- [Korean]
- Analyses of Creep Properties of Ni-base Superalloy Powders as Cooling Rate after Solid Solution Heat Treatment
-
Chan Jun, Youngseon Lee, Byeong Beom Bae, Hong-Kyu Kim, Seong Suk Hong, Donghoon Kim, Jondo Yun, Eun Yoo Yoon
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):247-253. Published online June 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.247
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
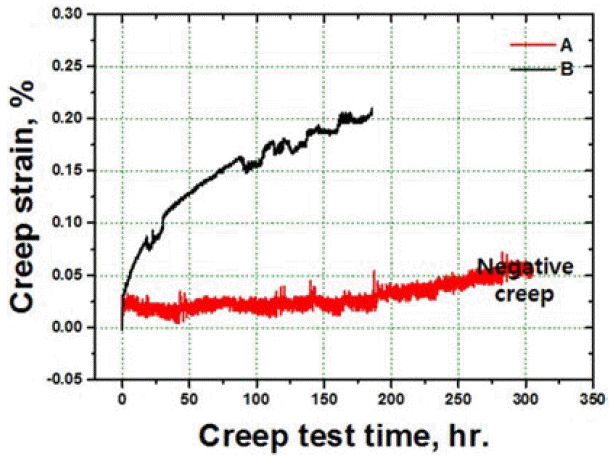
In this study, solid solution heat treatment of consolidated nickel-based superalloy powders is carried out by hot isotactic pressing. The effects of the cooling rate of salt quenching, and air cooling on the microstructures and the mechanical properties of the specimens are analyzed . The specimen that is air cooled shows the formation of serrated grain boundaries due to their obstruction by the carbide particles. Moreover, the specimen that is salt quenched shows higher strength than the one that is air cooled due to the presence of fine and close-packed tertiary gamma prime phase. The tensile elongation at high temperatures improves due to the presence of grain boundary serrations in the specimen that is air cooled. On the contrary, the specimen that is salt quenched and consists of unserrated grain boundaries shows better creep properties than the air cooled specimen with the serrated grain boundaries, due to the negative creep phenomenon.
- [Korean]
- Analyses of Densification and Consolidation of Copper Powders during High-Pressure Torsion Process Using Finite Element Method
-
Dong Jun Lee, Eun Yoo Yoon
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):6-9. Published online February 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.6
-
-
869
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
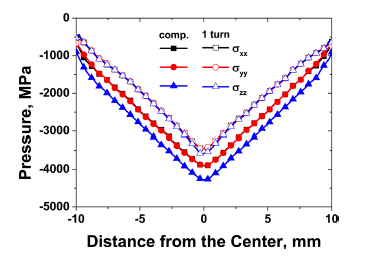
In this study, the behavior of densification of copper powders during high-pressure torsion (HPT) at room temperature is investigated using the finite element method. The simulation results show that the center of the workpiece is the first to reach the true density of copper during the compressive stage because the pressure is higher at the center than the periphery. Subsequently, whole workpiece reaches true density after compression due to the high pressure. In addition, the effective strain is increased along the radius during torsional stage. After one rotation, the periphery shows that the effective strain is increased up to 25, which is extensive deformation. These high pressure and severe strain do not only play a key role in consolidation of copper powders but also make the matrix harder by grain refinement. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
Soo-Hyun Joo, Dong-Hai Pi, Jing Guo, Hidemi Kato, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(3): 383. CrossRef
|