- [English]
- Using Carboxylmethylated Cellulose as Water-Borne Binder to Enhance the Electrochemical Properties of Li4Ti5O12-Based Anodes
-
Lili Liu, Chongling Cheng, Hongjiang Liu, Liyi Shi, Dayang Wang
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):315-320. Published online October 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.315
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
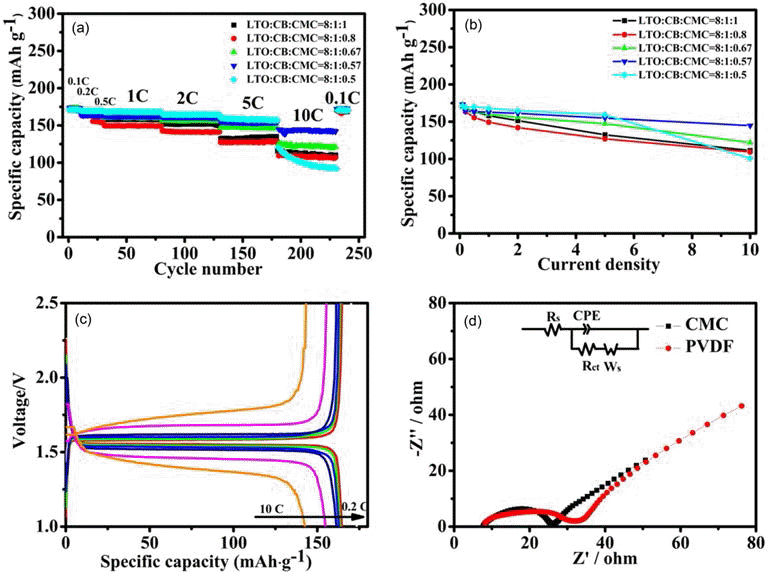
The present work reports a systematic study of using carboxymethylated cellulose (CMC) as water-borne binder to produce Li4Ti5O12-based anodes for manufacture of high rate performance lithium ion batteries. When the LTO-to-CB-to-CMC mass ratio is carefully optimized to be 8:1:0.57, the special capacity of the resulting electrodes is 144 mAh·g−1 at 10 C and their capacity retention was 97.7% after 1000 cycles at 1 C and 98.5% after 500 cycles at 5 C, respectively. This rate performance is comparable or even better than that of the electrolytes produced using conventional, organic, polyvinylidene fluoride binder.
|