- [Korean]
- Characterization of Classification of Synthesized Ni Nanopowders by Pulsed Wire Evaporation Method
-
Joong-Hark Park, Geon-Hong Kim, Dong-Jin Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):389-394. Published online October 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.389
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
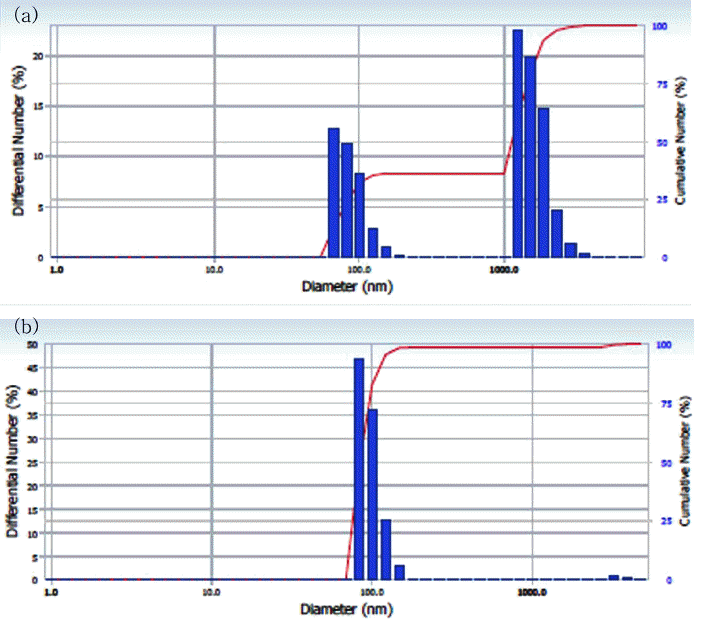
Ni wires with a diameter and length of 0.4 and 100 mm, respectively, and a purity of 99.9% are electrically exploded at 25 cycles per minute. The Ni nanopowders are successfully synthesized by a pulsed wire evaporation (PWE) method, in which Ar gas is used as the ambient gas. The characterization of the nanopowders is carried out using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and a high-resolution transmission electronmicroscope (HRTEM). The Ni nanopowders are classified for a multilayer ceramic condenser (MLCC) application using a type two Air-Centrifugal classifier (model: CNI, MP-250). The characterization of the classified Ni nanopowders are carried out using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and particle size analysis (PSA) to observe the distribution and minimum classification point (minimum cutting point) of the nanopowders.
- [Korean]
- Electromagnetic Wave Shielding Effect of Nano-powder Dispersed Epoxy Resin Composite
-
Jun-Young Han, Chul-Hee Lee, Min-Gyu Choi, Soon-Jik Hong, Joong-Hark Park, Dong-Jin Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):234-239. Published online August 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.234
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Electronic products are a major part of evolving industry and human life style; however most of them are known to emit electromagnetic waves that have severe health hazards. Therefore, different materials and fabrication techniques are understudy to control or limit transfer of such waves to human body. In this study, nanocomposite powder is dispersed into epoxy resin and shielding effects such as absorption, reflection, penetration and multiple reflections are investigated. In addition, nano size powder (Ni, Fe2O3, Fe-85Ni, C-Ni) is fabricated by pulsed wire evaporation method and dispersed manually into epoxy. Characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction, Scanning electron microscopy and Transmission electron microscopy are used to investigate the phase analysis, size and shape as well as dispersion trend of a nano powder on epoxy matrix. Shielding effect is measured by standard test method to investigate the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of planar materials, ASTM D4935. At lower frequency, sample consisting nano-powder of Fe-85%Wt Ni shows better electromagnetic shielding effect compared to only epoxy, only Ni, Fe2O3 and C-Ni samples.
|