- [Korean]
- Friction Stir Spot Welding Characteristics of Dissimilar Materials of Aluminum-Based Damping Composites and Steel Plates
-
Si-Seon Park, Young-Keun Jeong
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):43-49. Published online February 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00010
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
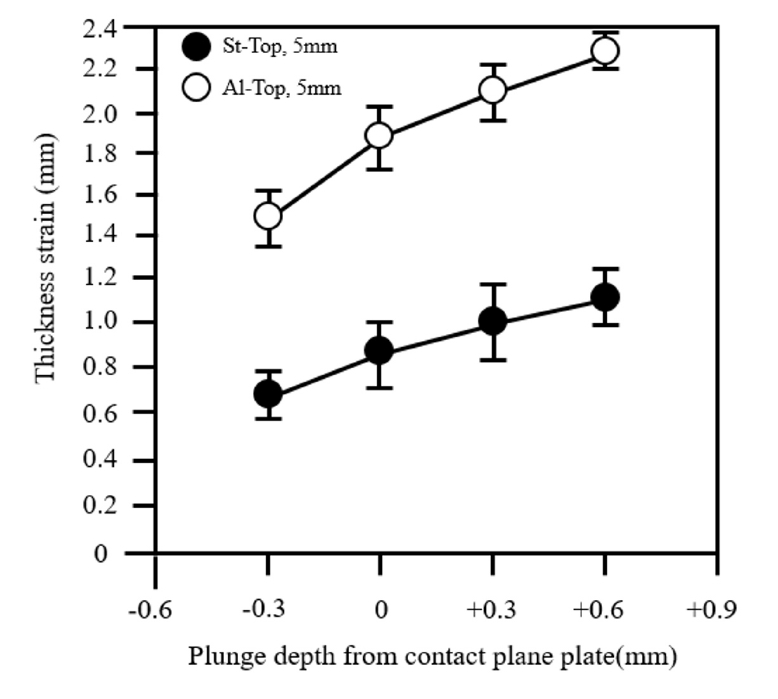
- Friction Stir Spot Welding (FSSW) is a solid-state welding technology that is rapidly growing in the automotive industry. Achieving superior welding characteristics requires the proper selection of tool geometry and process conditions. In this study, FSSW was performed on dissimilar materials comprising AA5052-HO/hot-melt aluminum alloy sheets and Steel Plate Cold Rolled for Deep Drawing Use(SPCUD) steel sheets. The effects of tool geometry, plate arrangement, and tool plunge depth on the welding process were investigated. At the joint interface between the aluminum alloy and the steel sheet, new intermetallic compounds (IMCs) were observed. As the plunge depth increased, thicker and more continuous IMC layers were formed. However, excessive plunge depth led to discontinuous layers and cracking defects. An analysis of the IMCs revealed a correlation between the IMC thickness and the shear tensile load. Furthermore, compared to the conventional Al-Top arrangement, the St-Top arrangement exhibited reduced deformation and superior shear tensile load values. These findings indicate that plate arrangement significantly influences the mechanical properties of the joint.
|