- [English]
- Preparation of Flake-shape Cobalt Powders by High-Energy Ball Milling for rSOC Current Collectors
-
Poong-Yeon Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Hyeon Ju Kim, Su-Jin Yun, Si Young Chang, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):383-389. Published online October 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00241
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
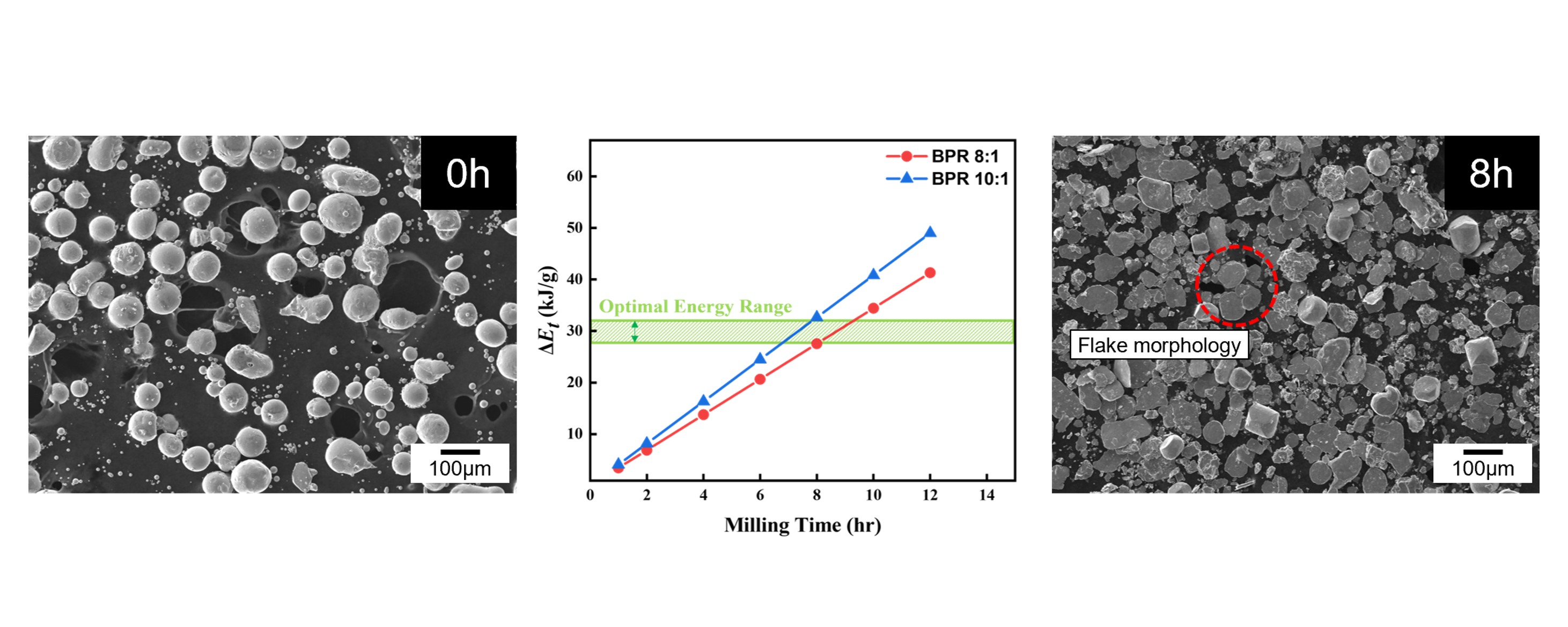
- Reversible solid oxide cells (rSOCs), which enable two-way conversion between electricity and hydrogen, have gained attention with the rise of hydrogen energy. However, foam-type current collectors in rSOC stacks exhibit poor structural controllability and limited electrode contact area. To address these limitations, this study aimed to convert spherical cobalt powders into flake-type morphology via high-energy ball milling, as a preliminary step toward fabricating flake-based current collectors.
Milling parameters—specifically, the ball-to-powder ratio (BPR), milling time, and process control agent (PCA) content—were varied. At an 8:1 BPR, over 90% of the powder became flake-shaped after 8 hours, while extended milling caused cold welding. In contrast, a 10:1 BPR resulted in dominant fragmentation. The Burgio–Rojac model quantified energy input and defined the optimal range for flake formation. Increasing the PCA to 4 wt% delayed flake formation to 16 hours and induced cold welding, as shown by bimodal particle size distributions. These results support the development of Co-based current collectors for use in rSOCs.
- [English]
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
-
Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):299-308. Published online August 29, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00234
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
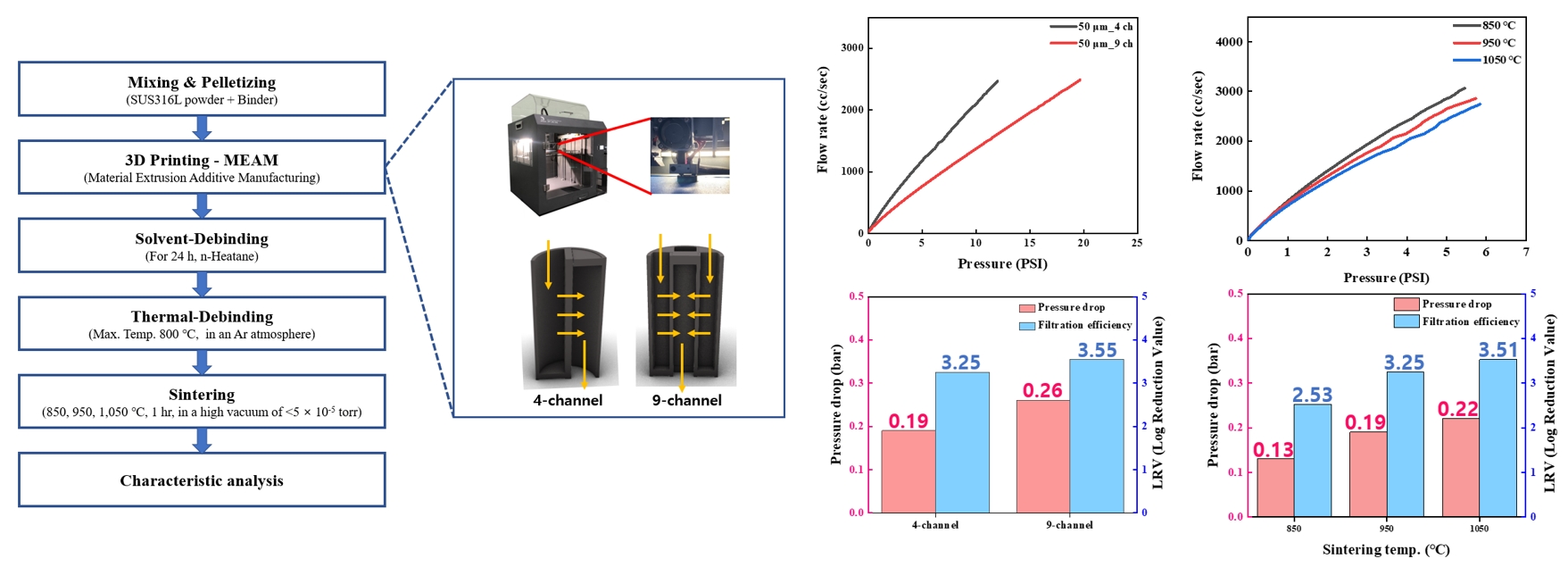
- The development of high-performance metal filters is essential for maintaining ultra-clean environments in semiconductor manufacturing. In this study, cross-sealed honeycomb filters were fabricated using STS316L powder via material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) for semiconductor gas filtration. The effects of filter geometry (4 or 9 channels) and sintering temperature (850°C, 950°C, or 1,050°C) on performance were examined. First, 4-channel and 9-channel filters sintered at the same temperature (950°C) exhibited similar porosities of 50.08% and 50.57%, but the 9-channel filter showed a higher pressure-drop (0.26 bar) and better filtration-efficiency (3.55 LRV) than the 4-channel filter (0.19 bar and 3.25 LRV, respectively). Second, for filters with the same geometry (4-channel) increasing the sintering temperature reduced porosity from 64.52% to 40.33%, while the pressure-drop increased from 0.13 bar to 0.22 bar and filtration-efficiency improved from 2.53 LRV to 3.51 LRV. These findings demonstrate that filter geometry and sintering temperature are key factors governing the trade-off between air permeability, pressure-drop, and filtration efficiency. This work provides insights and data for optimizing MEAM-based high-performance metal powder filter design.
- [Korean]
- A Study on Pore Properties of SUS316L Powder Porous Metal Fabricated by Electrostatic Powder Coating Process
-
Min-Jeong Lee, Yu-Jeong Yi, Hyeon-Ju Kim, Manho Park, Byoung-Kee Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):415-419. Published online October 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.415
-
-
814
View
-
6
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Porous metals demonstrate not only excessively low densities, but also novel physical, thermal, mechanical, electrical, and acoustic properties. Thus, porous metals exhibit exceptional performance, which are useful for diesel particulate filters, heat exchangers, and noise absorbers. In this study, SUS316L foam with 90% porosity and 3,000 μm pore size is successfully manufactured using the electrostatic powder coating (ESPC) process. The mean size of SUS316L powders is approximately 12.33 μm. The pore properties are evaluated using SEM and Archimedes. As the quantity of powder coating increases, pore size decreases from 2,881 to 1,356 μm. Moreover, the strut thickness and apparent density increase from 423.7 to 898.3 μm and from 0.278 to 0.840 g/cm3, respectively. It demonstrates that pore properties of SUS316L powder porous metal are controllable by template type and quantity of powder coating. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 299. CrossRef
|