- [Korean]
- Size Control of Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoclusters according to Reaction Factors and Consequent Change in Their Magnetic Attraction
-
Sanghoon Lee, Arim Byun, Jin-sil Choi
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):297-304. Published online August 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.297
-
-
1,064
View
-
13
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
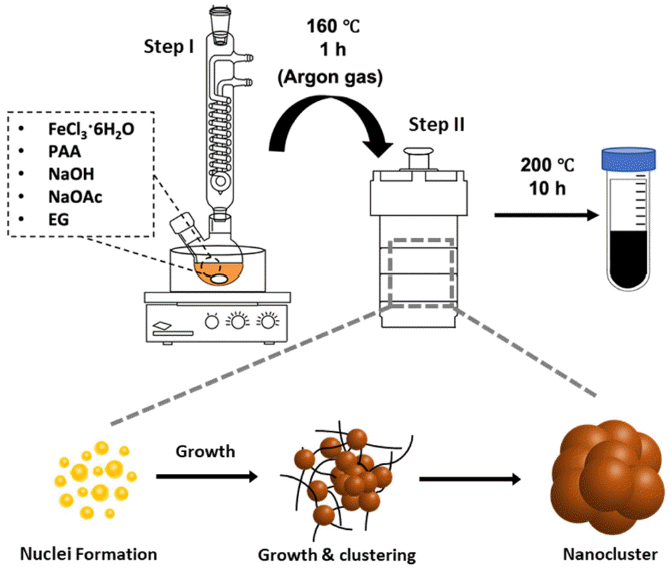
Iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoclusters exhibit significant potential in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields due to their strong magnetic properties, stability in solutions, and compatibility with living systems. They excel in magnetic separation processes, displaying high responsiveness to external magnetic fields. In contrast to conventional Fe2O3 nanoparticles that can aggregate in aqueous solutions due to their ferrimagnetic properties, these nanoclusters, composed of multiple nanoparticles, maintain their magnetic traits even when scaled to hundreds of nanometers. In this study, we develop a simple method using solvothermal synthesis to precisely control the size of nanoclusters. By adjusting precursor materials and reducing agents, we successfully control the particle sizes within the range of 90 to 420 nm. Our study not only enhances the understanding of nanocluster creation but also offers ways to improve their properties for applications such as magnetic separation. This is supported by our experimental results highlighting their size-dependent magnetic response in water. This study has the potential to advance both the knowledge and practical utilization of Fe2O3 nanoclusters in various applications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Enzymatic properties of iron oxide nanoclusters and their application as a colorimetric glucose detection probe
Dahyun Bae, Minhee Kim, Jin-sil Choi
RSC Advances.2025; 15(6): 4573. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Photoelectrochromic Devices Composed of Anodized TiO2 and WO3 Nanostructures
-
Sanghoon Lee, Hyeongcheol Cha, Yoon-Chae Nah
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):326-330. Published online October 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.326
-
-
667
View
-
3
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
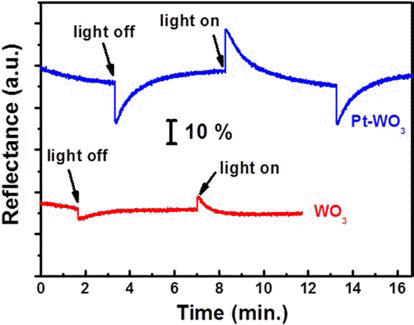
In this study, we demonstrate the photoelectrochromic devices composed of TiO2 and WO3 nanostructures prepared by anodization method. The morphology and the crystal structure of anodized TiO2 nanotubes and WO3 nanoporous layers are investigated by SEM and XRD. To fabricate a transparent photoelectrode on FTO substrate, a TiO2 nanotube membrane, which has been detached from Ti substrate, is transferred to FTO substrate and annealed at 450°C for 1 hr. The photoelectrode of TiO2 nanotube and the counter electrode of WO3 nanoporous layer are assembled and the inner space is filled with a liquid electrolyte containing 0.5 M LiI and 5 mM I2 as a redox mediator. The properties of the photoelectrochromic devices is investigated and Pt-WO3 electrode system shows better electrochromic performance compared toWO3 electrode. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped TiO2 coatings on reduced graphene oxide for enhancing the visible light photocatalytic activity
Yifan Zhang, Hye Mee Yang, Soo-Jin Park
Current Applied Physics.2018; 18(2): 163. CrossRef - Photocatalytic and Adsorption Properties of WO3 Nanorods Prepared by Hydrothermal Synthesis
Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(6): 483. CrossRef - Synthesis and Photo Catalytic Activity of 10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 Composite Powders
Hyeong-Chul Kim, Jae-Kil Han
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 33. CrossRef
|