- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Performance Enhancement of Sintered Bi-Te Pellets by Rotary-type Atomic Layer Deposition
-
Myeong Jun Jung, Ji Young Park, Su Min Eun, Byung Joon Choi
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):130-139. Published online April 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.130
-
-
1,481
View
-
13
Download
-
4
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
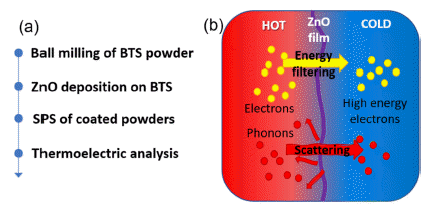
Thermoelectric materials and devices are energy-harvesting devices that can effectively recycle waste heat into electricity. Thermoelectric power generation is widely used in factories, engines, and even in human bodies as they continuously generate heat. However, thermoelectric elements exhibit poor performance and low energy efficiency; research is being conducted to find new materials or improve the thermoelectric performance of existing materials, that is, by ensuring a high figure-of-merit (zT) value. For increasing zT, higher σ (electrical conductivity) and S (Seebeck coefficient) and a lower к (thermal conductivity) are required. Here, interface engineering by atomic layer deposition (ALD) is used to increase zT of n-type BiTeSe (BTS) thermoelectric powders. ALD of the BTS powders is performed in a rotary-type ALD reactor, and 40 to 100 ALD cycles of ZnO thin films are conducted at 100°C. The physical and chemical properties and thermoelectric performance of the ALD-coated BTS powders and pellets are characterized. It is revealed that electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are decoupled, and thus, zT of ALD-coated BTS pellets is increased by more than 60% compared to that of the uncoated BTS pellets. This result can be utilized in a novel method for improving the thermoelectric efficiency in materials processing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef - Thermal Confinement and Filtering Effect of SnSe by Insertion of Atomic-Layer-Deposited ZnO Interfacial Layer
Myeong Jun Jung, Su Min Eun, Hogyoung Kim, Seong Keun Kim, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 42(14): 3545. CrossRef - Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 236. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Recent Studies on Performance Enhancement of Polycrystal SnSe Thermoelectric Materials
-
Myeong Jun Jung, Byung Joon Choi
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):152-158. Published online April 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.152
-
-
1,320
View
-
8
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
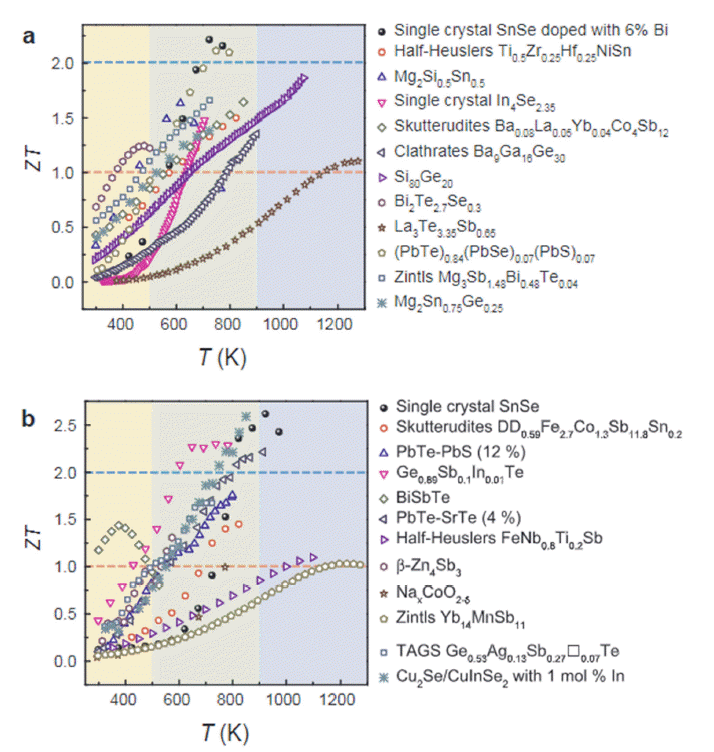
Thermoelectric materials can reversely convert heat and electricity into each other; therefore, they can be very useful for energy harvesting from heat waste. Among many thermoelectrical materials, SnSe exhibits outstanding thermoelectric performance along the particular direction of a single crystal. However, single-crystal SnSe has poor mechanical properties and thus it is difficult to apply for mass production. Therefore, polycrystalline SnSe materials may be used to replace single-crystal SnSe by overcoming its inferior thermoelectric performance owing to surface oxidation. Considerable efforts are currently focused on enhancing the thermoelectric performance of polycrystalline SnSe. In this study, we briefly review various enhancement methods for SnSe thermoelectric materials, including doping, texturing, and nano-structuring. Finally, we discuss the future prospects of SnSe thermoelectric powder materials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Mechanism Behind the High zT of SnSe2 Added SnSe at High Temperatures
JunSu Kim, Seong-Mee Hwang, Hyunjin Park, Yinglu Tang, Won-Seon Seo, Chae Woo Ryu, Heesun Yang, Weon Ho Shin, Hyun-Sik Kim
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(11): 857. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Rotation Speed Dependence of ZnO Coating Layer on SnSe powders by Rotary Atomic Layer Deposition Reactor
-
Myeong Jun Jung, Ye Jun Yun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):239-245. Published online June 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.239
-
-
642
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
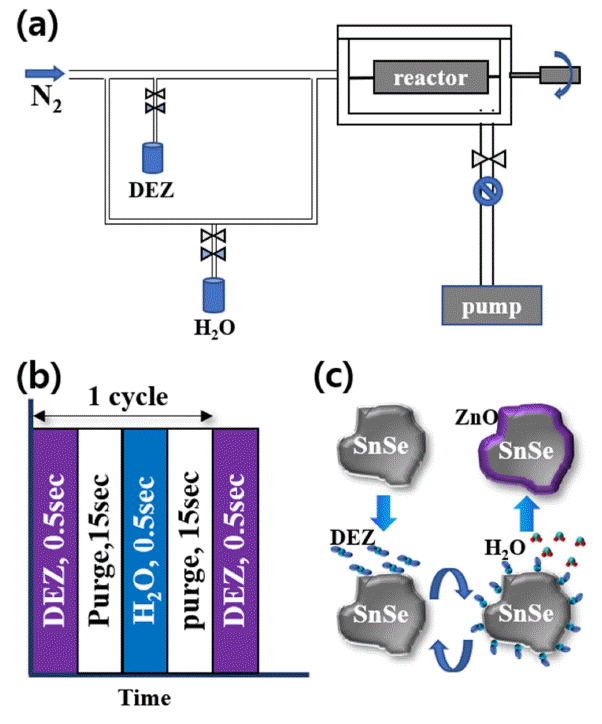
The SnSe single crystal shows an outstanding figure of merit (ZT) of 2.6 at 973 K; thus, it is considered to be a promising thermoelectric material. However, the mass production of SnSe single crystals is difficult, and their mechanical properties are poor. Alternatively, we can use polycrystalline SnSe powder, which has better mechanical properties. In this study, surface modification by atomic layer deposition (ALD) is chosen to increase the ZT value of SnSe polycrystalline powder. SnSe powder is ground by a ball mill. An ALD coating process using a rotary-type reactor is adopted. ZnO thin films are grown by 100 ALD cycles using diethylzinc and H2O as precursors at 100°C. ALD is performed at rotation speeds of 30, 40, 50, and 60 rpm to examine the effects of rotation speed on the thin film characteristics. The physical and chemical properties of ALD-coated SnSe powders are characterized by scanning and tunneling electron microscopy combined with energy-dispersive spectroscopy. The results reveal that a smooth oxygenrich ZnO layer is grown on SnSe at a rotation speed of 30 rpm. This result can be applied for the uniform coating of a ZnO layer on various powder materials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Thermal Confinement and Filtering Effect of SnSe by Insertion of Atomic-Layer-Deposited ZnO Interfacial Layer
Myeong Jun Jung, Su Min Eun, Hogyoung Kim, Seong Keun Kim, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 42(14): 3545. CrossRef
|