- [Korean]
- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
-
YongKwan Lee, Hyun-chul Kim, Myungsuk Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kyoungtae Park, JaeJin Sim
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):330-343. Published online August 29, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00136
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
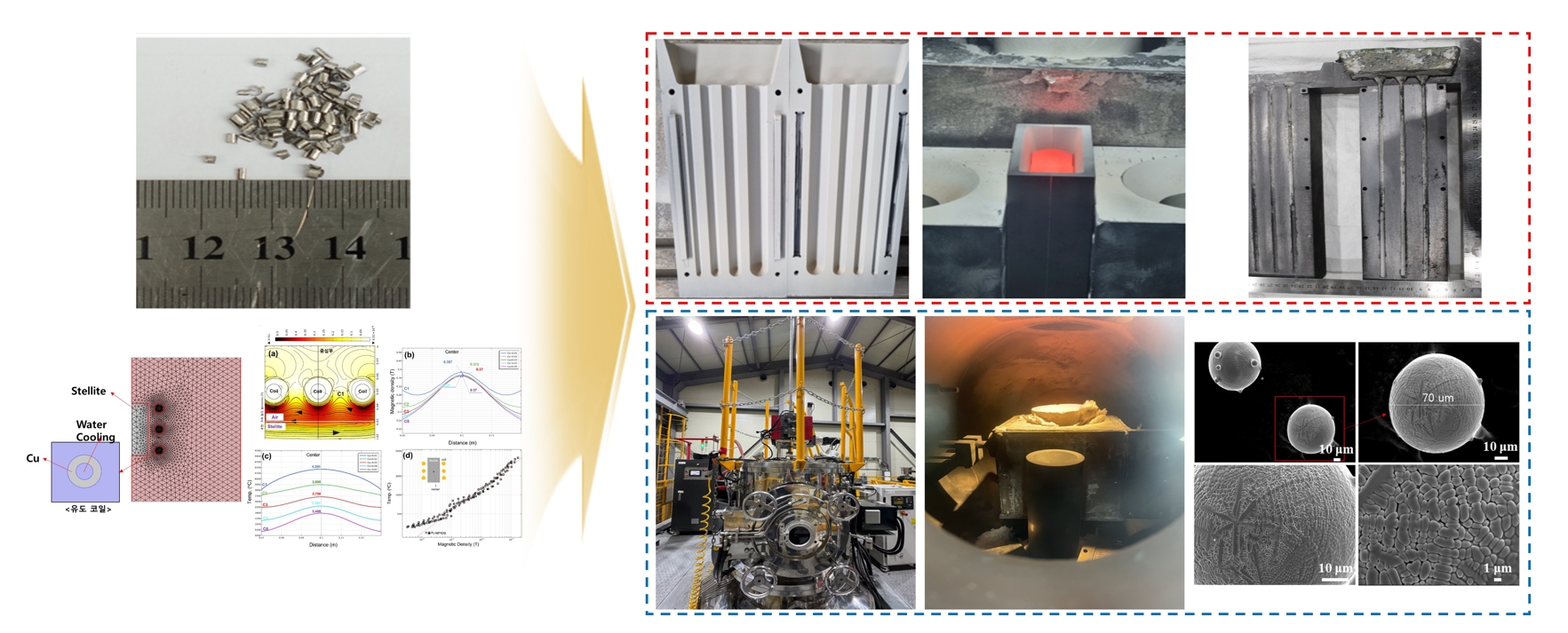
- Co-Cr alloys are widely used in cutting tools and turbine components due to their high strength and resistance against wear and corrosion. However, scrap generated during hardfacing is often discarded due to impurities and oxidation, and research on its recycling remains limited. This study aimed to optimize the recycling process of Stellite 6 scrap to reduce waste and minimize costs while maintaining material quality. Melting, casting, and powdering processes were designed using HSC Chemistry, FactSage, and COMSOL Multiphysics, with optimization of key parameters such as the crucible material and temperature control. The recycled alloy and powder were analyzed using X-ray fluorescence analysis, inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy, and X-ray diffractometry, showing mechanical and chemical properties comparable to commercial Stellite 6. The Co and Cr contents were maintained, with a slight increase in Fe. These findings demonstrate the potential for producing high-quality recycled Stellite 6 materials, contributing to the sustainable utilization of metal resources in high-performance applications.
- [Korean]
- Analysis of Wafer Cleaning Solution Characteristics and Metal Dissolution Behavior according to the Addition of Chelating Agent
-
Myungsuk Kim, Keunhyuk Ryu, Kun-Jae Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):25-30. Published online February 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.25
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The surface of silicon dummy wafers is contaminated with metallic impurities owing to the reaction with and adhesion of chemicals during the oxidation process. These metallic impurities negatively affect the device performance, reliability, and yield. To solve this problem, a wafer-cleaning process that removes metallic impurities is essential. RCA (Radio Corporation of America) cleaning is commonly used, but there are problems such as increased surface roughness and formation of metal hydroxides. Herein, we attempt to use a chelating agent (EDTA) to reduce the surface roughness, improve the stability of cleaning solutions, and prevent the re-adsorption of impurities. The bonding between the cleaning solution and metal powder is analyzed by referring to the Pourbaix diagram. The changes in the ionic conductivity, H2O2 decomposition behavior, and degree of dissolution are checked with a conductivity meter, and the changes in the absorbance and particle size before and after the reaction are confirmed by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analyses. Thus, the addition of a chelating agent prevents the decomposition of H2O2 and improves the life of the silicon wafer cleaning solution, allowing it to react smoothly with metallic impurities.
|