- [English]
- Design of Conductive Inks Containing Carbon Black and Silver Nanowires for Patternable Screen-Printing on Fabrics
-
Seokhwan Kim, Geumseong Lee, Jinwoo Park, Dahye Shin, Ki-Il Park, Kyoung Jin Jung, Yuho Min
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):500-507. Published online December 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00409
-
-
1,999
View
-
58
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
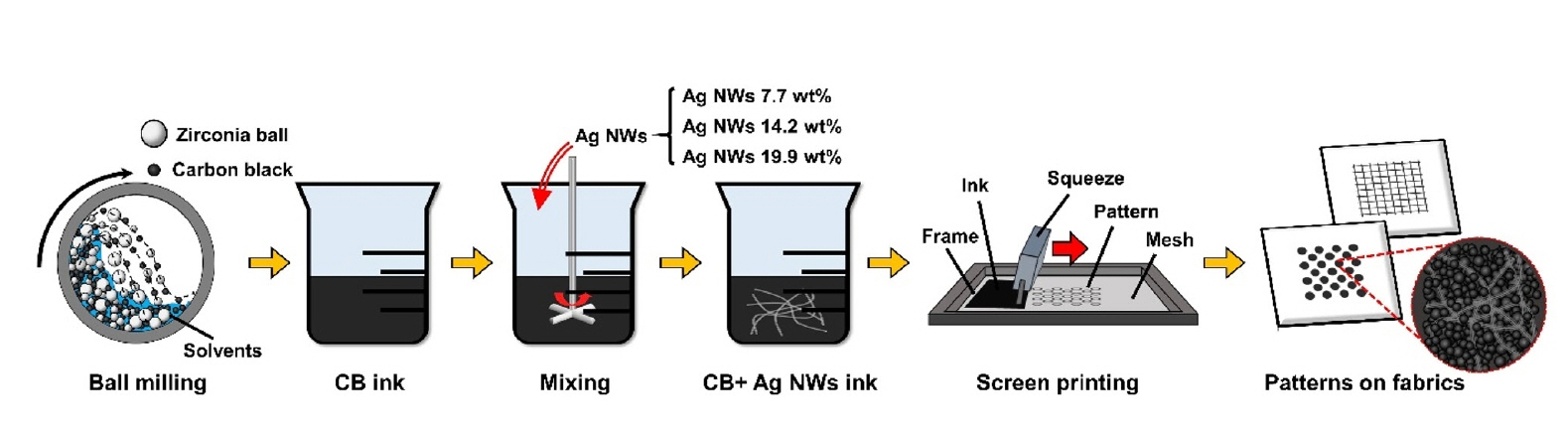
- This study developed conductive inks composed of carbon black (CB) and silver nanowires (Ag NWs) for cost-effective screen-printing on fabrics. The Ag NW density within the CB matrix was precisely controlled, achieving tunable electrical conductivity with minimal Ag NW usage. The resulting inks were successfully patterned into shapes such as square grids and circles on textile surfaces, demonstrating excellent conductivity and fidelity. Adding 19.9 wt% Ag NWs reduced sheet resistance by ~92% compared to CB-only inks, highlighting the effectiveness and potential of this hybrid approach for cost-effective, high-performance textile-based electronics. The one-dimensional morphology of Ag NWs facilitated the formation of conductive percolation networks, creating efficient electron pathways within the CB matrix even at low loadings. This work advances the field of CB-based conductive inks and provides a scalable and practical method for producing functional, patterned electronic textiles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
Nahid Islam, Manisha Das, Bashir Ahmed Johan, Syed Shaheen Shah, Atif Saeed Alzahrani, Md. Abdul Aziz
ACS Applied Electronic Materials.2025; 7(16): 7503. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Bangpungtongseong-san Extract-loaded Particles for Tablet Dosage Form
-
Jinwoo Park, Sung Giu Jin
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):227-232. Published online June 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.227
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The purpose of this study is to optimize the powder formulation and manufacturing conditions for the solidification of an extract of the herb Bangpungtongseong-san (BPTS). To develop BPTS-loaded particles for the tablet dosage form, various BPTS-loaded particles composed of BPTS, dextrin, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), silicon dioxide, ethanol, and water are prepared using spray-drying and high shear granulation (high-speed mixing). Their physical properties are evaluated using scanning electron microscopy and measurements of the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, hardness, and disintegration time. The optimal BPTS-loaded particles exhibit improved flowability and compressibility. In particular, the BPTS-loaded particles containing silicon dioxide show significantly improved flowability and compressibility (the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, and Carr’s index are 35.27 ± 0.58°, 1.18 ± 0.06, and 15.67 ± 1.68%, respectively), hardness (18.97 ± 1.00 KP), and disintegration time (17.60 ± 1.50 min) compared to those without silicon dioxide. Therefore, this study suggests that particles prepared by high-speed mixing can be used to greatly improve the flowability and compressibility of BPTS using MCC and silicon dioxide.
|