Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Morphological Control of Secondary Phase using Yb2O3 and Ca-Al-Si-O-based Glass on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of AlN
- Dong Kyu Choi, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong Hun Yeo, Hyo Soon Shin, Dae Yong Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):498-502. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.498
- 853 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
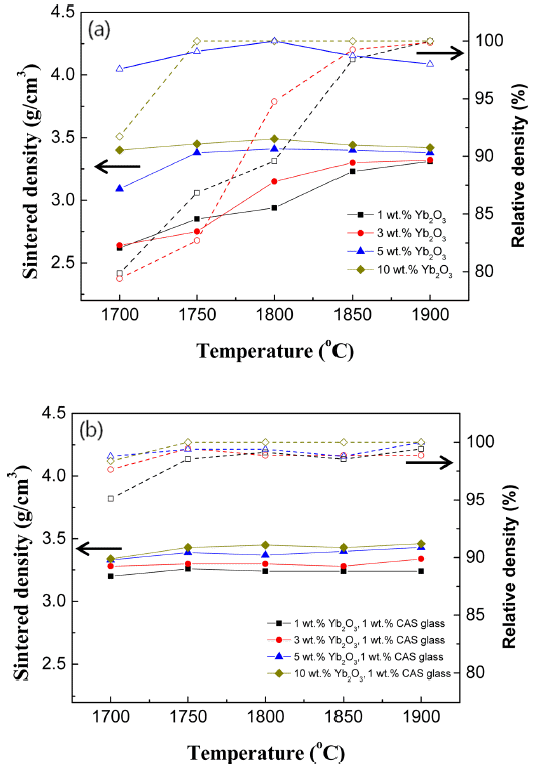
PDF We investigate the effects of Yb2O3 and calcium aluminosilicate (CAS) glass as sintering additives on the sintering behavior of AlN. The AlN specimens are sintered at temperatures between 1700°C and 1900°C for 2 h in a nitrogen atmosphere. When the Yb2O3 content is low (within 3 wt.%), an isolated shape of secondary phase is observed at the AlN grain boundary. In contrast, when 3 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added, a continuous secondary phase is formed at the AlN grain boundary. The thermal conductivity decreases when the CAS glass is added, but the sintering density does not decrease. In particular, when 10 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added to AlN, the flexural strength is the highest, at 463 MPa. These results are considered to be influenced by changes in the microstructure of the secondary phase of AlN.
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Properties and Thermal Stability of Ti0.5Al0.5N/CrN Nano-multilayered Coatings
- Seung-Su Ahn, Jong-Keuk Park, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):406-413. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.406

- 495 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ti0.5Al0.5N/CrN nano-multilayers, which are known to exhibit excellent wear resistances, were prepared using the unbalanced magnetron sputter for various periods of 2–7 nm. Ti0.5Al0.5N and CrN comprised a cubic structure in a single layer with different lattice parameters; however, Ti0.5Al0.5N/CrN exhibited a cubic structure with the same lattice parameters that formed the superlattice in the nano-multilayers. The Ti0.5Al0.5/CrN multilayer with a period of 5.0 nm exceeded the hardness of the Ti0.5Al0.5N/CrN single layer, attaining a value of 36 GPa. According to the low-angle X-ray diffraction, the Ti0.5Al0.5N/CrN multilayer maintained its as-coated structure up to 700°C and exhibited a hardness of 32 GPa. The thickness of the oxidation layer of the Ti0.5Al0.5N/CrN multilayered coating was less than 25% of that of the single layers. Thus, the Ti0.5Al0.5N/CrN multilayered coating was superior in terms of hardness and oxidation resistance as compared to its constituent single layers.
- [Korean]
- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
- Kyung Min Kim, Su-Hyun Baik, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):494-500. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.494
- 1,464 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
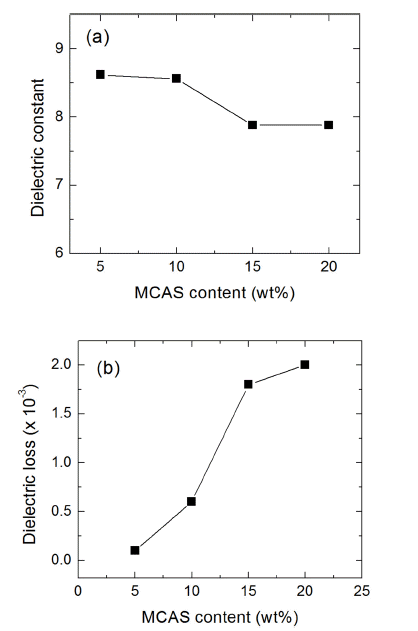
PDF In this study, the effect of the content of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 (MCAS) glass additives on the properties of AlN ceramics is investigated. Dilatometric analysis and isothermal sintering for AlN compacts with MCAS contents varying between 5 and 20 wt% are carried out at temperatures ranging up to 1600°C. The results showed that the shrinkage of the AlN specimens increases with increasing MCAS content, and that full densification can be obtained irrespective of the MCAS content. Moreover, properties of the AlN-MCAS specimens such as microhardness, thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and dielectric loss are analyzed. Microhardness and thermal conductivity decrease with increasing MCAS content. An acceptable candidate for AlN application is obtained: an AlN-MCAS composite with a thermal conductivity over 70 W/m·K and a dielectric loss tangent (tan δ) below 0.6 × 10−3, with up to 10 wt% MCAS content.
- [Korean]
- Sintering Behavior and Thermal Conductivity of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics with MgO–CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 Nano-glass Additive
- Su-Hyun Baik, Kyung Min Kim, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):426-434. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.426
- 1,179 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
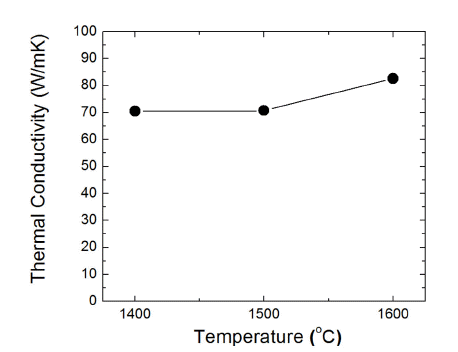
PDF In this study, MgO–CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 (MCAS) nanocomposite glass powder having a mean particle size of 50 nm and a specific surface area of 40 m2/g is used as a sintering additive for AlN ceramics. Densification behaviors and thermal properties of AlN with 5 wt% MCAS nano-glass additive are investigated. Dilatometric analysis and isothermal sintering of AlN-5wt% MCAS compact demonstrates that the shrinkage of the AlN specimen increases significantly above 1,300°C via liquid phase sintering of MCAS additive, and complete densification could be achieved after sintering at 1,600°C, which is a reduction in sintering temperature by 200°C compared to conventional AlN-Y2O3 systems. The MCAS glass phase is satisfactorily distributed between AlN particles after sintering at 1,600°C, existing as an amorphous secondary phase. The AlN specimen attained a thermal conductivity of 82.6 W/m·K at 1,600°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
Kyung Min Kim, Su-Hyun Baik, Sung-Soo Ryu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(6): 494. CrossRef
- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
- [Korean]
- Insulating Behavior of Sintered AlN Ceramics Prepared by High-Energy Bead Milling of AlN Powder
- Sung-Soo Ryu, Sung-Min Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):444-449. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.444
- 791 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
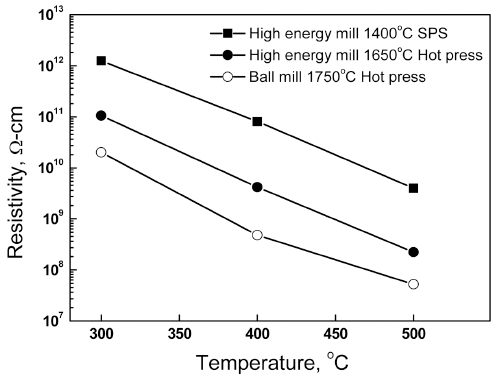
PDF Aluminum nitride (AlN) powder specimens are treated by high-energy bead milling and then sintered at various temperatures. Depending on the solvent and milling time, the oxygen content in the AlN powder varies significantly. When isopropyl alcohol is used, the oxygen content increases with the milling time. In contrast, hexane is very effective at suppressing the oxygen content increase in the AlN powder, although severe particle sedimentation after the milling process is observed in the AlN slurry. With an increase in the milling time, the primary particle size remains nearly constant, but the particle agglomeration is reduced. After spark plasma sintering at 1400°C, the second crystalline phase changes to compounds containing more Al2O3 when the AlN raw material with an increased milling time is used. When the sintering temperature is decreased from 1750°C to 1400°C, the DC resistivity increases by approximately two orders of magnitude, which implies that controlling the sintering temperature is a very effective way to improve the DC resistivity of AlN ceramics.
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of Material Properties and Machining Surface in Electrical Discharge Machining of Ti2AlN and Ti2AlC Materials
- Eui-Song Choi, Chang-Hoon Lee, Gyung-Rae Baek, KwangHo Kim, Myung Chang Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):163-168. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.163
- 1,011 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ti alloys are extensively used in high-technology application because of their strength, oxidation resistance at high temperature. However, Ti alloys tend to be classified very difficult to cut material. In this paper, The powder synthesis, spark plasma sintering (SPS), bulk material properties such as electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are systematically examined on Ti2AlN and Ti2AlC materials having most light-weight and oxidation resistance among the MAX phases. The bulk samples mainly consisted of Ti2AlN and Ti2AlC materials with density close to theoretical value were synthesized by a SPS method. Machining characteristics such as machining time, surface quality are analyzed with measurement of voltage and current waveform according to machining condition of micro-electrical discharge machining with micro-channel shape.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study on Ablation Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy and Ti2AlN Bulks Irradiated by Femto-second Laser
Ki Ha Hwang, Hua Feng Wu, Won Suk Choi, Sung Hak Cho, Myungchang Kang
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2019; 18(7): 90. CrossRef
- Comparative Study on Ablation Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy and Ti2AlN Bulks Irradiated by Femto-second Laser
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


