- [English]
- The Effect of a CNT/MnO2 Nanoparticle Composite–Based Multi-Shell Typed Electrode for a Fiber Supercapacitor (FSC)
-
Yeonggwon Kim, Hyung Woo Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00416
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
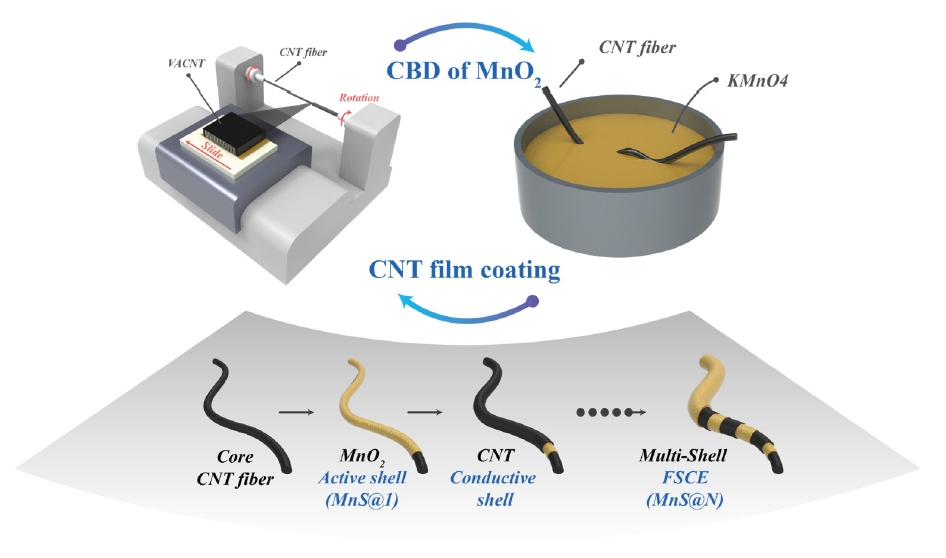
- Fiber supercapacitors have attracted significant interest as potential textile energy storage devices due to their remarkable flexibility and rapid charge/discharge capabilities. This study describes the fabrication of a composite fiber supercapacitor (FSC) electrode through a multi-shell architecture, featuring layers of carbon nanotube (CNT) conductive shells and MnO₂ nanoparticle active shells. The number of layers was adjusted to assess their impact on FSC energy storage performance. Increasing the number of shells reduced electrode resistance and enhanced pseudocapacitive characteristics. Compared to the MnS@1 electrode, the MnS@5 electrode exhibited a high areal capacitance of 301.2 mF/cm², a 411% increase, but showed a higher charge transfer resistance (RCT) of 701.6 Ω. This is attributed to reduced ion diffusion and charge transfer ability resulting from the thicker multi-shell configuration. These results indicate that fine-tuning the quantity of shells is crucial for achieving an optimal balance between energy storage efficiency and stability.
|