Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Calcination Temperature on the Microstructure and Photocatalytic Activity of Electrospun BiVO4 Nanofiber
- Myeongjun Ji, Jeong Hyun Kim, Cheol-Hui Ryu, Yun Taek Ko, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):226-232. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.226
- 1,215 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
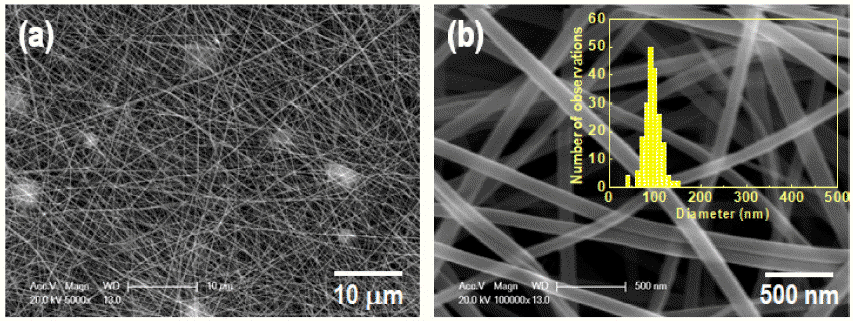
PDF Bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is considered a potentially attractive candidate for the visible-light-driven photodegradation of organic pollutants. In an effort to enhance their photocatalytic activities, BiVO4 nanofibers with controlled microstructures, grain sizes, and crystallinities are successfully prepared by electrospinning followed by a precisely controlled heat treatment. The structural features, morphologies, and photo-absorption performances of the asprepared samples are systematically investigated and can be readily controlled by varying the calcination temperature. From the physicochemical analysis results of the synthesized nanofiber, it is found that the nanofiber calcines at a lower temperature, shows a smaller crystallite size, and lower crystallinity. The photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B (RhB) reveals that the photocatalytic activity of the BiVO4 nanofibers can be improved by a thermal treatment at a relatively low temperature because of the optimization of the conflicting characteristics, crystallinity, crystallite size, and microstructure. The photocatalytic activity of the nanofiber calcined at 350°C for the degradation of RhB under visible-light irradiation exhibits a greater photocatalytic activity than the nanofibers synthesized at 400°C and 450°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
Jimin Lee, Minseob Lim, Tae Sung Kim, Kee-Ryung Park, Jong-Sik Lee, Hong-Baek Cho, Joo Hyun Park, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2021; 548: 149198. CrossRef
- Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
- [Korean]
- Multicomponent IGZO Ceramics for Transparent Electrode Target Fabricated from Oxides and Nitrates
- Hyun-Kwun Lee, Ji-Hye Yoon, Kyeong-Sik Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):375-382. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.375
- 572 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
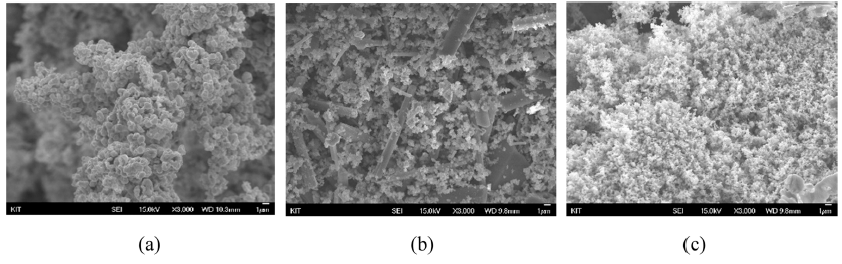
PDF Homogeneous multicomponent indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) ceramics for transparent electrode targets are prepared from the oxides and nitrates as the source materials, and their properties are characterized. The selected compositions were In2O3:Ga2O3:ZnO = 1:1:2, 1:1:6, and 1:1:12 in mole ratio based on oxide. As revealed by X-ray diffraction analysis, calcination of the selected oxide or nitrides at 1200°C results in the formation of InGaZnO4, InGaZn3O6, and InGaZn5O8 phases. The 1:1:2, 1:1:6, and 1:1:12 oxide samples pressed in the form of discs exhibit relative densities of 96.9, 93.2, and 84.1%, respectively, after sintering at 1450°C for 12 h. The InGaZn3O6 ceramics prepared from the oxide or nitrate batches comprise large grains and exhibit homogeneous elemental distribution. Under optimized conditions, IGZO multicomponent ceramics with controlled phases, high densities, and homogeneous microstructures (grain and elemental distribution) are obtained.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


