- [Korean]
- Development of Lithium Lanthanum Titanate (LLTO) Membrane Manufacturing Process for Selective Separation of Lithium Ion
-
Young Il Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Kwang Ho Shin, InYeong Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee, Sung-Kyun Jung, Bin Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):22-28. Published online February 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.22
-
-
2,507
View
-
40
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
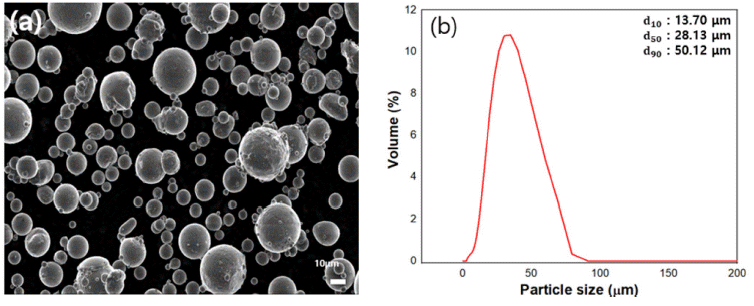
The global demand for raw lithium materials is rapidly increasing, accompanied by the demand for lithiumion batteries for next-generation mobility. The batch-type method, which selectively separates and concentrates lithium from seawater rich in reserves, could be an alternative to mining, which is limited owing to low extraction rates. Therefore, research on selectively separating and concentrating lithium using an electrodialysis technique, which is reported to have a recovery rate 100 times faster than the conventional methods, is actively being conducted. In this study, a lithium ion selective membrane is prepared using lithium lanthanum titanate, an oxide-based solid electrolyte material, to extract lithium from seawater, and a large-area membrane manufacturing process is conducted to extract a large amount of lithium per unit time. Through the developed manufacturing process, a large-area membrane with a diameter of approximately 20 mm and relative density of 96% or more is manufactured. The lithium extraction behavior from seawater is predicted by measuring the ionic conductivity of the membrane through electrochemical analysis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Study on Particle and Crystal Size Analysis of Lithium Lanthanum Titanate Powder Depending on Synthesis Methods (Sol-Gel & Solid-State reaction)
Jeungjai Yun, Seung-Hwan Lee, So Hyun Baek, Yongbum Kwon, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim, Bin Lee, Rhokyun Kwak, Da-Woon Jeong
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 324. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Improving Flow Property of AlSi10Mg Powder for Additive Manufacturing via Surface Treatment using Methyltrichlorosilane
-
Sang Cheol Park, In Yeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee, Soong Ju Oh, Bin Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):363-369. Published online October 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.363
-
-
949
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
AlSi10Mg alloys are being actively studied through additive manufacturing for application in the automobile and aerospace industries because of their excellent mechanical properties. To obtain a consistently high quality product through additive manufacturing, studying the flowability and spreadability of the metal powder is necessary. AlSi10Mg powder easily forms an oxide film on the powder surface and has hydrophilic properties, making it vulnerable to moisture. Therefore, in this study, AlSi10Mg powder was hydrophobically modified through silane surface treatment to improve the flowability and spreadability by reducing the effects of moisture. The improved flowability according to the number of silane surface treatments was confirmed using a Carney flowmeter. In addition, to confirm the effects of improved spreadability, the powder prior to surface treatment and that subjected to surface treatment four times were measured and compared using s self-designed recoating tester. The results of this study confirmed the improved flowability and spreadability based on the modified metal powder from hydrophilic to hydrophobic for obtaining a highquality additive manufacturing product. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Recycling of Hardmetal Tool through Alkali Leaching Process and Fabrication Process of Nano-sized Tungsten Carbide Powder using Self-propagation High-temperature Synthesis
-
Hee-Nam Kang, Dong Il Jeong, Young Il Kim, In Yeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Cheol Woo Nam, Seok-Jun Seo, Jin Yeong Lee, Bin Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):47-55. Published online February 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.47
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Tungsten carbide is widely used in carbide tools. However, its production process generates a significant number of end-of-life products and by-products. Therefore, it is necessary to develop efficient recycling methods and investigate the remanufacturing of tungsten carbide using recycled materials. Herein, we have recovered 99.9% of the tungsten in cemented carbide hard scrap as tungsten oxide via an alkali leaching process. Subsequently, using the recovered tungsten oxide as a starting material, tungsten carbide has been produced by employing a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) method. SHS is advantageous as it reduces the reaction time and is energy-efficient. Tungsten carbide with a carbon content of 6.18 wt % and a particle size of 116 nm has been successfully synthesized by optimizing the SHS process parameters, pulverization, and mixing. In this study, a series of processes for the highefficiency recycling and quality improvement of tungsten-based materials have been developed.
- [Korean]
- Review on Characterization Method and Recent Research Trend about Metal Powder for Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) Process
-
Bin Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Yong Son, Kyoung-Tae Park, Taek-Soo Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):509-519. Published online December 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.509
-
-
1,547
View
-
15
Download
-
9
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
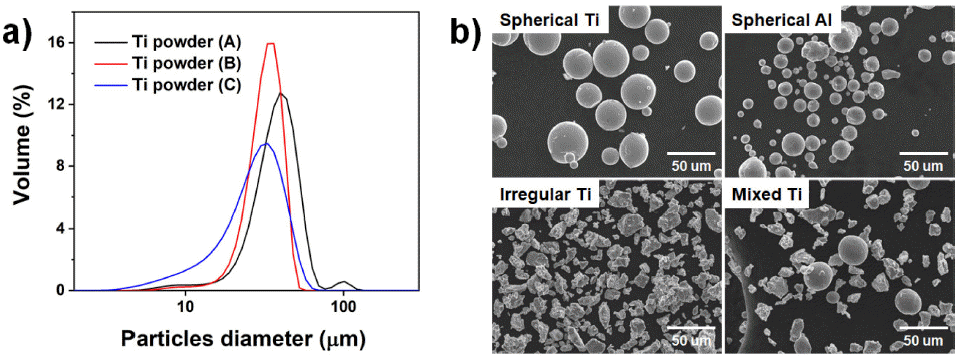
A well-established characterization method is required in powder bed fusion (PBF) metal additive manufacturing, where metal powder is used. The characterization methods from the traditional powder metallurgy process are still being used. However, it is necessary to develop advanced methods of property evaluation with the advances in additive manufacturing technology. In this article, the characterization methods of powders for metal PBF are reviewed, and the recent research trends are introduced. Standardization status and specifications for metal powder for the PBF process which published by the ISO, ASTM, and MPIF are also covered. The establishment of powder characterization methods are expected to contribute to the metal powder industry and the advancement of additive manufacturing technology through the creation of related databases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
Yu Cao, Xiaohui Dong, Yulong Zhu, Tao Huang, Bin Jiang, Chenghang Zhang
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2026; 263: 140. CrossRef -
Enhanced flow properties of SiO
2
nanoparticles coated low-cost hydrogenation-dehydrogenation Ti-6Al-4V powder for powder bed fusion process
Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Tae hu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(2): 95. CrossRef -
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
Jongik Lee, Taehoo Kang, Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Sanghee Jung, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 333. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - A Study on Fabrication of PCD Endmill Holder using PBF Additive Manufacturing Technology
Min-Woo Sa, Ho-Min Son, Kyung-Hwan Park, Sang-Geun Lee, Dae-Ho Shin, Dong-Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2024; 23(6): 124. CrossRef - Rheological Characteristic Analysis Methods and Tests of Metal Powders for PBF Additive Manufacturing
Wan-Sik Woo, Ho-Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2023; 22(10): 1. CrossRef - Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef - Enhancing spreadability of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation titanium powder and novel method to characterize powder spreadability for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, InYeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Dongju Lee, Bin Lee
Materials & Design.2022; 223: 111247. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Optimization of Metal Powder Particle Size Distribution for Powder Bed Fusion Process via Simulation
-
Hwaseon Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Jieun Nam, Yong Son, Taek-Soo Kim, Bin Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):44-51. Published online February 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.44
-
-
1,534
View
-
10
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
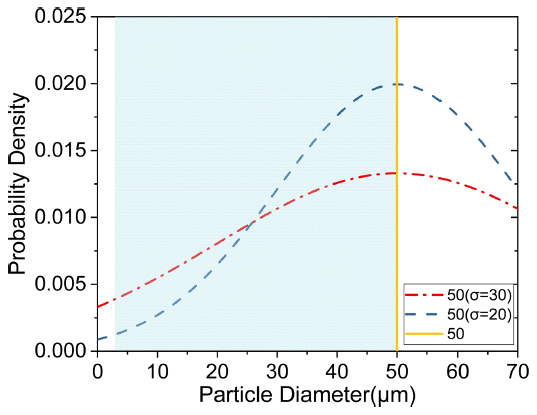
Powder characteristics, such as density, size, shape, thermal properties, and surface area, are of significant importance in the powder bed fusion (PBF) process. The powder required is exclusive for an efficient PBF process. In this study, the particle size distribution suitable for the powder bed fusion process was derived by modeling the PBF product using simulation software (GeoDict). The modeling was carried out by layering sintered powder with a large particle size distribution, with 50 μm being the largest particle size. The results of the simulation showed that the porosity decreased when the mean particle size of the powder was reduced or the standard deviation increased. The particle size distribution of prepared titanium powder by the atomization process was also studied. This study is expected to offer direction for studies related to powder production for additive manufacturing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the International Symposium on Innovation in Materials Processing (ISIMP, 26–29 October 2021)”
Hyunjoo Choi, Jungjoon Kim, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung Seop Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2023; 64(10): 2542. CrossRef
|