Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Ni by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of NiO/Camphene Slurry
- Jae-Hun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh, Chang-Yong Hyun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):6-10. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.6
- 913 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, freeze drying of a porous Ni with unidirectionally aligned pore channels is accomplished by using a NiO powder and camphene. Camphene slurries with NiO content of 5 and 10 vol% are prepared by mixing them with a small amount of dispersant at 50°C. Freezing of a slurry is performed at -25°C while the growth direction of the camphene is unidirectionally controlled. Pores are generated subsequently by sublimation of the camphene during drying in air for 48 h. The green bodies are hydrogen-reduced at 400°C and then sintered at 800°C and 900°C for 1 h. X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that the NiO powder is completely converted to the Ni phase without any reaction phases. The sintered samples show large pores that align parallel pores in the camphene growth direction as well as small pores in the internal walls of large pores. The size of large and small pores decreases with increasing powder content from 5 to 10 vol%. The influence of powder content on the pore structure is explained by the degree of powder rearrangement in slurry and the accumulation behavior of powders in the interdendritic spaces of solidified camphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Porous Cu-Co using Freeze Drying Process of Camphene Slurry with Oxide Composite Powders
Gyuhwi Lee, Ju-Yeon Han, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 193. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Porous Cu-Co using Freeze Drying Process of Camphene Slurry with Oxide Composite Powders
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Mo-Cu by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of Metal Oxide Powders
- Hyunji Kang, Ju-Yeon Han, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):1-5. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.1

- 977 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, porous Mo-5 wt% Cu with unidirectionally aligned pores is prepared by freeze drying of camphene slurry with MoO3-CuO powders. Unidirectional freezing of camphene slurry with dispersion stability is conducted at -25°C, and pores in the frozen specimens are generated by sublimation of the camphene crystals. The green bodies are hydrogen-reduced at 750°C and sintered at 1000°C for 1 h. X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that MoO3-CuO composite powders are completely converted to a Mo-and-Cu phase without any reaction phases by hydrogen reduction. The sintered bodies with the Mo-Cu phase show large and aligned parallel pores to the camphene growth direction as well as small pores in the internal walls of large pores. The pore size and porosity decrease with increasing composite powder content from 5 to 10 vol%. The change of pore characteristics is explained by the degree of powder rearrangement in slurry and the accumulation behavior of powders in the interdendritic spaces of solidified camphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristic Evaluation of WC Hard Materials According to Ni Content Variation by a Pulsed Current Activated Sintering Process
Hyun-Kuk Park
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2020; 30(12): 672. CrossRef - Effect of α-lath size on the mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V using core time hydrogen heat treatment
Gye-Hoon Cho, Jung-Min Oh, Hanjung Kwon, Jae-Won Lim
Materials Science and Technology.2020; 36(7): 858. CrossRef
- Characteristic Evaluation of WC Hard Materials According to Ni Content Variation by a Pulsed Current Activated Sintering Process
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Al2O3 Film by Freeze Tape Casting
- Ran-Hee Shin, Jun-Mo Koo, Young-Do Kim, Yoon-Soo Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):438-442. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.438

- 686 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous thick film of alumina which is fabricated by freeze tape casting using a camphene-camphor-acrylate vehicle. Alumina slurry is mixed above the melting point of the camphene-camphor solvent. Upon cooling, the camphene-camphor crystallizes from the solution as particle-free dendrites, with the Al2O3 powder and acrylate liquid in the interdendritic spaces. Subsequently, the acrylate liquid is solidified by photopolymerization to offer mechanical properties for handling. The microstructure of the porous alumina film is characterized for systems with different cooling rate around the melting temperature of camphor-camphene. The structure of the dendritic porosity is compared as a function of ratio of camphene-camphor solvent and acrylate content, and Al2O3 powder volume fraction in acrylate in terms of the dendrite arm width.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of CNT on a Camphene Impregnated Titanium Porous Body by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Hogyu Kim, Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):122-128. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.122
- 776 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
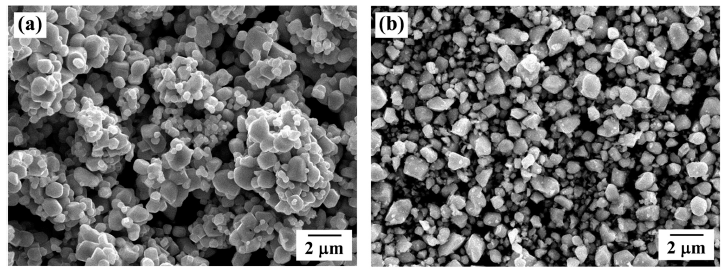
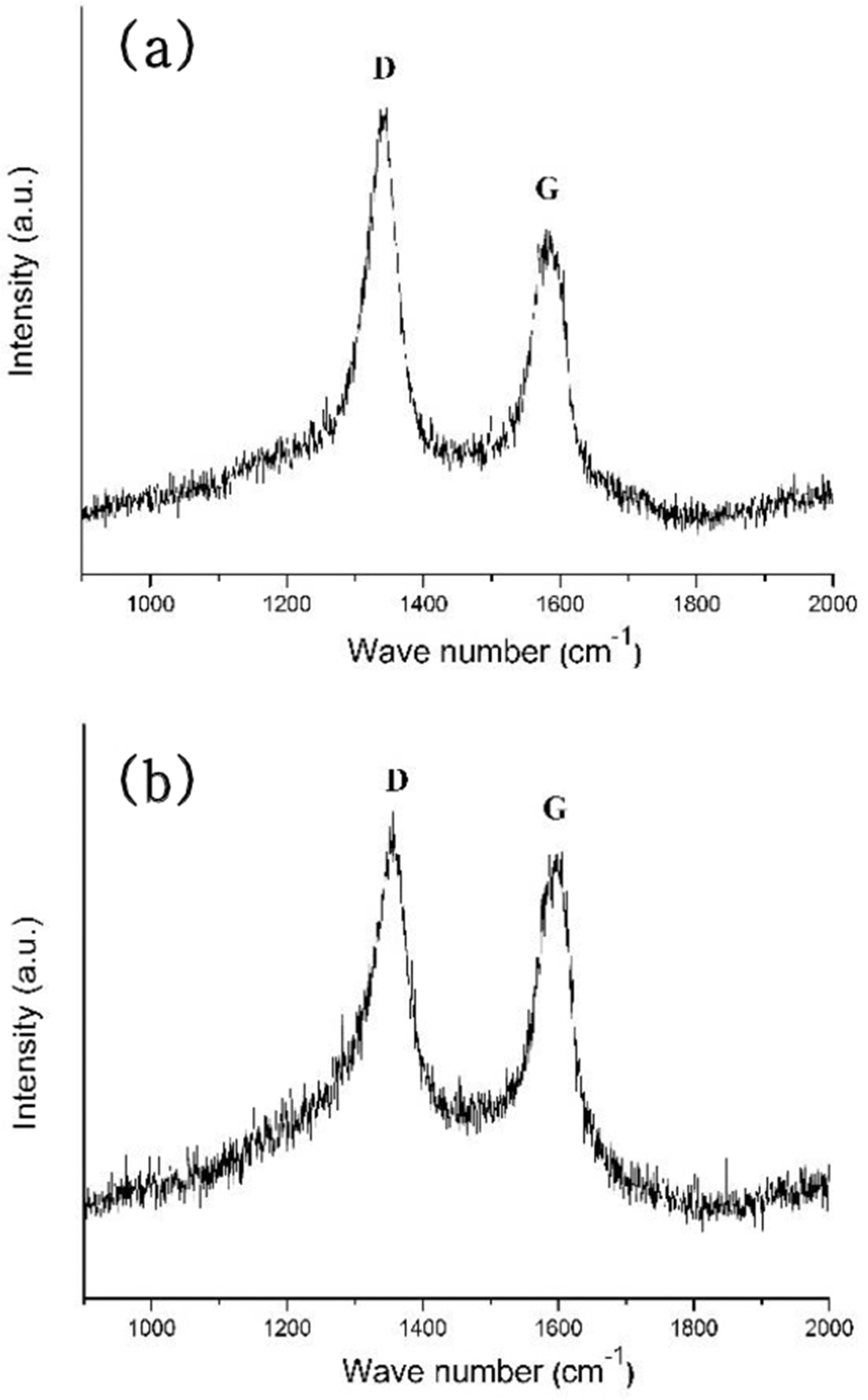
PDF In this study, titanium(Ti) meshes and porous bodies are employed to synthesize carbon nanotubes(CNTs) using methane(CH4) gas and camphene solution, respectively, by chemical vapor deposition. Camphene is impregnated into Ti porous bodies prior to heating in a furnace. Various microscopic and spectroscopic techniques are utilized to analyze CNTs. It is found that CNTs are more densely and homogeneously populated on the camphene impregnated Ti-porous bodies as compared to CNTs synthesized with methane on Ti-porous bodies. It is elucidated that, when synthesized with methane, few CNTs are formed inside of Ti porous bodies due to methane supply limited by internal structures of Ti porous bodies. Ti-meshes and porous bodies are found to be multi-walled with high degree of structural disorders. These CNTs are expected to be utilized as catalyst supports in catalytic filters and purification systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent progress in additive manufacturing of porous titanium: From design to applications
Haoxin Song, Chen Wang, Wenzheng Yu, Mingsen Zhang, Jinqiang Shao, Hanwen Liang, Tingting Wu, Xiaoxiao Dong
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1026: 180451. CrossRef - Solvent induced surface modifications on hydrogen storage performance of ZnO nanoparticle decorated MWCNTs
Madhavi Konni, Anima S. Dadhich, Saratchandra Babu Mukkamala
Sustainable Energy & Fuels.2018; 2(2): 466. CrossRef - Influence of nickel nanoparticles on hydrogen storage behaviors of MWCNTs
Ye-Ji Han, Soo-Jin Park
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 85. CrossRef
- Recent progress in additive manufacturing of porous titanium: From design to applications
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Cu-Ni by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of CuO-NiO Powder Mixture
- Han Gil Seo, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):34-38. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.34

- 885 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cu-Ni alloys with unidirectionally aligned pores were prepared by freeze-drying process of CuO-NiO/camphene slurry. Camphene slurries with dispersion stability by the addition of oligomeric polyester were frozen at -25°C, and pores in the frozen specimens were generated by sublimation of the camphene during drying in air. The green bodies were hydrogen-reduced at 300°C and sintered at 850°C for 1 h. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that CuO-NiO composite powders were completely converted to Cu-Ni alloy without any reaction phases by hydrogen reduction. The sintered samples showed large and aligned parallel pores to the camphene growth direction, and small pores in the internal wall of large pores. The pore size and porosity decreased with increase in CuO-NiO content from 5 to 10 vol%. The change of pore characteristics was explained by the degree of powder rearrangement in slurry and the accumulation behavior of powders in the interdendritic spaces of solidified camphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancement in electrical conductivity of pastes containing submicron Ag-coated Cu filler with palmitic acid surface modification
Eun Byeol Choi, Jong-Hyun Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 67. CrossRef - Investigation for Microstructure and Hardness of Welded Zone of Cu-Ni Alloy using W92-Ni-Fe Sintering Tool
Tae-Jin Yoon, Sang-Won Park, Myung-Chang Kang, Joong-Suk Noh, Sung-Wook Chung, Chung-Yun Kang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 181. CrossRef - Controlling Structural and Electrical Properties of Pt Nanopowder-Dispersed SiO2Film
Jae Ho Lee, In Joo Shin, Sung Woo Lee, Hyeong Cheol Kim, Byung Joon Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(5): 355. CrossRef
- Enhancement in electrical conductivity of pastes containing submicron Ag-coated Cu filler with palmitic acid surface modification
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


