- [Korean]
- Rotation Speed Dependence of ZnO Coating Layer on SnSe powders by Rotary Atomic Layer Deposition Reactor
-
Myeong Jun Jung, Ye Jun Yun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):239-245. Published online June 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.239
-
-
638
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
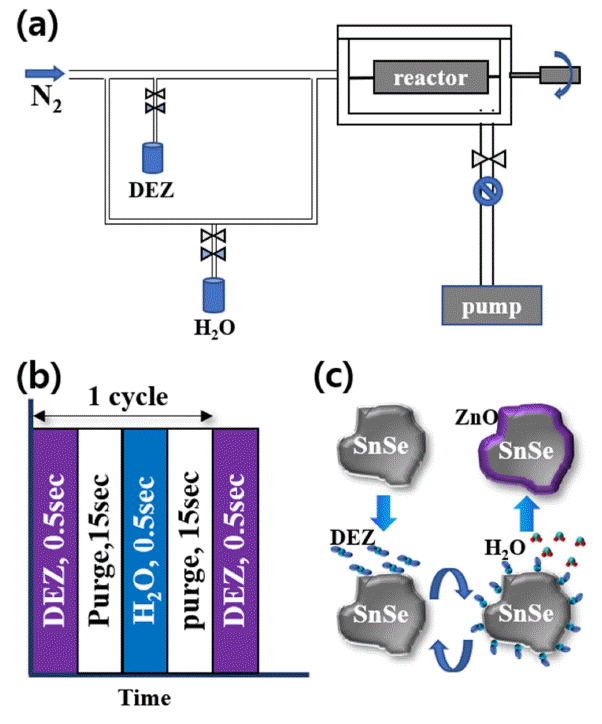
The SnSe single crystal shows an outstanding figure of merit (ZT) of 2.6 at 973 K; thus, it is considered to be a promising thermoelectric material. However, the mass production of SnSe single crystals is difficult, and their mechanical properties are poor. Alternatively, we can use polycrystalline SnSe powder, which has better mechanical properties. In this study, surface modification by atomic layer deposition (ALD) is chosen to increase the ZT value of SnSe polycrystalline powder. SnSe powder is ground by a ball mill. An ALD coating process using a rotary-type reactor is adopted. ZnO thin films are grown by 100 ALD cycles using diethylzinc and H2O as precursors at 100°C. ALD is performed at rotation speeds of 30, 40, 50, and 60 rpm to examine the effects of rotation speed on the thin film characteristics. The physical and chemical properties of ALD-coated SnSe powders are characterized by scanning and tunneling electron microscopy combined with energy-dispersive spectroscopy. The results reveal that a smooth oxygenrich ZnO layer is grown on SnSe at a rotation speed of 30 rpm. This result can be applied for the uniform coating of a ZnO layer on various powder materials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Thermal Confinement and Filtering Effect of SnSe by Insertion of Atomic-Layer-Deposited ZnO Interfacial Layer
Myeong Jun Jung, Su Min Eun, Hogyoung Kim, Seong Keun Kim, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 42(14): 3545. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Ti-Mn-Cu Alloys with Magnetic Pulsed Compaction
-
Ye Jun Yun, Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):20-24. Published online February 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.20
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
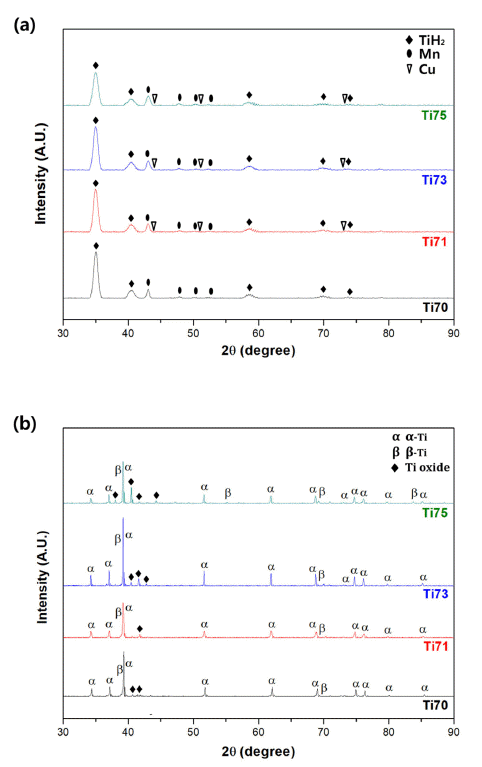
Ti-based alloys are widely used in biomaterials owing to their excellent biocompatibility. In this study, Ti- Mn-Cu alloys are prepared by high-energy ball milling, magnetic pulsed compaction, and pressureless sintering. The microstructure and microhardness of the Ti-Mn-Cu alloys with variation of the Cu addition and compaction pressure are analyzed. The correlation between the composition, compaction pressure, and density is investigated by measuring the green density and sintered density for samples with different compositions, subjected to various compaction pressures. For all compositions, it is confirmed that the green density increases proportionally as the compaction pressure increases, but the sintered density decreases owing to gas formation from the pyrolysis of TiH2 powders and reduction of oxides on the surface of the starting powders during the sintering process. In addition, an increase in the amount of Cu addition changes the volume fractions of the α-Ti and β-Ti phases, and the microstructure of the alloys with different compositions also changes. It is demonstrated that these changes in the phase volume fraction and microstructure are closely related to the mechanical properties of the Ti-Mn-Cu alloys.
|