- [English]
- A Review of Inorganic Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries: Challenges and Progress
-
Seul Ki Choi, Jaehun Han, Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jaewon Choi, MinHo Yang
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):293-301. Published online August 30, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00206
-
-
11,754
View
-
284
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
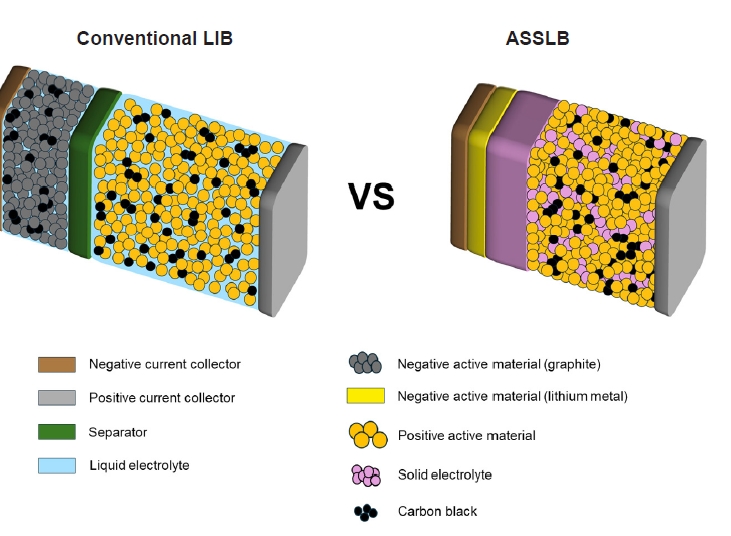
- All-solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs) are receiving attention as a prospective next-generation secondary battery technology that can reduce the risk of commercial lithium-ion batteries by replacing flammable organic liquid electrolytes with non-flammable solid electrolytes. The practical application of ASSLBs requires developing robust solid electrolytes that possess ionic conductivity at room temperature on a par with that of organic liquids. These solid electrolytes must also be thermally and chemically stable, as well as compatible with electrode materials. Inorganic solid electrolytes, including oxide and sulfide-based compounds, are being studied as promising future candidates for ASSLBs due to their higher ionic conductivity and thermal stability than polymer electrolytes. Here, we present the challenges currently facing the development of oxide and sulfide-based solid electrolytes, as well as the research efforts underway aiming to resolve these challenges.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
Osma J. Gomez, Adam Antar, Alex T. Hall, Leopoldo Tapia-Aracayo, Joshua Seo, Nam Kim, Zihan Sun, Ryan Lim, Fu Chen, Yue Li, John Cumings, Gary Rubloff, Sang Bok Lee, David Stewart, Yang Wang
Journal of Materials Chemistry A.2025; 13(34): 28368. CrossRef - Uniform lithium deposition using Cu teepee structures for anode-free lithium metal batteries
Seo Yun Jung, Jaehun Han, Seul Ki Choi, Se Youn Cho, Jong Ho Won, Jaewon Choi, Minho Yang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 522: 167302. CrossRef - Garnet-type LLZO electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: Interfaces, conductivity, in-situ processing, and industrial prospects
Kaleab Habtamu Ayalew, Nithyadharseni Palaniyandy, Mkhulu K. Mathe, Phumlani F. Msomi
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 524: 168098. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Developing Continuous Stabilization Process for Textile-Grade PAN Fiber-Based Carbon Fiber Using UV Irradiation
-
Joon Ha Moon, Honggyu Seong, Jiseon Yoo, Se Youn Cho, Jaewon Choi
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):418-423. Published online October 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.418
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
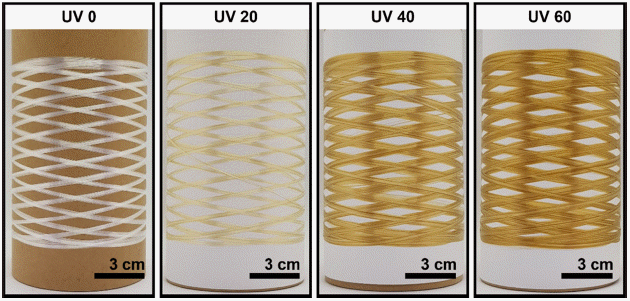
Carbon fibers (CFs) are considered promising composite materials for various applications. However, the high cost of CFs (as much as $26 per kg) limits their practical use in the automobile and energy industries. In this study, we developed a continuous stabilization process for manufacturing low-cost CFs. We employed a textile-grade polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber as a low-cost precursor and UV irradiation technique to shorten the thermal stabilization time. We confirmed that UV irradiation on the textile-grade PAN fibers could lower the initial thermal stabilization temperature and also lead to a higher reaction. These resulted in a shorter overall stabilization time and enhancement of the tensile properties of textilegrade PAN-based CFs. Our study found that only 70 min of stabilization time with UV irradiation was required to prepare textile-grade PAN-based low-cost CFs with a tensile strength of 2.37 ± 0.22GPa and tensile modulus of 249 ± 5 GPa.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of the Multi-layered SnO Nanoparticles and Enhanced Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Heat treatment
-
So Yi Lee, Yoon Myung, Kyu-Tae Lee, Jaewon Choi
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):455-461. Published online December 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.455
-
-
1,712
View
-
6
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this study, multilayered SnO nanoparticles are prepared using oleylamine as a surfactant at 165°C. The physical and chemical properties of the multilayered SnO nanoparticles are determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Interestingly, when the multilayered SnO nanoparticles are heated at 400°C under argon for 2 h, they become more efficient anode materials, maintaining their morphology. Heat treatment of the multilayered SnO nanoparticles results in enhanced discharge capacities of up to 584 mAh/g in 70 cycles and cycle stability. These materials exhibit better coulombic efficiencies. Therefore, we believe that the heat treatment of multilayered SnO nanoparticles is a suitable approach to enable their application as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Synthesis and electrochemical properties of multi-layered SnO/rGO composite as anode materials for sodium ion batteries
So Yi Lee, Honggyu Seong, Geongil Kim, Youngho Jin, Joon Ha Moon, Wonbin Nam, Sung Kuk Kim, MinHo Yang, Jaewon Choi
Applied Surface Science.2023; 612: 155859. CrossRef
|