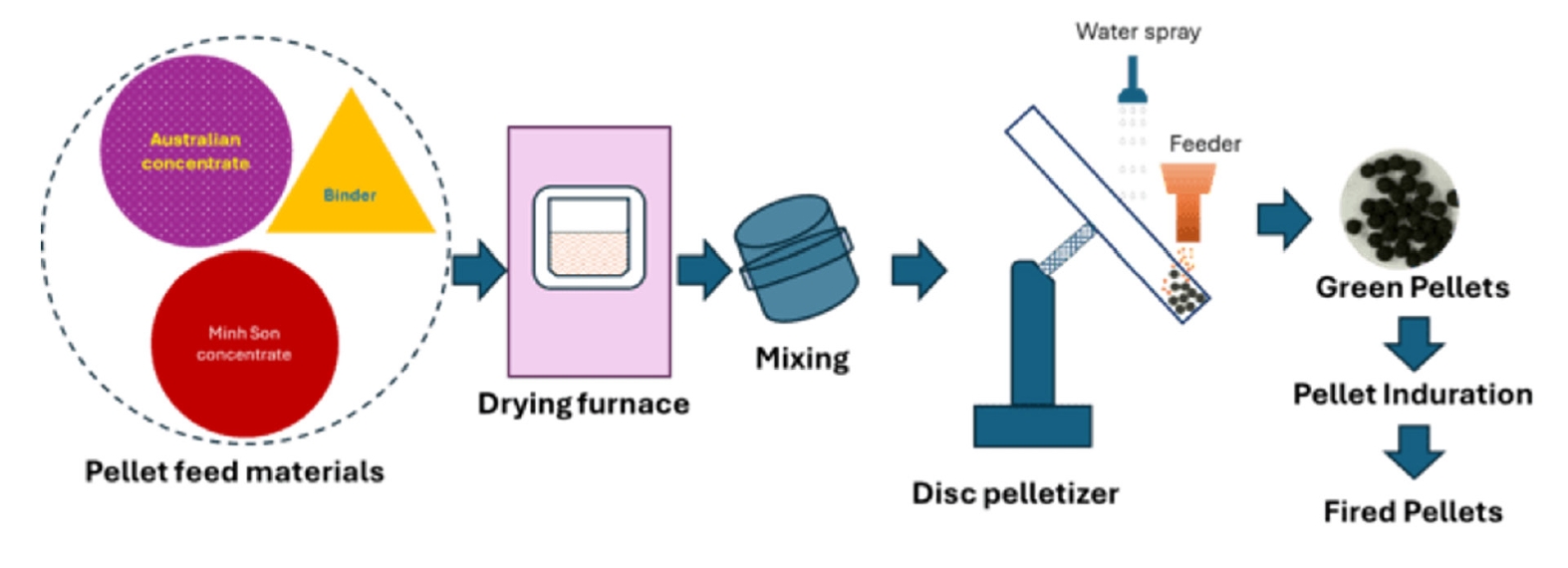
- Iron ore concentrates from Australia and Minh Son are dried, blended with binder, pelletized, and fired oxidatively. The process aims to optimize pellet strength and microstructure by adjusting raw material ratios and firing conditions.
Graphical abstract
- Pelletizing iron ore fines has become an essential step in modern iron and steel production, driven by the declining availability of high-grade lump ores and the growing need to make effective use of finer iron-bearing materials [1-8]. By agglomerating fine particles into pellets, the process not only improves furnace efficiency but also enhances key metallurgical properties such as reducibility and mechanical strength. In addition to pelletization, other agglomeration techniques such as compacting and briquetting are also gaining attention as viable routes for recycling iron ore fines and waste streams [9-12]. These technologies offer greater flexibility in raw material use and can be adapted for various reduction environments, supporting both sustainability and cost-effectiveness in ironmaking.
- Pelletization technology originated in Sweden and Germany in the early 20th century, where initial advancements demonstrated that pelletized fines outperformed lump and sintered ores in reduction efficiency. In the mid-20th century, the United States further industrialized the process, particularly with low-grade Taconite ores. Since the 1960s, pellet production has expanded globally, reaching hundreds of millions of tons annually [5, 13-15].
- Ongoing research has focused on improving pellet quality [1, 16-18]. Studies have explored the development of new organic binders (e.g., Pefidur) to replace traditional bentonite, thereby reducing impurities and enhancing metallurgical properties. Other investigations have aimed to modify the mineral structure of pellets, producing self-fluxing or dolomite-containing pellets to improve blast furnace performance. Enhancing energy efficiency through heat recovery and the use of alternative fuels has also been widely investigated [19-23].
- In Vietnam, iron ore pellets are increasingly incorporated into blast furnace operations at facilities such as Hoa Phat Dung Quat Steel Joint Stock Company and the Viet - Trung Mining and Metallurgy Co.,Ltd. Reports indicate that incorporating 20–25% pellets into the blast furnace charge enhances productivity, reduces coke consumption, and lowers the cost of pig iron production. Moreover, pellet usage addresses the challenge of limited domestic reserves of high-grade magnetite ore.
- Despite global progress in pelletization research, systematic studies examining the specific influence of oxidative firing parameters—particularly firing temperature and holding time—on the mechanical performance of pellets from local Vietnamese ores are lacking. These factors are essential for maximizing pellet quality and ensuring the viability of domestic ores in high-efficiency blast furnaces [10-12, 24].
- This study aims to fill that gap by systematically examining the effects of oxidative firing temperature and duration on the compressive strength of iron ore pellets made from Australian and Minh Son concentrates. By correlating microstructural evolution with mechanical performance, the research seeks to define optimal firing conditions that enhance pellet strength—supporting the development of efficient and localized pellet production technologies in Vietnam.
I. Introduction
- 2.1. Raw Materials and Pellet Preparation
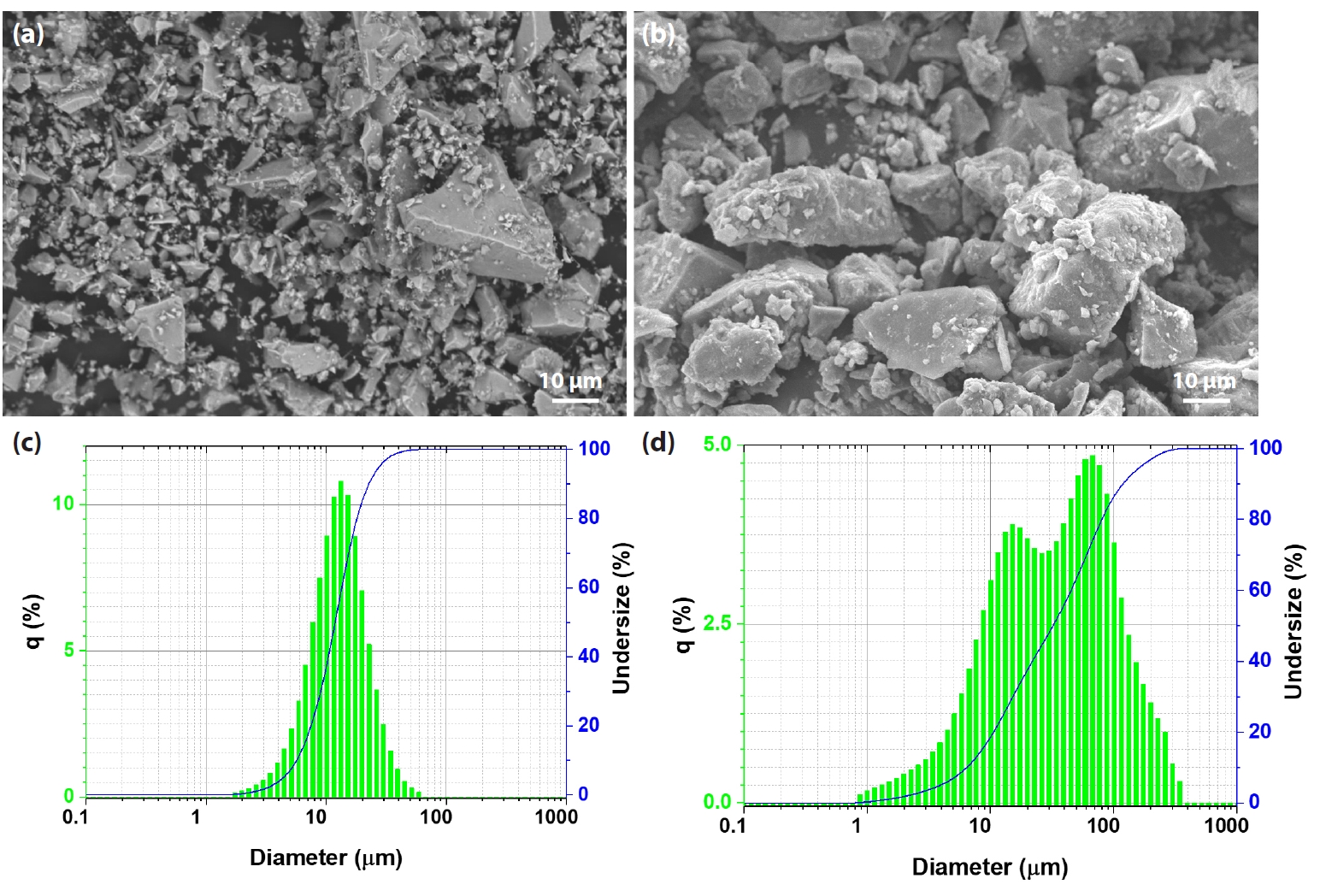
- Iron ore concentrates sourced from Australia and Minh Son Company (Vietnam) were used in this study. Both materials were supplied by Hoa Phat Hai Duong Steel Joint Stock Company [10, 11]. Indian bentonite, with the chemical composition shown in Table 2, was added as a binder at an addition rate of approximately 1.5 wt%. Fig. 1 presents SEM images and particle size distributions of the Australian and Minh Son iron ore concentrates. In Fig. 1a, the Australian concentrate exhibits a fine and relatively homogeneous microstructure, with particles displaying mostly angular shapes and narrow size variation. In contrast, the SEM image of the Minh Son concentrate (Fig. 1b) reveals a coarser texture, where particles are larger, more irregular in shape, and display a broader size range. The corresponding particle size distribution curves (Fig. 1c and 1d) quantitatively confirm these observations. The Australian ore features a much finer distribution, with a median particle size (d50) of approximately 13 μm, while the Minh Son ore shows a d50 of around 50 μm, indicating the presence of significantly coarser grains.
- 2.2. Firing, Mechanical Testing, and Microstructural Characterization
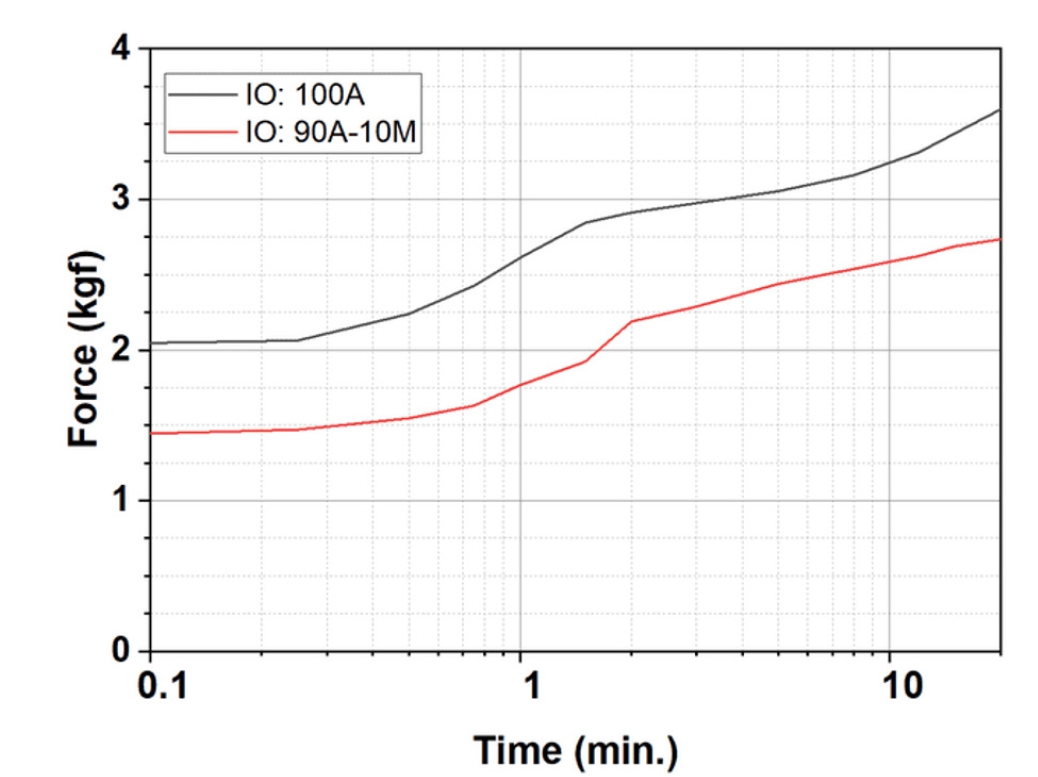
- In this study, four iron ore compositions were prepared: 100% Australian ore (denoted as IO: 100A), 100% Minh Son ore (IO: 100M), and two blends — 90% Australian + 10% Minh Son (IO: 10A–90M) and 20% Australian + 80% Minh Son (IO: 20A–80M). Green pellets were formed using a disc pelletizer, incorporating bentonite and water under controlled conditions. Following pelletization, the green pellets were evaluated for mechanical intergrity using a 5 kgf press [25]. As shown in Fig. 2, all samples satisfied the typical requirement of approximately 1 kg per pellet [1, 2], consistent with reported values for blended magnetite–hematite ores (1.25–1.55 kgf/pellet) [26]. The pellets were subsequently oxidatively fired in a silicon carbide (SiC) electric furnace at target temperatures of 1050°C, 1100°C, and 1150°C, with holding times of 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, and 120 min. Compressive strength was then measured post-firing, based on testing a minimum of five pellets per condition to ensure statistical reliability.
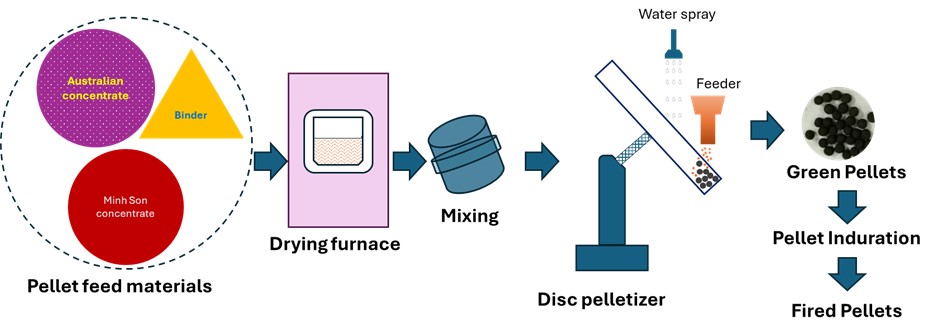
- The schematic diagram of the pelletization process is presented in Fig. 3. It illustrates the drying of iron ore concentrates, followed by blending with a binder and water spraying, green pellet formation, heat hardening to produce fired pellets, and subsequent evaluation of their properties.
- Microstructural analysis of the fired pellets was performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Elemental distribution was investigated via energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) on fracture surfaces and cross-sections. Phase identification was conducted using X-ray diffraction (XRD), with powdered samples obtained from ground fired pellets. The diffraction data were analyzed using Profex software and supporting tools [27, 28] to identify crystalline phases and assess oxidation transformations.
II. Materials and Methods
- 3.1. Compressive Strength Testing
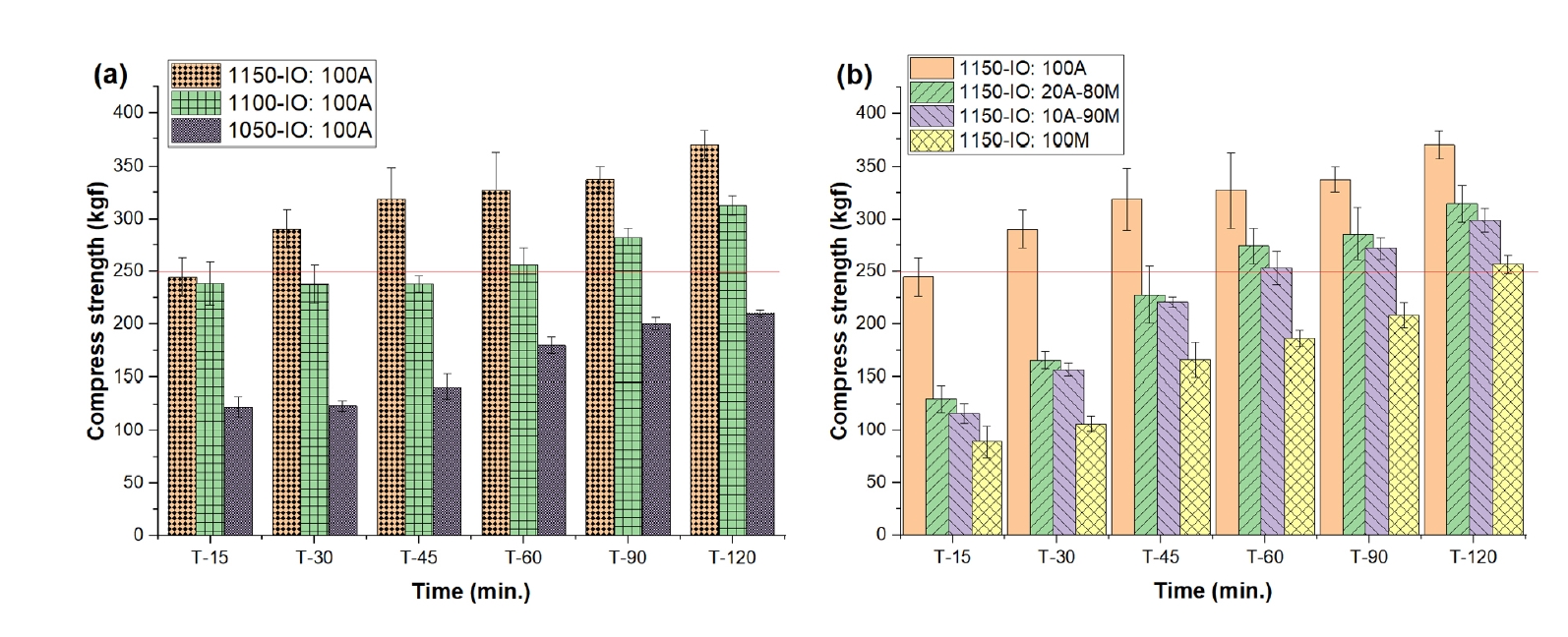
- Fig. 4 presents the compressive strength of oxidatively fired pellets at various temperatures and holding times. At 1050°C, the pellets exhibited relatively low strength, with the 100% Australian ore (IO: 100A) reaching only 122.78 kgf/pellet. Extending the holding time led to progressive improvement, achieving 180.26 kgf/pellet after 60 min and 210.36 kgf/pellet after 120 min. As the firing temperature increased, a notable enhancement in mechanical performance was observed. At 1100°C and 1150°C, the IO: 100A pellets achieved compressive strengths of 238.54 kgf/pellet and 244.77 kgf/pellet, respectively, after just 15 min of holding. Further increases in holding time at 1150°C resulted in continued strength gains: 244.77 kgf/pellet at 15 min, then increasing to 290.94 kgf/pellet at 30 min, 319.18 kgf/pellet at 45 min, 348.86 kgf/pellet at 60 min, and a maximum of 370.01 kgf/pellet at 120 min.
- The performance of blended compositions at 1150°C also followed a similar trend, with compressive strengths measured at 60, 90, and 120 min as follows: 327.59, 337.59, and 370.01 kgf/pellet for IO: 100A; 274.48, 286.27, and 314.84 kgf/pellet for the 20% Australian + 80% Minh Son blend (IO: 20A–80M); 253.43, 272.31, and 299.57 kgf/pellet for the 10% Australian + 90% Minh Son blend (IO: 10A–90M); and 186.00, 208.00, and 257.00 kgf/pellet for 100% Minh Son (IO: 100M). These results indicate that the minimum strength requirement for blast furnace feedstock (≥250 kgf/pellet) [23, 29] was satisfied under specific conditions. The IO: 100A pellets met the requirement after 60 min at 1100°C and from 30 min onward at 1150°C. Blended pellets (IO: 20A–80M and IO: 10A–90M) reached the threshold after 60 min at 1150°C, while IO: 100M required 120 min.
- The improvement in compressive strength with increased temperature and holding time is attributed to the melting of the bentonite binder and localized fusion at ore particle interfaces, which enhance densification and the mechanical integrity of the fired pellets [2].
- 3.2. Morphological Changes of Fracture Surfaces
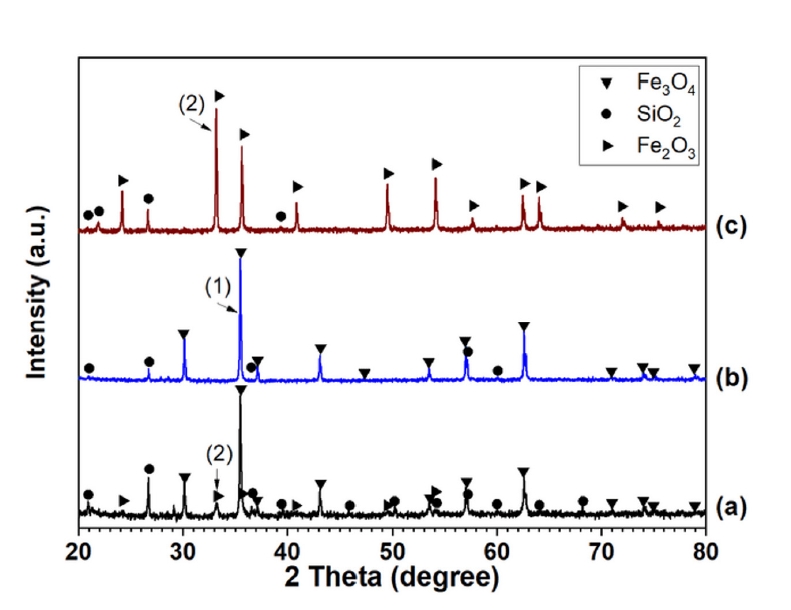
- Fig. 5 presents the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of (a) the initial Minh Son and (b) Australian iron ore concentrates, and (c) typically fired pellet. In these patterns, label (1) corresponds to the main diffraction peaks of the magnetite phase, and label (2) corresponds to the main diffraction peaks of the hematite phase. The analytical results are consistent with the initial information indicating that the Australian and Minh Son ores are primarily magnetite-type ores.
- Fig. 6 shows the observation of the fracture surfaces after compressive strength testing clearly revealed changes in color and morphology of the IO: 100A pellets. At firing temperatures of 1050°C and 1100°C, the pellets exhibited a dark brown color, characteristic of Fe2O3 (hematite) powder. At 1100°C, the color became lighter brown due to the transformation of coarse Fe2O3 crystals. Fracture surfaces at these temperatures also showed fragmented powder remnants after strength testing, indicating weak bonding between ore particles. At 1150°C, the brown color significantly faded, and the pellets exhibited a grayish-blue color. The fracture morphology shifted to larger fragments instead of powdery breakage as observed at lower temperatures, and no fine powder residues were collected after testing. This suggests that inter-particle bonding was significantly enhanced, likely due to the formation of a liquid phase during firing, contributing to the densification and strengthening of the pellets.
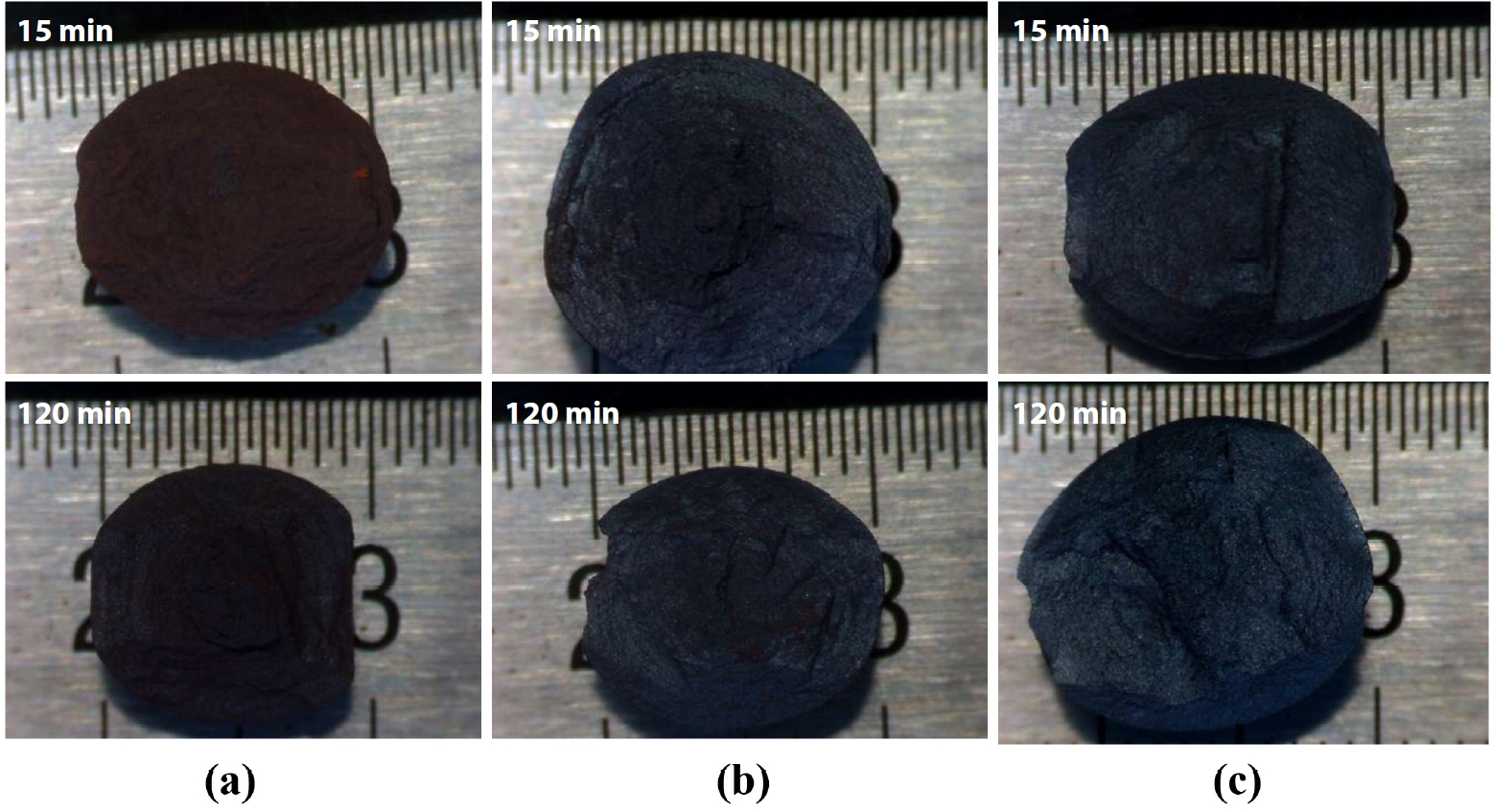
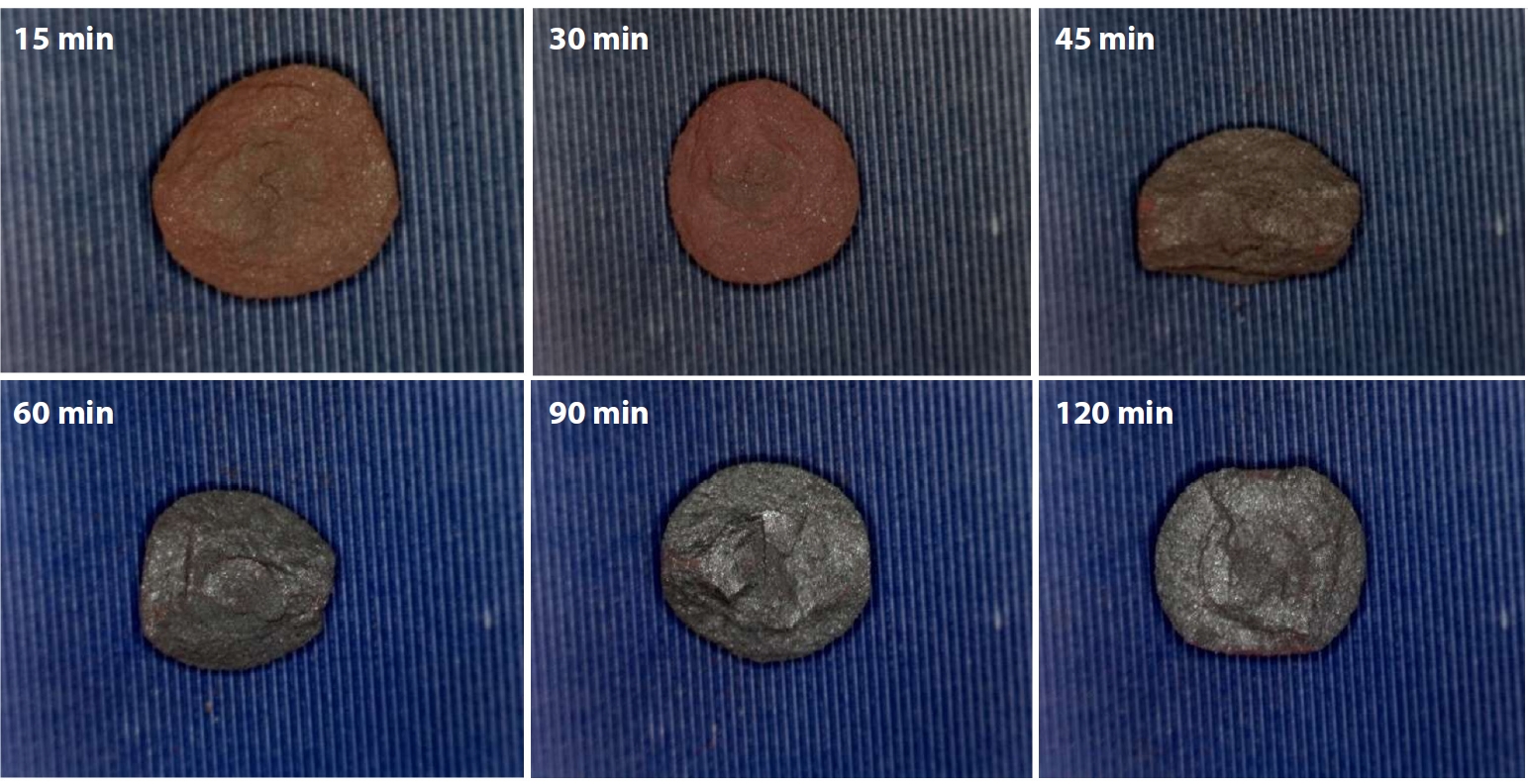
- Consistent with these observations, Fig. 7 shows the fracture surfaces of IO: 100M pellets (100% Minh Son ore) oxidatively fired at 1150°C for varying holding times. Clear changes in surface color and morphology were observed with increasing firing duration. At short holding times of 15 and 30 min, the pellets retained a reddish-brown hue, indicating incomplete oxidation and limited sintering. The fracture surfaces in this range were relatively powdery, suggesting weak inter-particle bonding. As the holding time increased to 45 and 60 min, the surface color gradually darkened, and fracture morphology began to show more coherent fragments. At 90 and especially 120 min, the pellets exhibited a grayish tone with denser and more compact fracture surfaces. The absence of fine powder residues and the shift toward blocky fracture pieces indicate improved sintering behavior, likely due to enhanced grain boundary diffusion and the onset of local liquid-phase formation. These observations are consistent with the increasing compressive strength reported for IO: 100M at extended firing times.
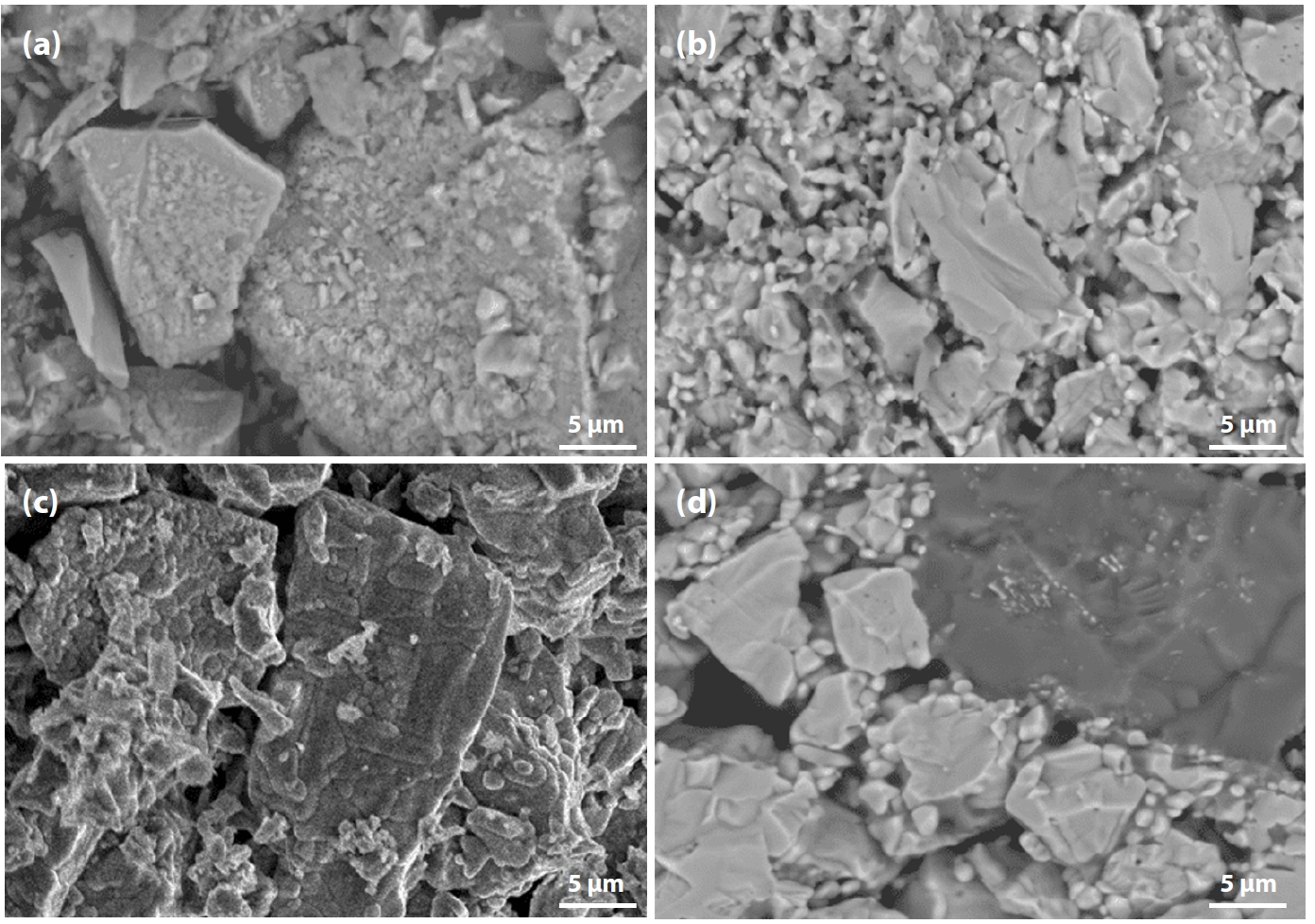
- High-resolution scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images at ×3000 magnification of the fracture surfaces of Australian pellets fired at 1050°C for 30 min, 1100°C for 30 and 120 min, and 1150°C for 30 min are presented in Fig. 8. As shown in Fig. 8a, the fracture surface of the pellet fired at 1050°C for 30 min exhibited discrete, sharp-edged particles—characteristic of the raw ore powder—with weak interparticle bonding, which accounts for the low compressive strength observed. At a higher firing temperature of 1100°C for 30 min, both trans-particle and inter-particle fracture features were observed, corresponding to a compressive strength approaching 250 kgf. When the holding time was extended to 120 min at 1100°C, stronger bonding between particles became evident, sharp particle edges disappeared, and the fracture mechanism shifted toward grain boundary failure, indicating the formation of a more cohesive microstructure and resulting in compressive strength exceeding 250 kgf. Similarly, the pellet fired at 1150°C for 30 min showed significant improvement in grain boundary cohesion due to liquid phase diffusion, and trans-particle fracture was dominant, achieving a compressive strength above 250 kgf.
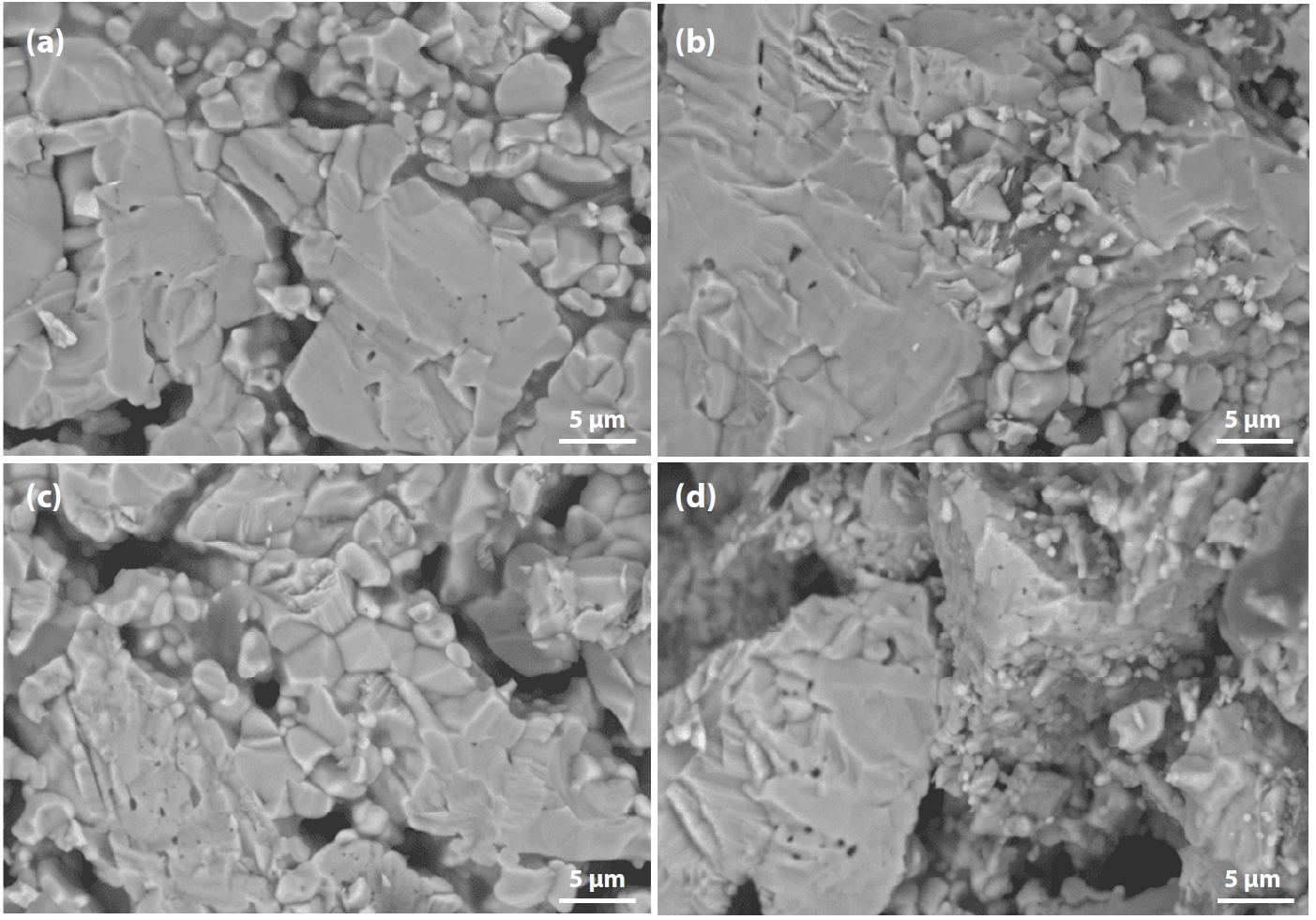
- The characteristic fracture surfaces of pellets fired at 1150°C for 60 min are shown in Fig. 9. It can be observed that pellet porosity varied notably:
- • In Fig. 9(a) (100% Australian ore), most fractures occurred through particle breakage, corresponding to the highest compressive strength.
- • In Fig. 9(d) (100% Minh Son ore), a mixture of large and small grains was observed, with fractures still occurring but with weaker interparticle bonding, resulting in the lowest strength.
- • When blending (c) 10% and (b) 20% Australian ore into Minh Son ore, particle bonding was notably improved.
- SEM image analysis showed that increasing the firing temperature from 1050°C to 1150°C or prolonging the holding time enhanced the solid bonding between fine ore particles. The edges of the ore grains became more rounded, and the dominant fracture mechanism shifted towards trans-particle fracture.The morphological changes of the fired pellets after oxidative firing can be explained by the following factors [18, 30-32]:
- 1. When fired at high temperatures in an oxidative atmosphere, magnetite ore particles begin to oxidize, forming Fe2O3 nanocrystals that grow and create bridging connections between particles. At 1050°C, this bonding can enhance pellet strength; however, due to the low temperature, the growth of Fe2O3 crystals is limited, resulting in insufficient compressive strength (only reaching 122–210 kgf/pellet), making the pellets unsuitable for blast furnace feedstock.
- 2. The recrystallization of Fe2O3 occurs when pellets are fired above 900°C. Complete transformation from magnetite to hematite takes place between 1050°C and 1150°C. Newly formed hematite crystals grow and bond tightly, significantly increasing pellet strength. The highest compressive strength was achieved for pellets oxidatively fired at 1150°C with a 2-h holding time.
- 3.3. Elemental Analysis in Fired Iron Ore Pellets
- To gain deeper insight into the elemental distribution and its correlation with pellet structure and mechanical properties, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and elemental mapping analyses were conducted on representative samples. These include fracture surfaces and cross-sections of pellets fired at 1150°C under varying conditions, as shown in Fig. 10 to 14.
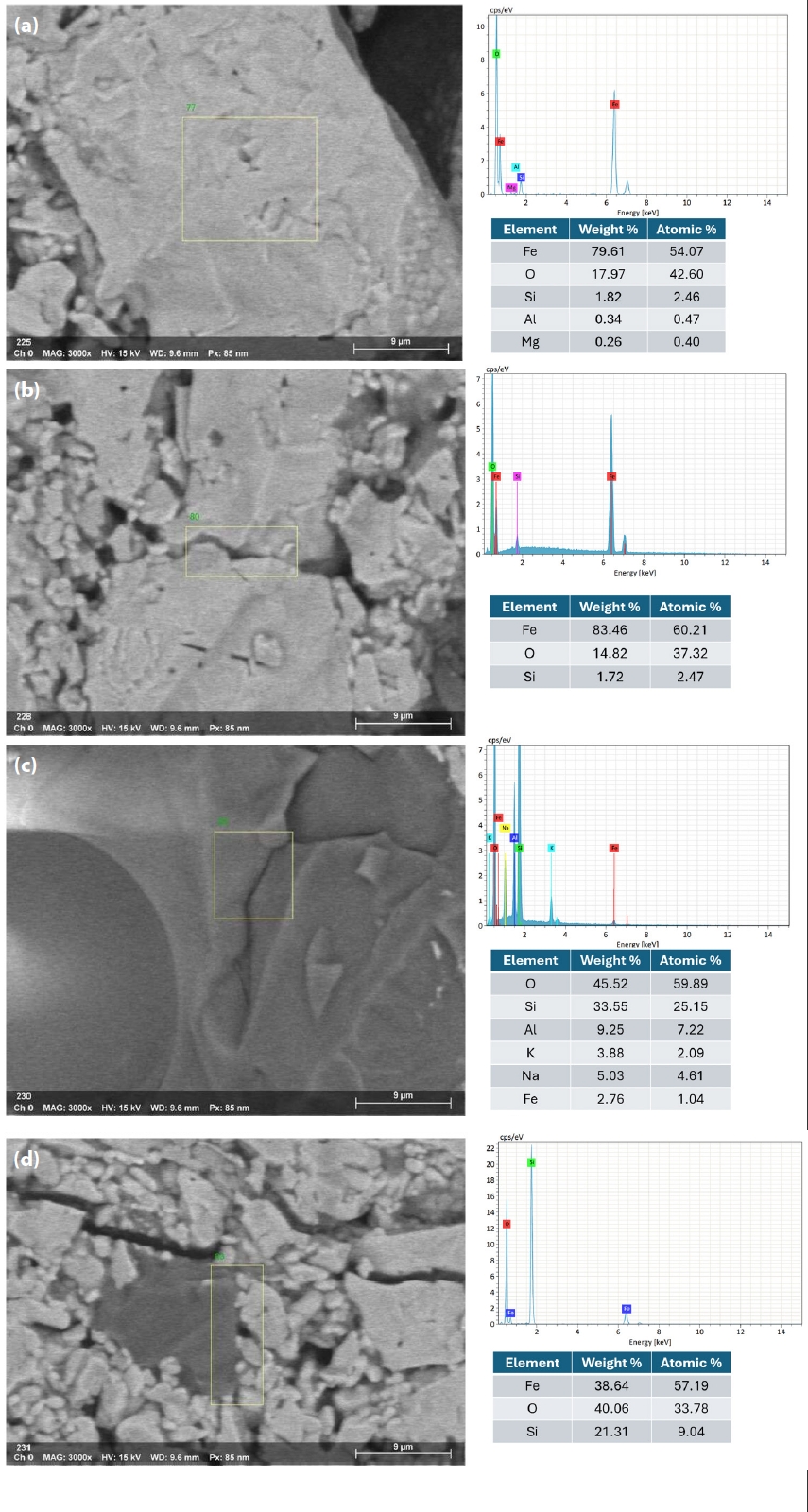
- Fig. 10 illustrates the EDX spectra obtained from various observation points on the fracture surface of an IO: 100A pellet (100% Australian ore) fired at 1150°C for 30 min. The analyzed area lies along the boundary between hematite particles and is marked by a higher concentration of Si in addition to Fe and O. This indicates the possible presence of SiO2 at grain interfaces, which may lead to the formation of silicate-rich phases influencing sintering behavior and the bonding between particles. In contrast, points located within the grain interiors (e.g., Fig. 10b and 10d) were primarily composed of Fe and O, consistent with hematite (Fe2O3). Meanwhile, grain boundaries (e.g., Fig. 10a and 10c) exhibited enrichment in light elements such as Na, K, Mg, and Al, indicating localized concentrations of alkali and alkaline earth metal oxides. This segregation is believed to facilitate liquid-phase formation during firing, enhancing particle cohesion and promoting pellet densification [1, 33]. Elena Yazhenskikh’s research [33] supports this, showing that eutectic temperatures in the Na2O–SiO2 and K2O–SiO2 binary systems are as low as 789 °C and 743 °C, respectively, while the ternary K2O–Na2O–SiO2 system reaches a eutectic point at just 540 °C – critical for phase evolution during sintering.
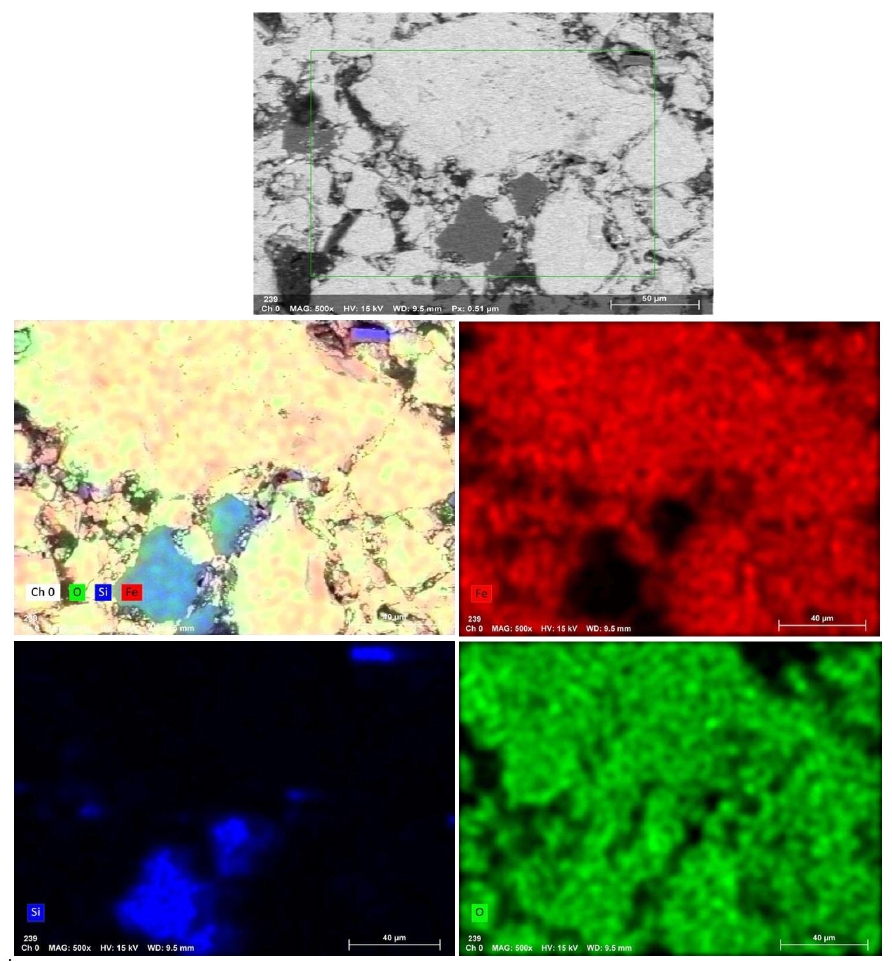
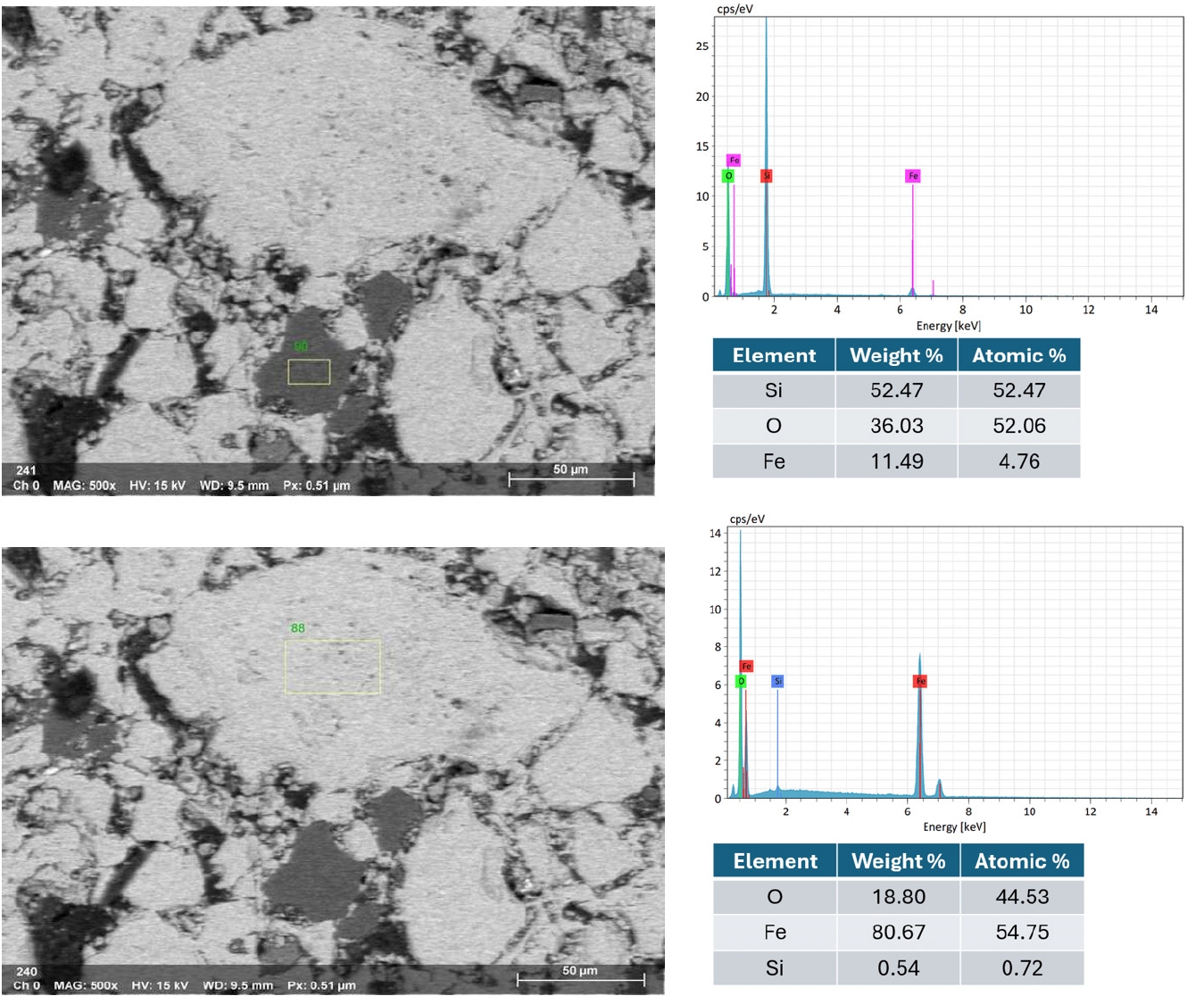
- Fig. 11 presents the EDS elemental mapping image of an IO: 100M pellet (100% Minh Son ore) fired at 1150°C for 120 min. The mapping clearly shows a heterogeneous microstructure with Si and O-rich phases distributed in isolated domains, while Fe-rich zones dominate the matrix. This microstructural contrast suggests incomplete homogenization, which correlates with the relatively lower strength of Minh Son pellets compared to Australian ore.
- The corresponding EDX point spectra in Fig. 12 confirm these observations. Fe and O dominate the matrix composition, while isolated regions show higher concentrations of Si, Al, Na, and K. These regions likely represent residual gangue phases or partially sintered mineral inclusions.
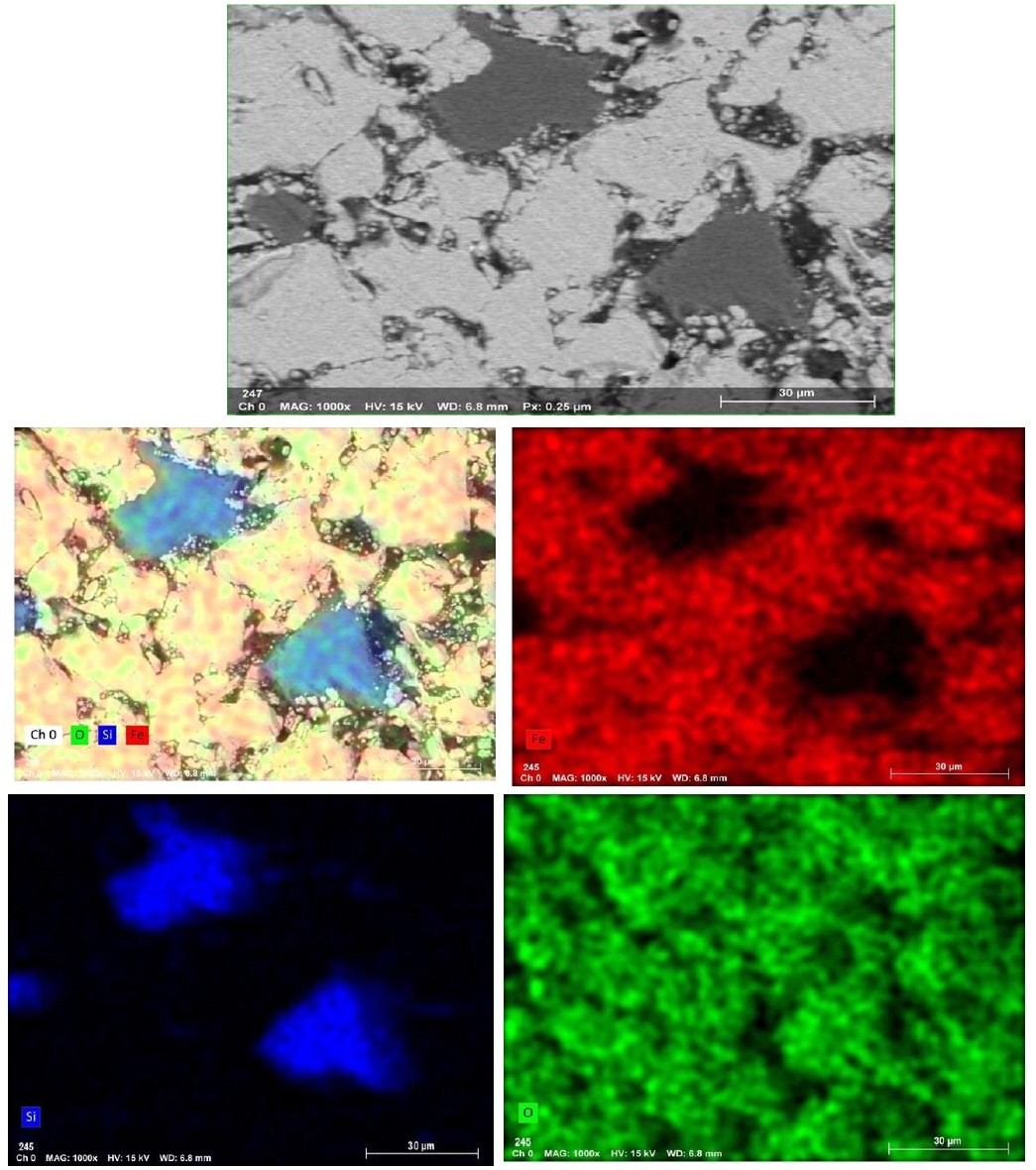
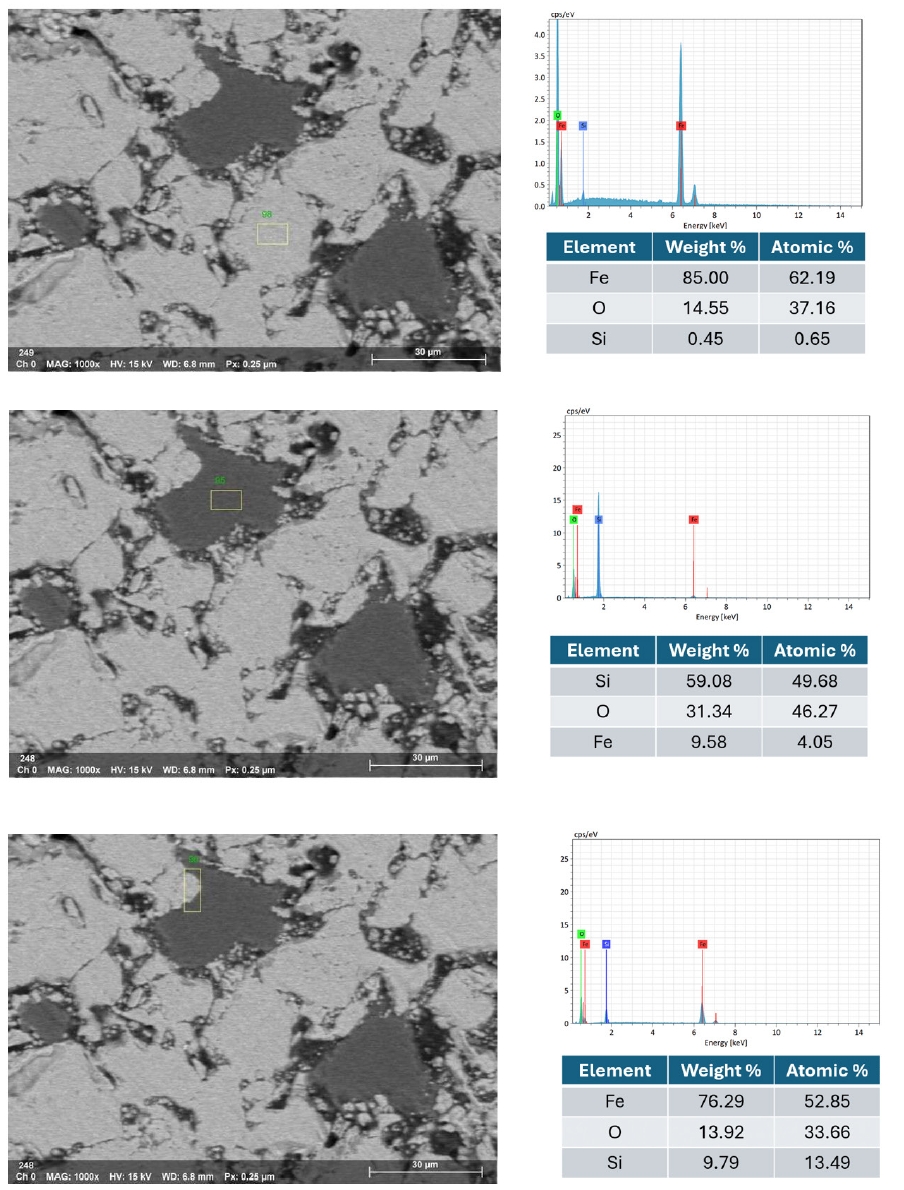
- For blended pellets, Fig. 13 and 14 show the elemental mapping and point spectra of IO: 20A–80M pellets fired at 1150°C for 60 min. The elemental maps indicate that Fe and O are more continuously present throughout the pellet matrix compared to IO: 100M, while Si-rich regions, although still observable, appear as smaller and less isolated domains that are more closely associated with the surrounding iron oxide phase. This integration of Si-rich areas into the Fe–O matrix, as opposed to forming large or segregated regions, is likely to facilitate stronger bonding between particles. These microstructural features are consistent with the higher compressive strength observed in the blended pellets compared to those made solely from Minh Son iron ore.
- Moreover, the quantitative EDX data (in the inset of Fig. 10, 12 and 14) support these visual findings. For instance, pellets with higher compressive strength consistently exhibit Fe weight fractions above 80%, while lower-strength samples show elevated Si and alkali oxide content, especially at grain boundaries.
- These results confirm that:
- • Fe–O-rich domains correspond to well-sintered hematite phases contributing to strength,
- • Si-rich and alkali-enriched regions tend to localize at boundaries or pores, potentially reducing interparticle bonding,
- • and blending coarse Minh Son with fine Australian ore helps refine elemental distribution and promote consolidation.
- Ultimately, elemental analysis via EDX demonstrates that chemical homogeneity and selective enrichment of sintering-aid oxides at key interfaces are critical for optimizing pellet strength under oxidative firing.
- To further elucidate the improvement in homogeneity and compressive strength observed when blending Minh Son with Australian ore, it is useful to consider the micromechanical theory of particle bonding in porous media. According to the Rumpf equation [1, 21]:
- where σC is the compressive strength, ε is the fractional porosity, γ is the liquid surface tension, d is the average particle size, and θsl is the liquid–solid contact angle. This relationship predicts that the compressive strength of the pellet is inversely proportional to the average particle size and porosity, and directly proportional to the degree of liquid-phase bonding at particle contacts. Blending the finer Australian ore (d50 ≈ 13 μm) with the coarser Minh Son ore (d50 ≈ 50 μm) results in a more optimized particle packing, reducing the effective porosity (ε and average particle size (d) within the green pellet. This bimodal particle size distribution allows the fine Australian particles to fill the interstitial voids between coarser Minh Son grains, leading to a denser and more homogeneous microstructure. As predicted by the Rumpf equation, such improvements in packing and particle bonding - especially in the presence of liquid-phase sintering aids at high temperature—directly translate into increased compressive strength and structural uniformity of the fired pellets. Therefore, the enhanced homogeneity and mechanical properties of blended pellets can be quantitatively explained by this theoretical framework, in agreement with both the microstructural observations and mechanical testing results of this study [1, 17, 21].
III. Results and Discussion
- This study investigated the influence of oxidative firing parameters and raw material characteristics on the pelletization behavior and mechanical properties of iron ore concentrates. Pellets were prepared from Australian ore, Minh Son ore, and their blends, with firing conducted at temperatures ranging from 1050°C to 1150°C and holding times from 15 to 120 min. The results demonstrated that both firing temperature and duration significantly affect the compressive strength of the pellets, with higher compressive strength values achieved at 1150°C and prolonged holding times. Among all compositions, pellets made from 100% Australian ore (IO: 100A) exhibited the highest compressive strength, exceeding the industrial threshold of 250 kgf/pellet even at moderate firing durations.
- Microstructural analysis revealed that improved strength is associated with the disappearance of sharp-edged particles, the development of trans-particle fracture, and enhanced grain boundary bonding. SEM-EDX and elemental mapping indicated that liquid-phase formation—facilitated by the localized enrichment of alkali and alkaline earth oxides—played a key role in promoting densification and interparticle bonding.
- Furthermore, blending the coarser Minh Son concentrate with the finer Australian concentrate (e.g., IO: 20A–80M and IO: 10A–90M) led to noticeable improvements in pellet strength compared to using Minh Son ore alone. This highlights the effectiveness of optimizing particle size distribution and raw material composition. The results offer practical insights for improving iron ore pellet production from mixed ore sources, with clear benefits for sintering efficiency and mechanical performance in industrial-scale ironmaking.
IV. Conclusion
-
Funding
This research is funded by Hanoi University of Science and Technology (HUST) under project number T2023-PC-056.
-
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
-
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
-
Author Information and Contribution
Ngo Quoc Dung: PhD candidate; responsible for conceptualization, experimental design and execution, original draft preparation, and acquisition of funding.
Tran Xuan Hai: Undergraduate student; contributed to experimental work and performed calculations related to the pelletization and mechanical testing processes.
Nguyen Minh Thuyet: PhD; supervised the research activities, provided critical revisions, and contributed to reviewing and editing the manuscript.
Nguyen Quang Tung: Research engineer; contributed to conceptualization and carried out computational analyses supporting experimental findings.
Arvind Barsiwal: PhD candidate; participated in reviewing and provided critical revisions.
Nguyen Hoang Viet: Professor; provided overall supervision, contributed to conceptual development, and participated in reviewing and editing the final manuscript.
-
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to Hoa Phat Hai Duong Steel Joint Stock Company for generously supplying the raw materials and fuel essential to this research. Their contribution was instrumental in enabling the successful completion of our study.
Article information
| Ore type |
Chemical composition, %wt |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFe | FeO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | S | P | |
| Australia | 65.5 | 26.80 | 8.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.014 |
| Minh Son | 66.5 | 20.67 | 5.0 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.061 | 0.002 |
| Binder material |
Chemical composition, %wt |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2O3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | |
| Indian bentonite type | 12.37 | 62.99 | 20.67 | 1.14 | 1.32 |
- 1. R. P. Bhagat: Agglomeration of Iron Ores, (2019).
- 2. R. C. Gupta: Theory and Laboratory Experiments in Ferrous Metallurgy, (2010).
- 3. A. K. Biswas: Principles of Blast Furnace Ironmaking: Theory and Practice, (Cootha), (1981) 528.
- 4. A. Ghosh and A. Chatterjee: Ironmaking and Steelmaking: Theory and Practice, (PHI Learning Privated Limited), (2008).
- 5. L. Lu: Iron Ore: Mineralogy, Processing and Environmental Sustainability, (2015) 1.
- 6. M. Geerdes, R. Chaigneau, I. Kurunov, O. Lingiardi and J. Ricketts: Modern Blast Furnace Ironmaking: An Introduction, 3rd ed., (PHI Learning Private Limited), (2015).
- 7. A. Chatterjee: Sponge Iron Production by Direct Reduction of Iron Oxide, 2nd ed., (PHI Learning Privated Limited), (2012).
- 8. H. B. Lüngen and J.-I. Yagi: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, (2019), 1.
- 9. N. Q. Dung, N. M. Thuyet, N. T. H. Oanh, and N. H. Viet: Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, (2025).
- 10. Q. D. Ngo, M. T. Nguyen and H. V. Nguyen: Key Eng. Mater., 1005 (2024) 3.Article
- 11. N. Q. Dũng, Đ. T. N. Ánh, N. S. Hiếu, N. Đ. Tuyên, N. Q. Tùng, C. T. M. Thu, L. V. Khởi, Đ. N. Q. Chiến, N. T. H. Oanh and N. H. Việt: J. Sci. Tech. Metals, 98 (2021) 2.
- 12. N. H. Viet, P. N. D. Quynh and N. T. H. Oanh: J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 21 (2021) 2563.Article
- 13. S. Moraes, J. R. B. Lima and T. R. Ribeiro, Iron Ores and Iron Oxide Materials, IntechOpen, (2018).
- 14. A. Babich, D. Senk and H. W. Gudenau, Ironmaking, (2016).
- 15. S. Kumar, B. Ravi, O. Sivrikaya and R. Nanda: Sci. Sinter., 51 (2019) 27.Article
- 16. K. Sastry, P. Dontula and C. Hosten: Powder Technol., 130 (2003) 231.Article
- 17. K. V. S. Sastry and D. W. Fuerstenau: Powder Technol., 7 (1973) 97.Article
- 18. H. Elahidoost, S. Sheibani, S. Raygan, L. Hosseini and N. Esmaeili: Adv. Powder Technol., 33 (2022) 103883.Article
- 19. V. Claremboux and S. K. Kawatra: Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 44 (2023) 138.Article
- 20. S. K. Kawatra and V. Claremboux: Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 43 (2022) 813.Article
- 21. S. K. Kawatra and V. Claremboux: Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 43 (2022) 529–544.Article
- 22. T. C. Eisele and S. K. Kawatra: Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 24 (2003) 1.Article
- 23. B. E. Monsen, E. S. Thomassen, I. Bragstad, E. Ringdalen and P. H. Hoegaas: Characterization of DR Pellets for DRI Applications, in AISTech 2015 Proceedings, vol. 1, Cleveland, OH, USA, May, (2015) 739.
- 24. N. H. Viet, P. N. D. Quynh and N. T. H. Oanh: A study on the reduction of iron ore pellets in a bed of non coking coal, in Proc. National Scientific Conference on Metallurgy and Materials Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam, (2016) 185.
- 25. P. K. Cuong, T. T. Dung, K. M. Tuyen, C. T. M. Thu and L. V. Khoi: Fabrication of a Compressive Strength Testing Device and Investigation of the Compressive Strength of Green Iron Ore Pellets, in Proc. Student Scientific Conference, Hanoi, Vietnam, (2020) KTVL.04.
- 26. P. S. Kumar, B. P. Ravi, O. Sivrikaya and R. K. Nanda: Sci. Sinter., 51 (2019) 27.Article
- 27. N. Doebelin and R. Kleeberg: J. Appl. Crystallogr, 48 (2015) 1573.Article
- 28. N. Q. Dung, L. V. Khoi, N. L. Khoa, V. Hai, D. X. Thanh, P. Anh, N. T. H. Oanh, N. D. Tuyen, N. M. Duc, L. H. Thang, P. H. Long, H. T. M. Loan, C. T. M. Thu, T. T. Phong, B. L. Hung, M. K. Luan, N. Q. Huy, V. Hiep, P. M. Tuan, N. M. Thuyet, N. H. Viet: “Unveiling phase changes in iron ore reduction: X-ray diffraction analysis with a user-friendly Colab interface integrated with the Materials Project API,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Adv. Mater. Technol. (ICAMT), Hanoi, Vietnam, Oct. 9–12, (2024) 171.
- 29. k. b. Anand, k. k. Swapan and M. Kumar: IOP Conference Series: Mater. Sci. Eng., 178 (2017) 012003.
- 30. T. Umadevi, N. F. Lobo, S. Desai, P. C. Mahapatra, R. Sah and M. Prabhu: ISIJ Int., 53 (2013) 1673.Article
- 31. S. P. E. Forsmo, S. E. Forsmo, P. O. Samskog and B. M. T. Björkman: Powder Technol, 183 (2008) 247.Article
- 32. G. Li, T. Jiang, Y. Zhang, and Z. Tang: Recrystallization of Fe2O3 During the Induration of Iron Ore Oxidation Pellets, in Recrystallization, K. M. Sztwiertnia (Ed.) IntechOpen (2012) 229.
- 33. E. Yazhenskikh, PhD. thesis. Development of a new database for thermodynamic modelling of the system Na2O-K2O-Al2O3-SiO2, Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, (2005) 27.
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

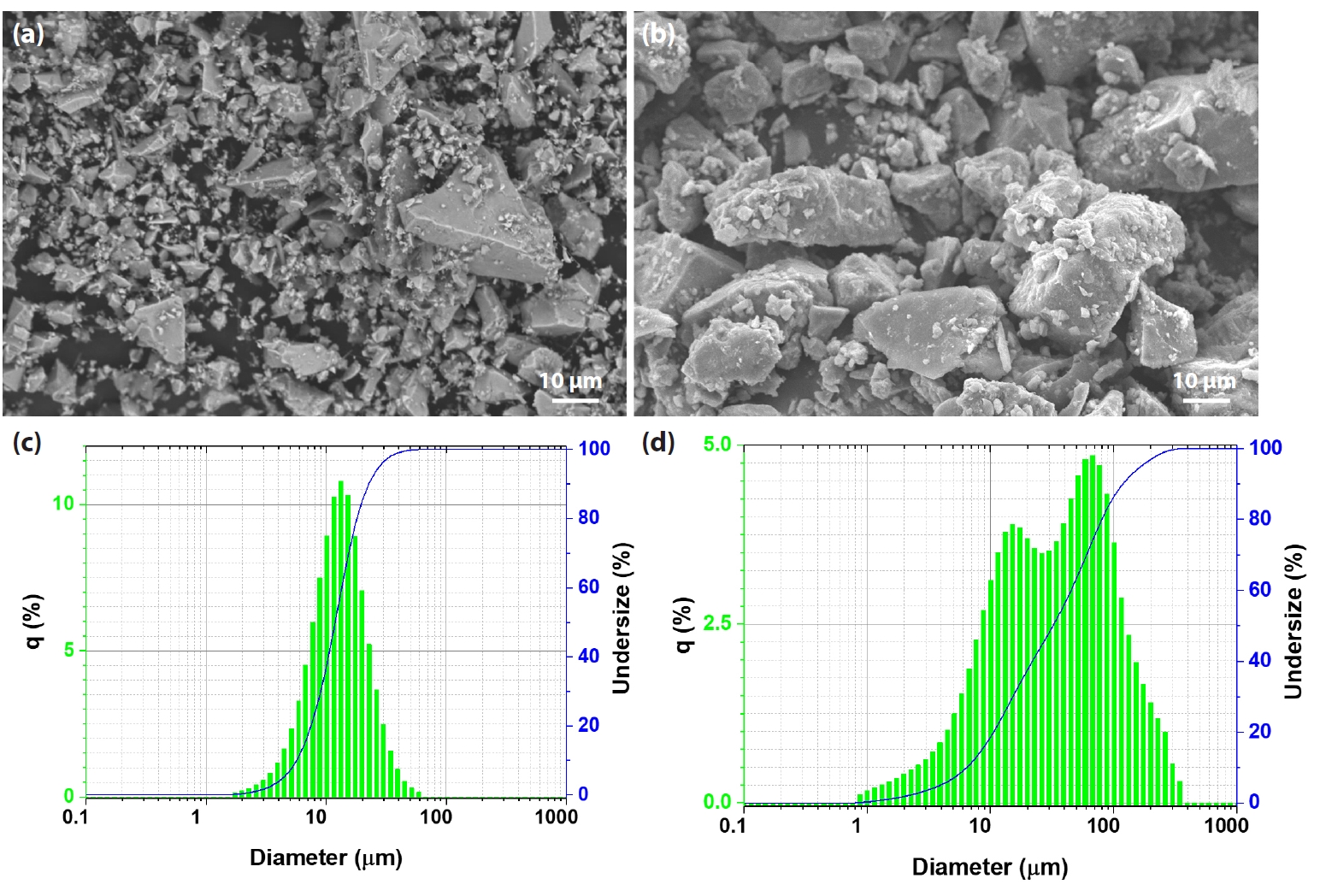
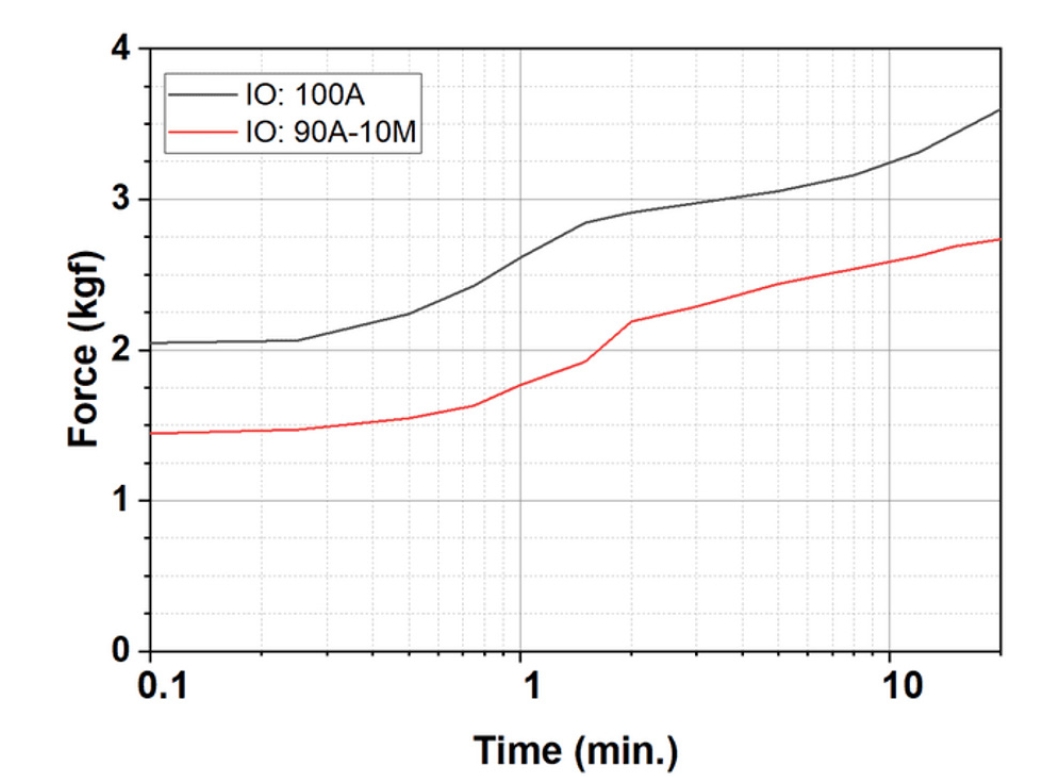
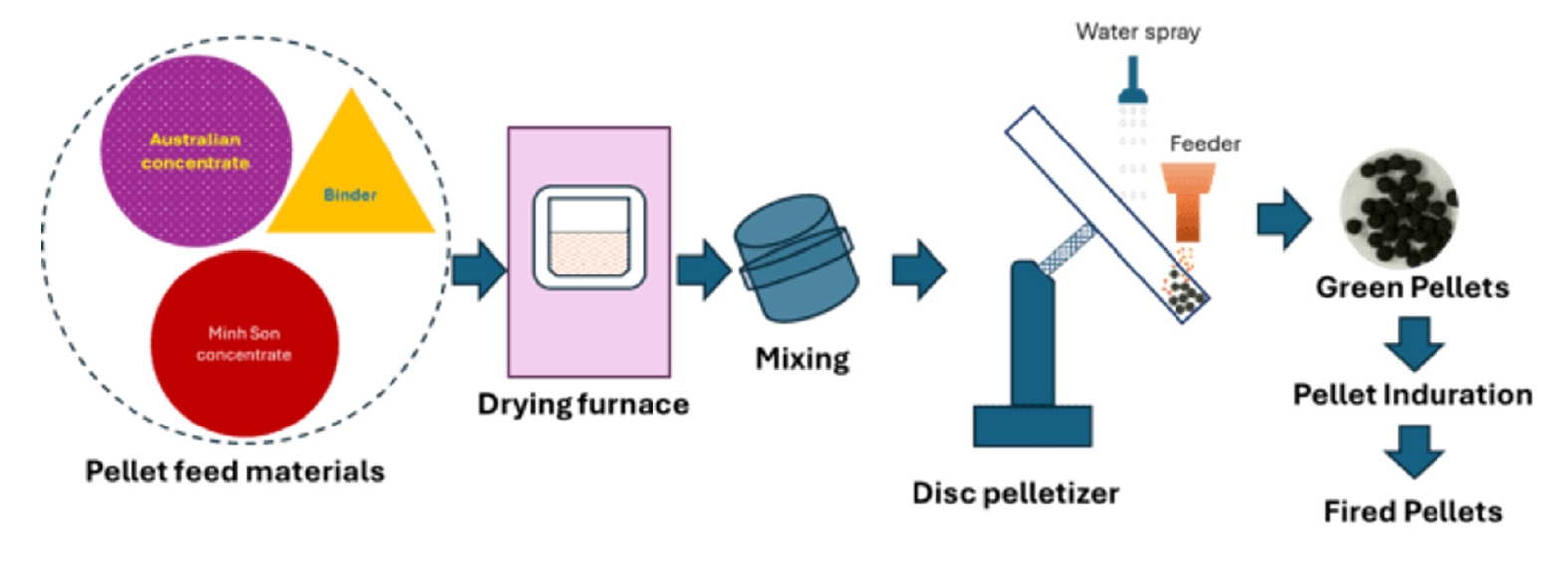
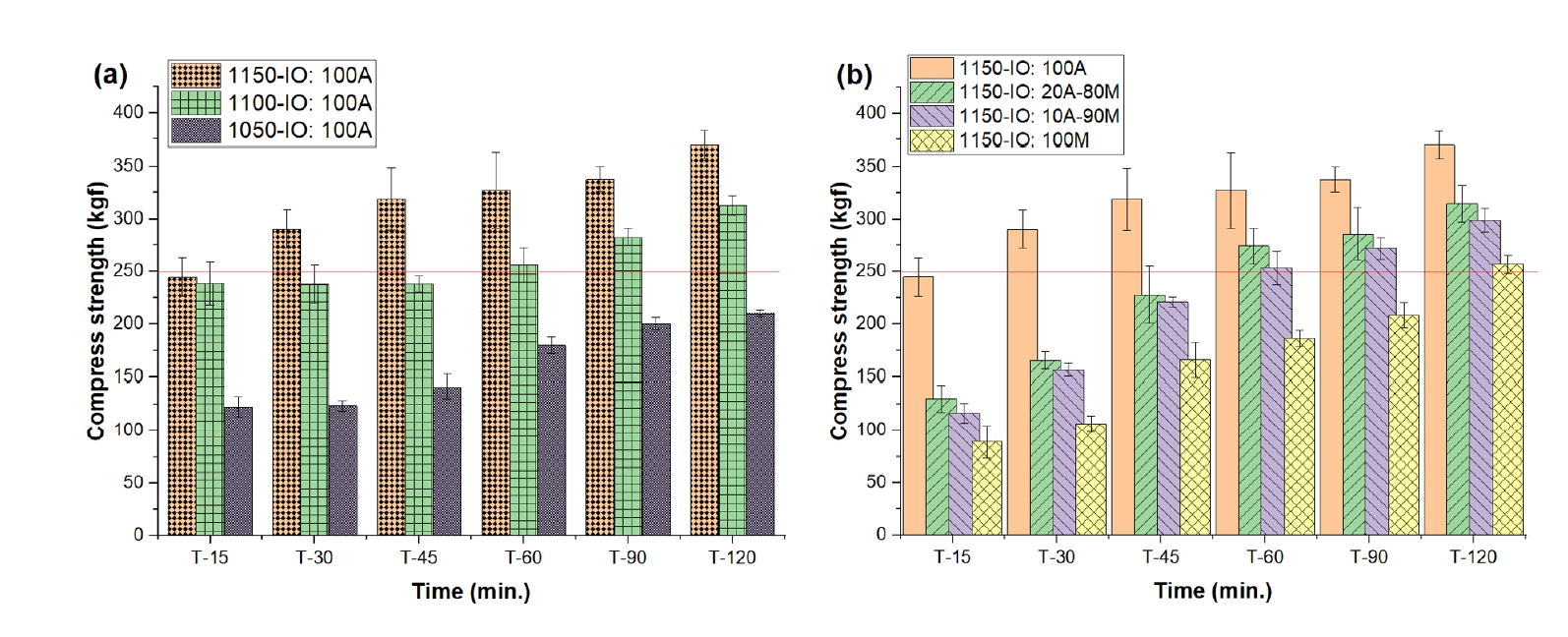
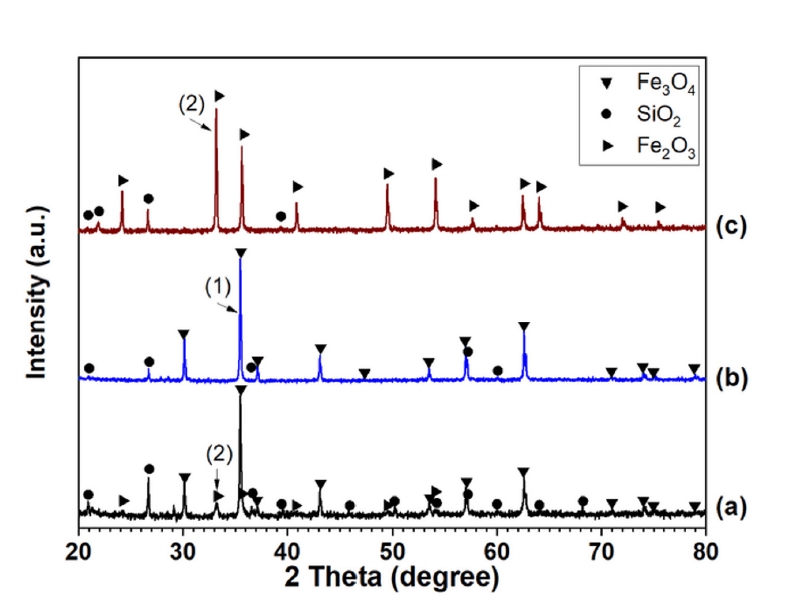
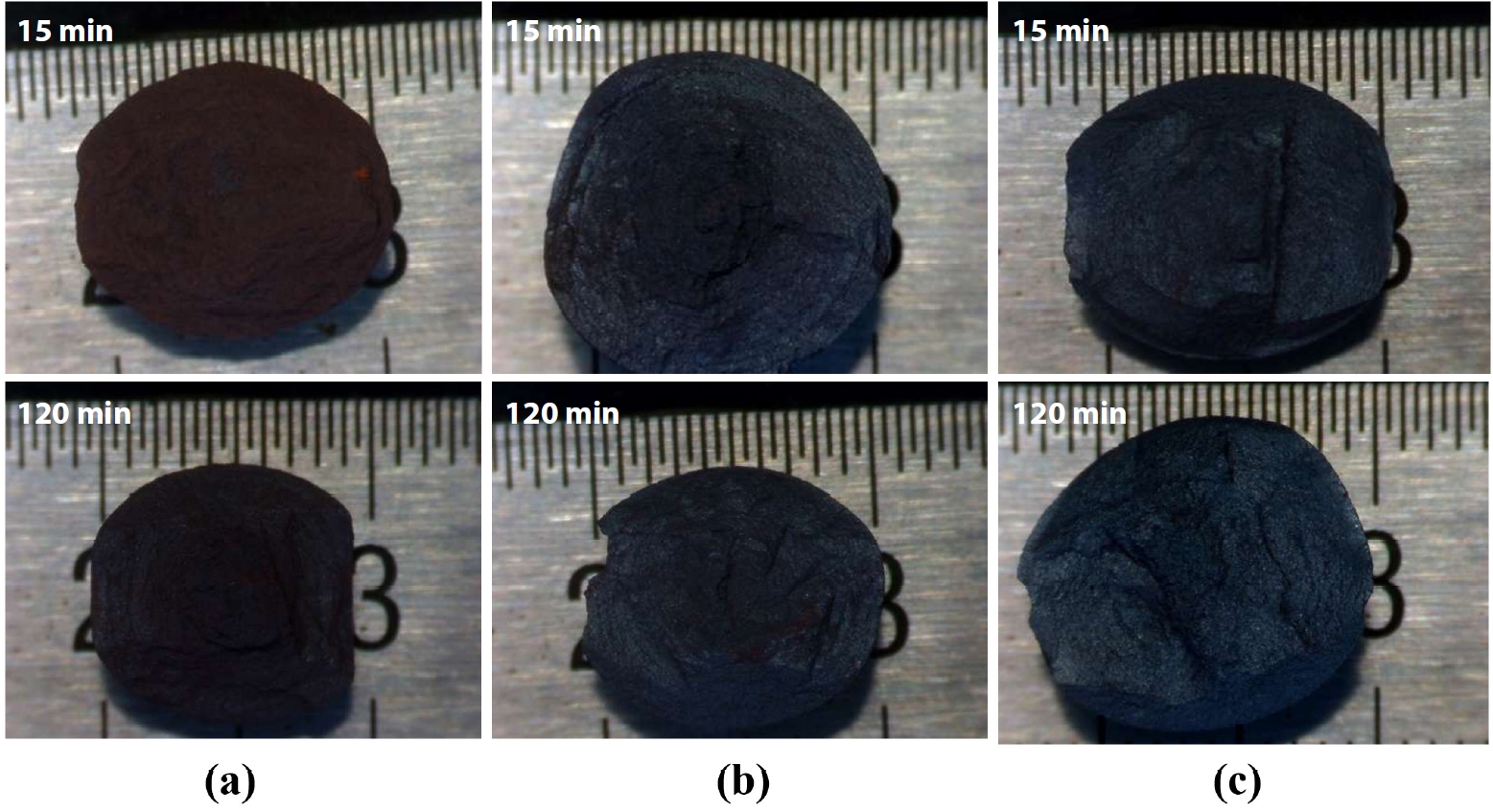
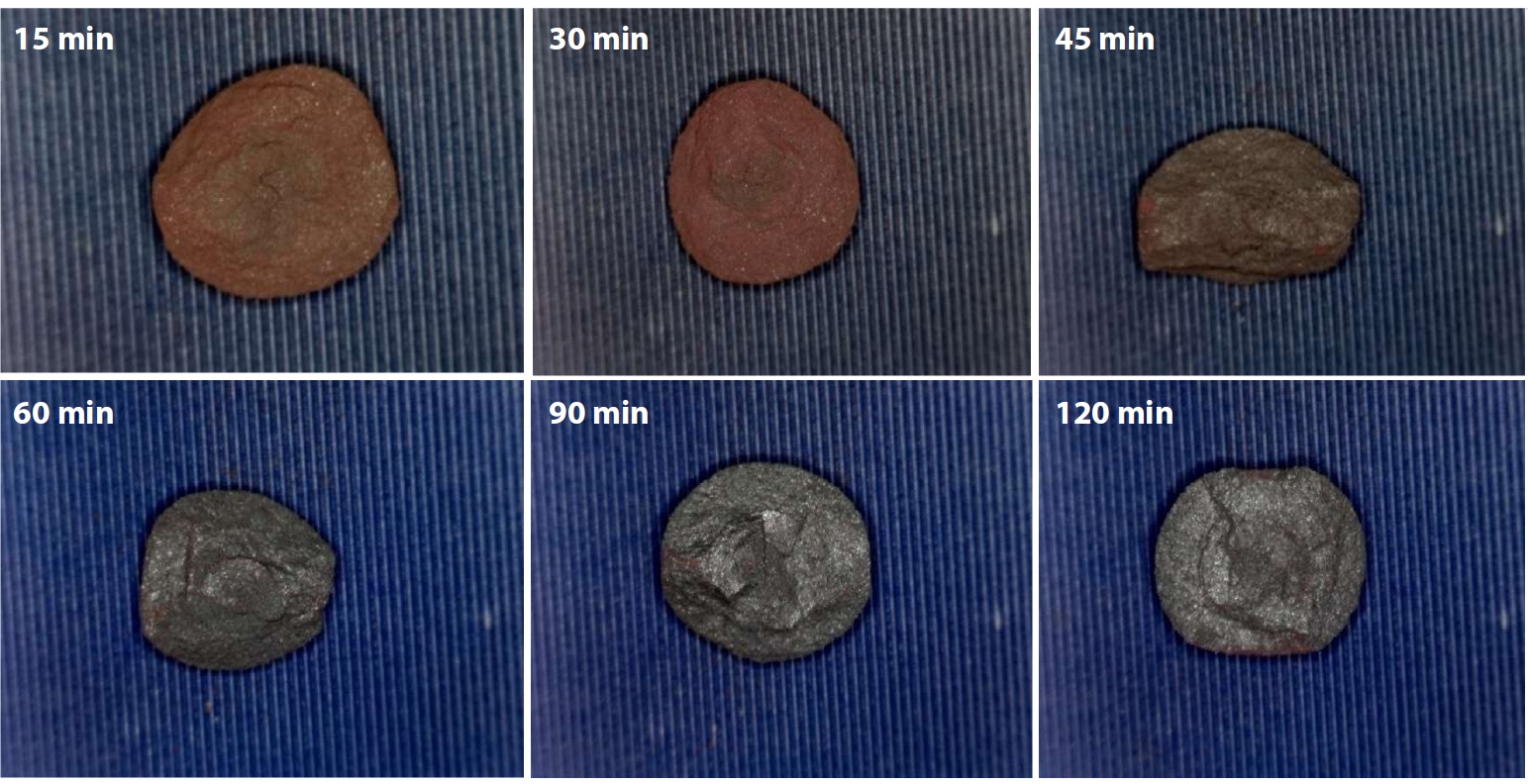
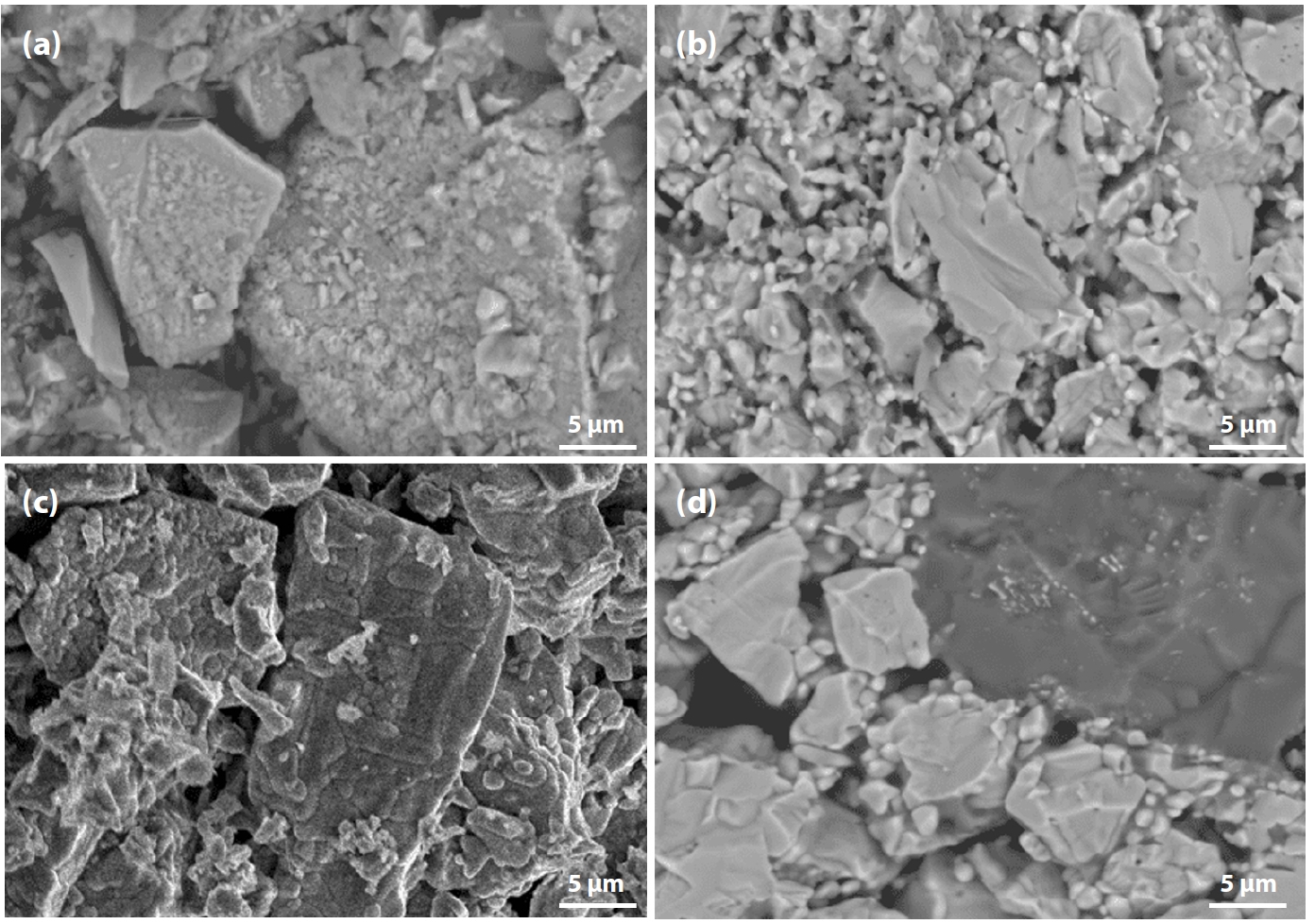
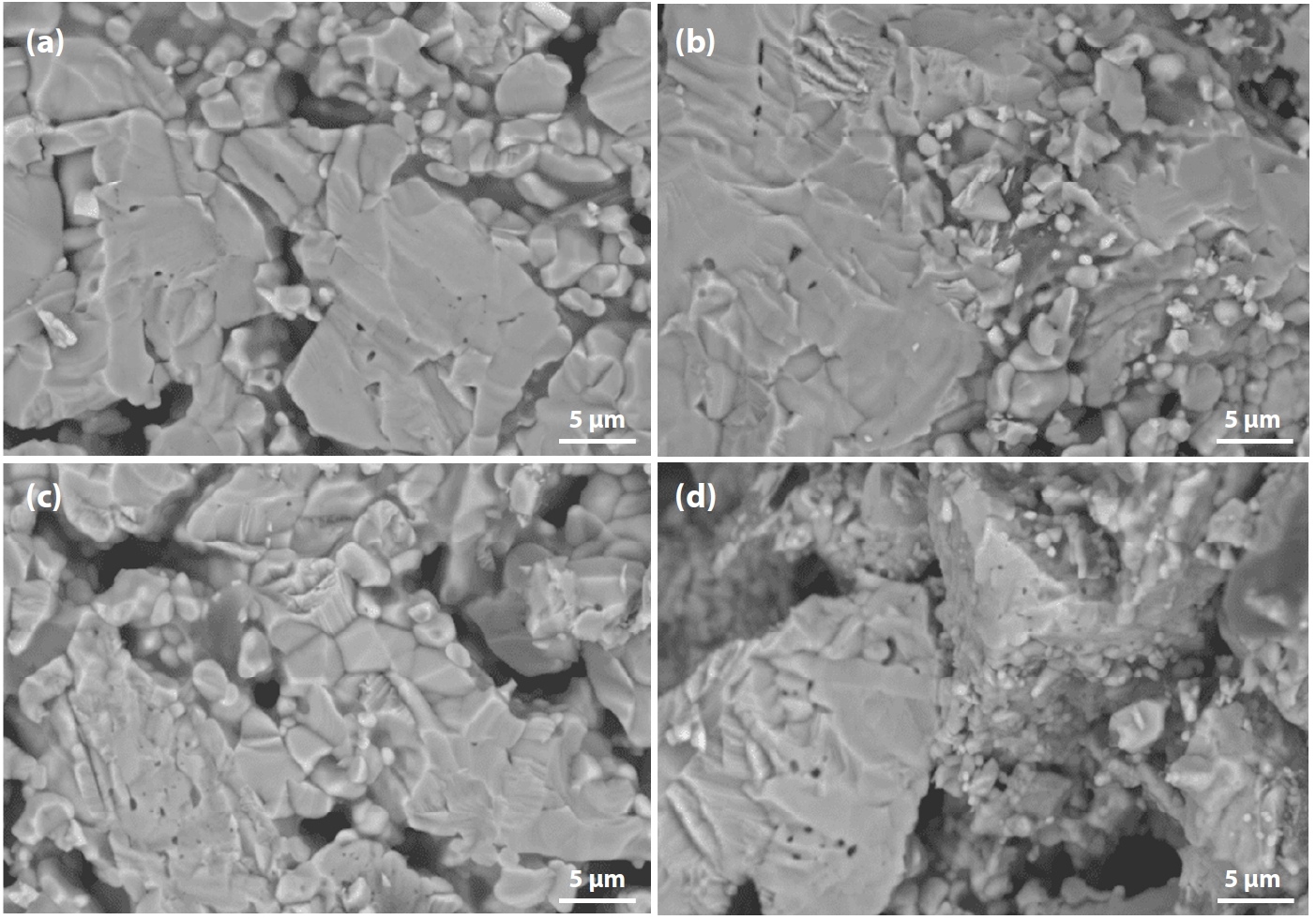
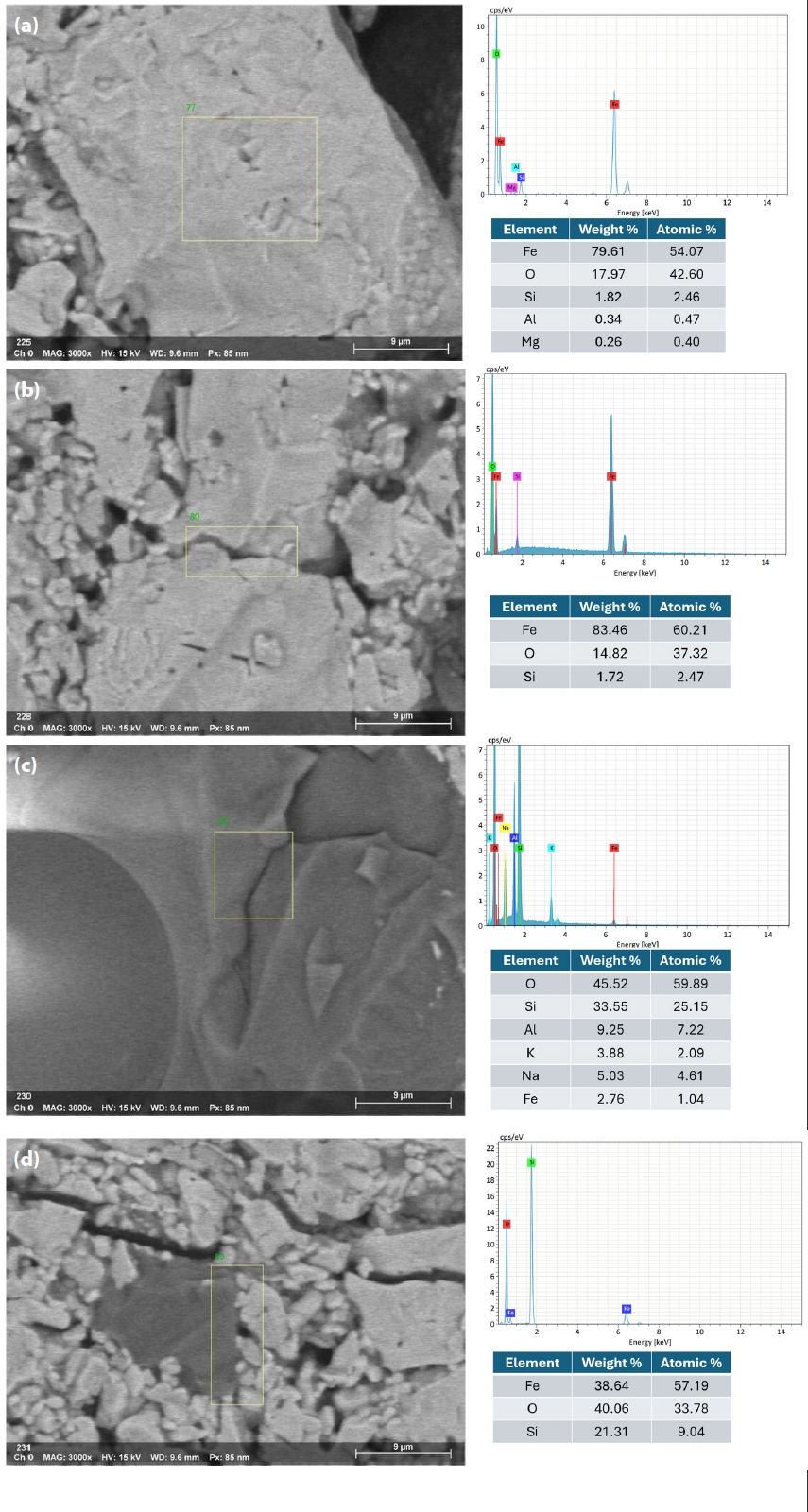
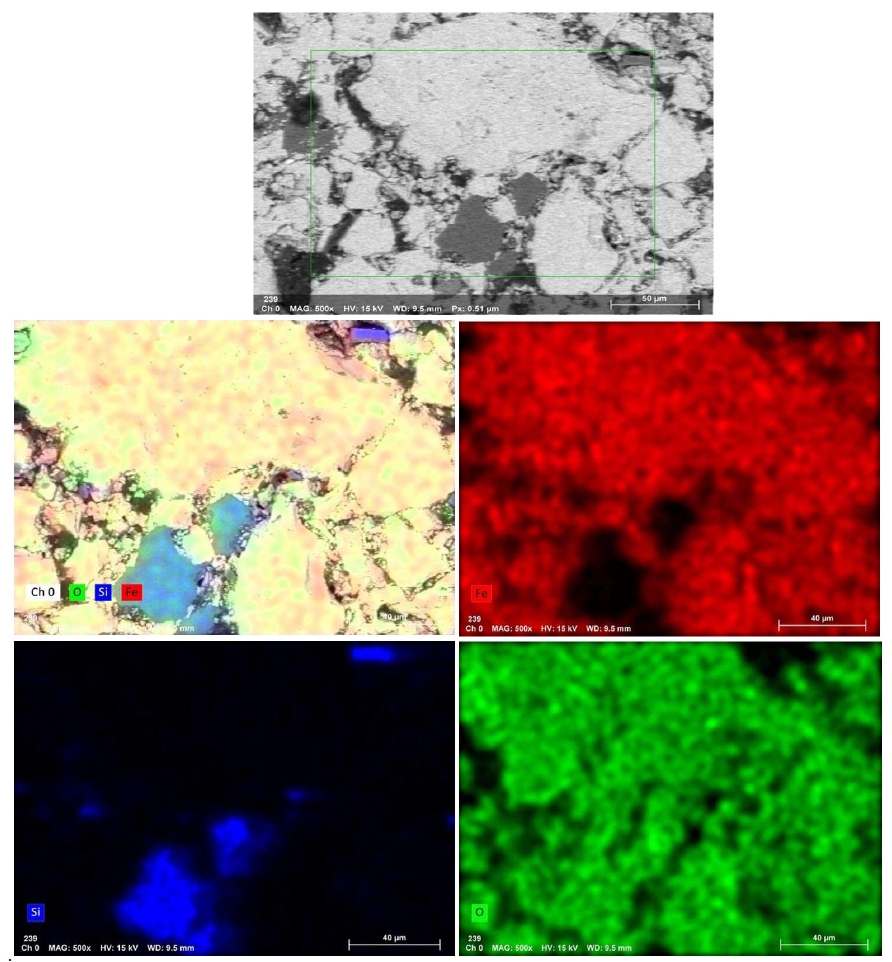
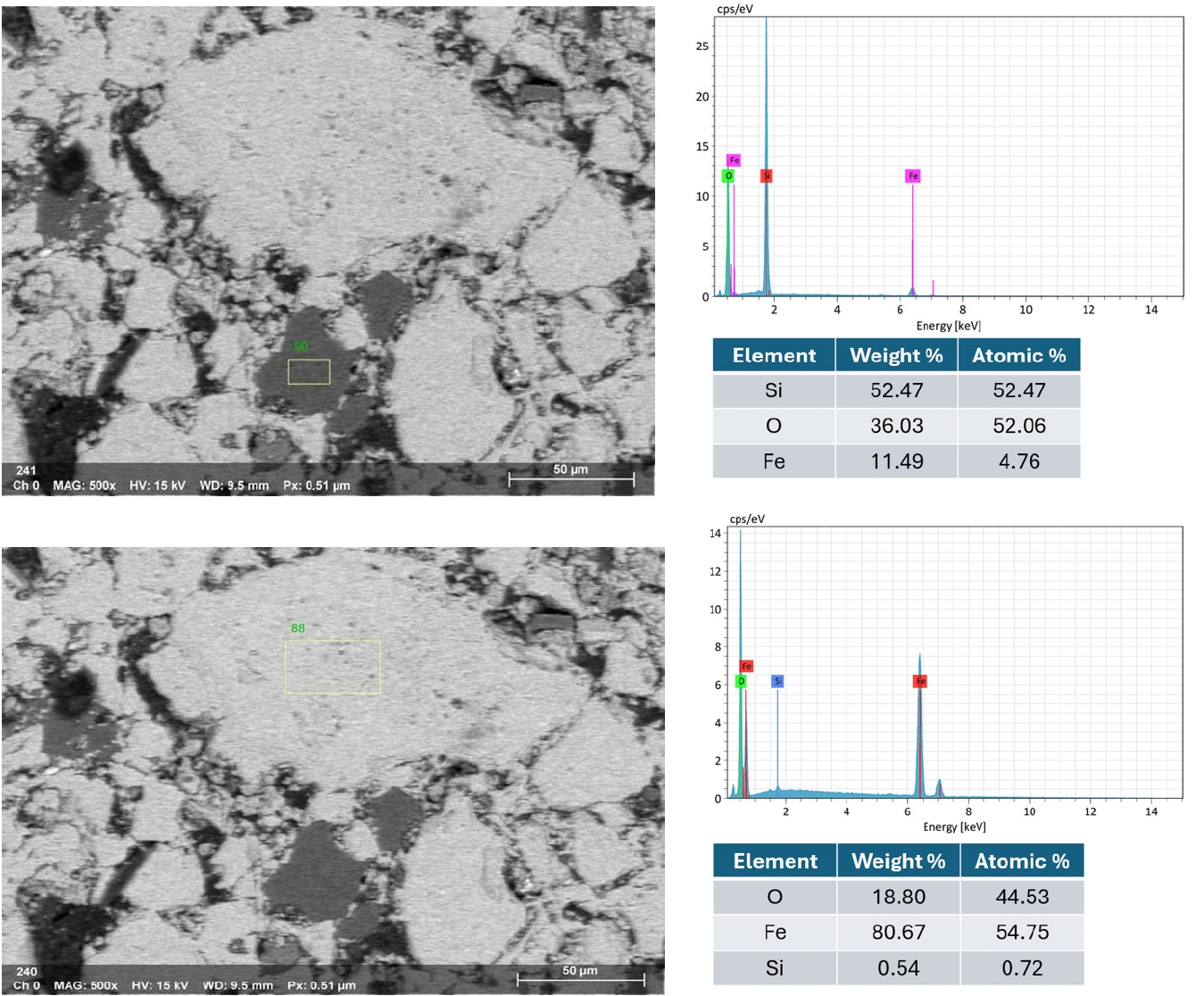
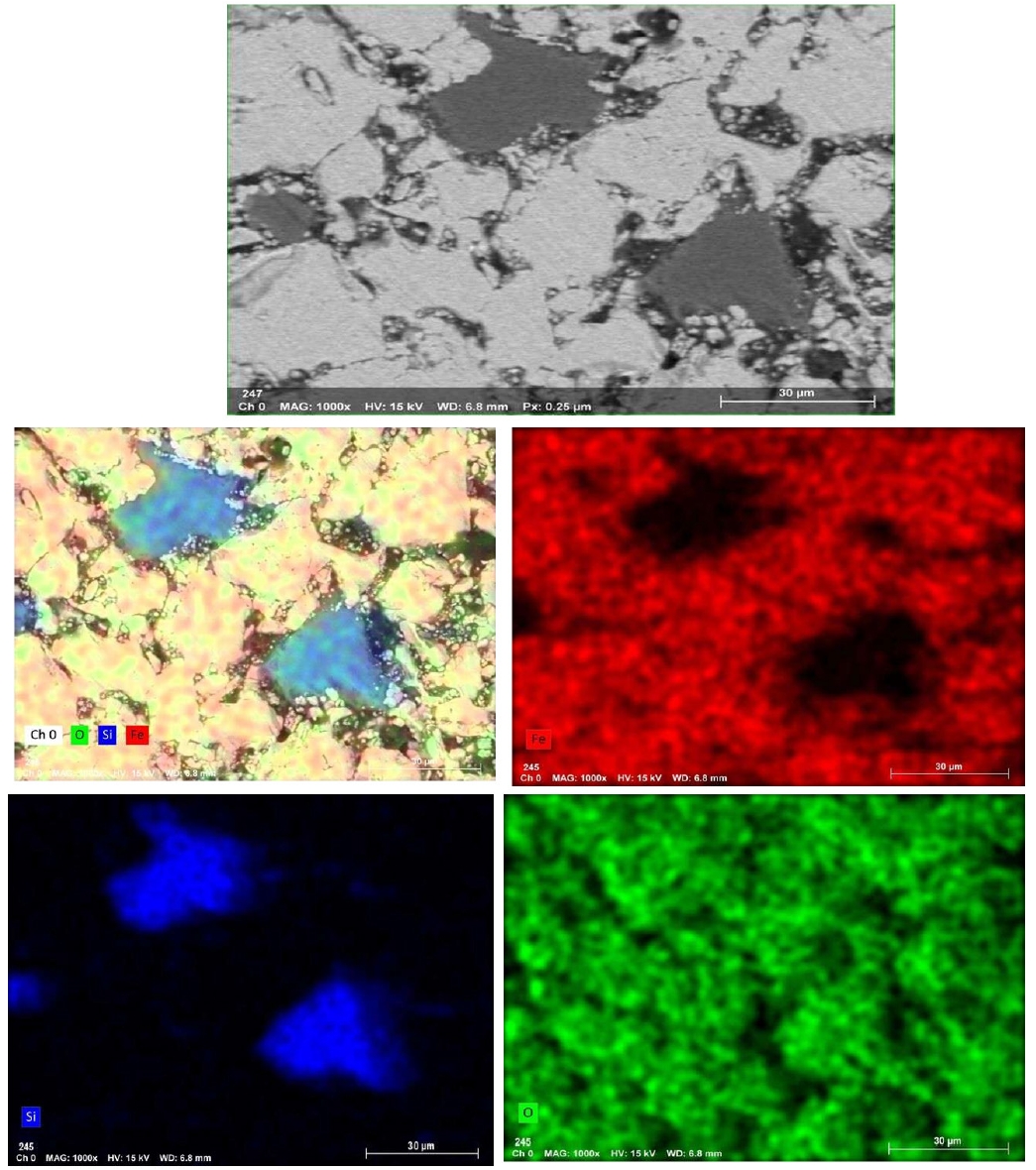
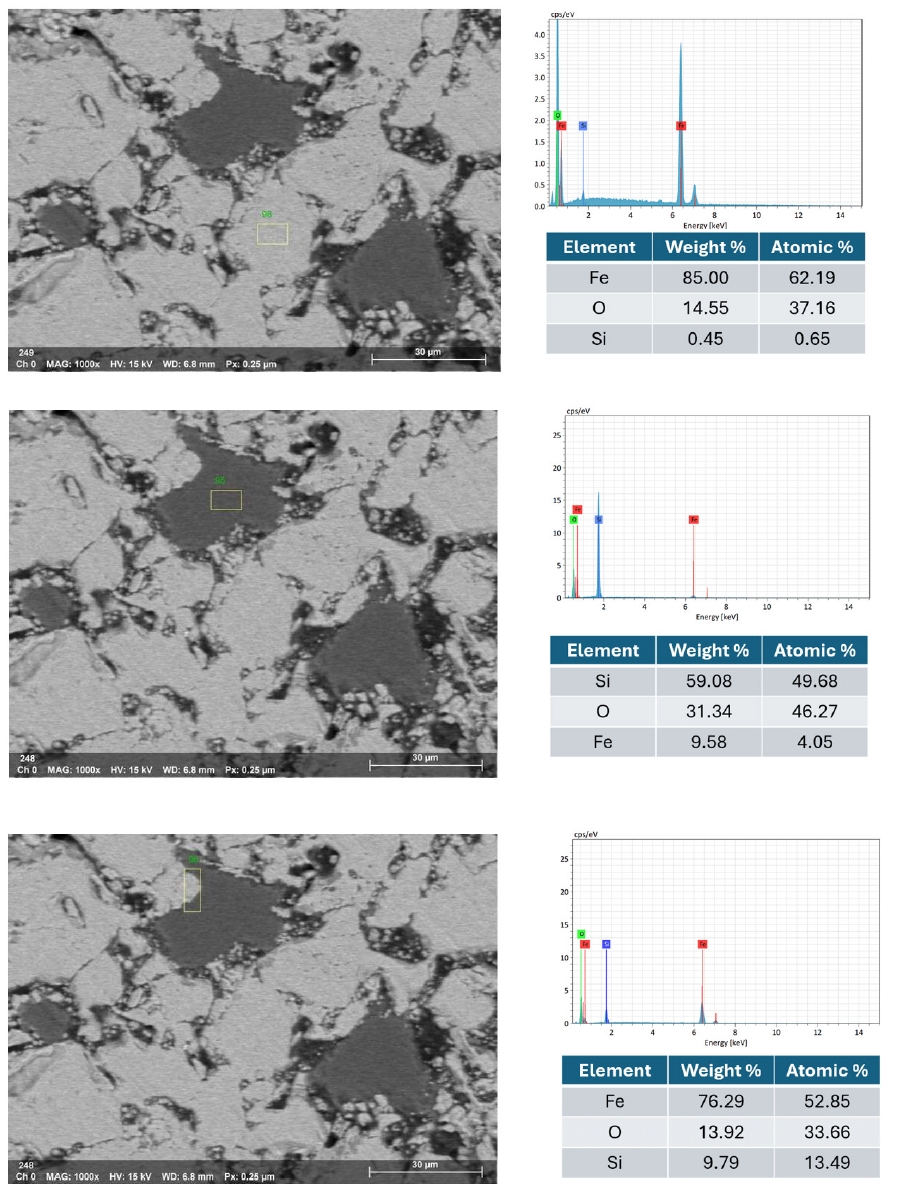
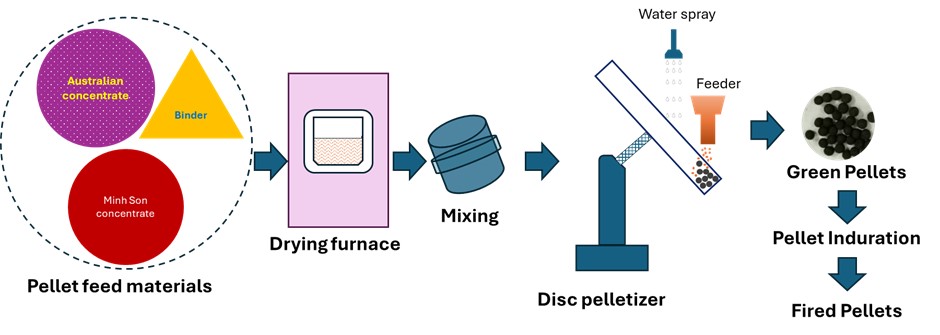
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
Fig. 5.
Fig. 6.
Fig. 7.
Fig. 8.
Fig. 9.
Fig. 10.
Fig. 11.
Fig. 12.
Fig. 13.
Fig. 14.
Graphical abstract
| Ore type | Chemical composition, %wt |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFe | FeO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | S | P | |
| Australia | 65.5 | 26.80 | 8.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.001 | 0.014 |
| Minh Son | 66.5 | 20.67 | 5.0 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.061 | 0.002 |
| Binder material | Chemical composition, %wt |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2O3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | |
| Indian bentonite type | 12.37 | 62.99 | 20.67 | 1.14 | 1.32 |
Table 1.
Table 2.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite this Article
Cite this Article















