Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Carbon-coated Tin Nano-powders by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ju-Suck Song, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):317-324. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.317
- 988 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
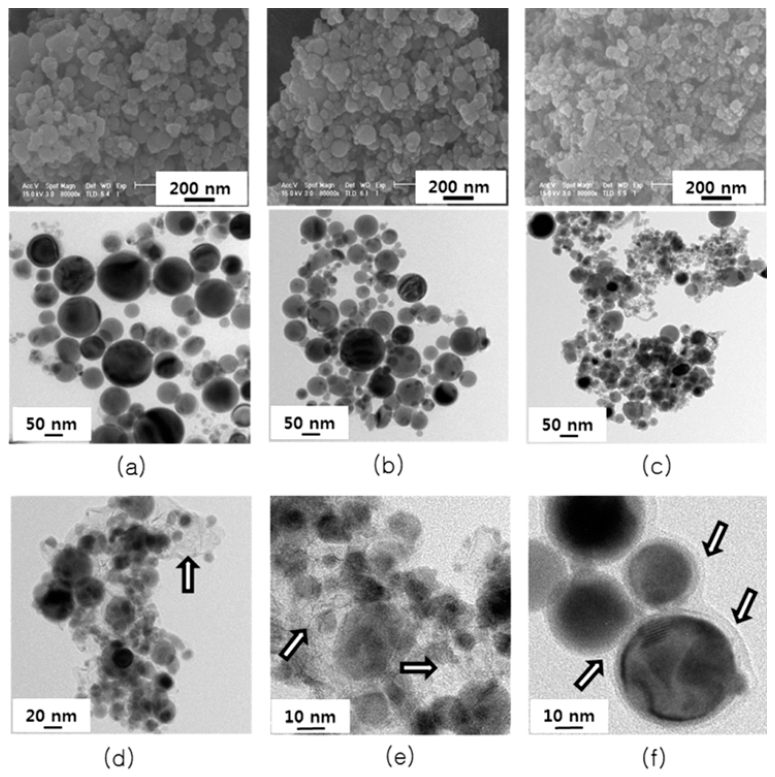
PDF Tin is one of the most promising anode materials for next-generation lithium-ion batteries with a high energy density. However, the commercialization of tin-based anodes is still hindered due to the large volume change (over 260%) upon lithiation/delithiation cycling. To solve the problem, many efforts have been focused on enhancing structural stability of tin particles in electrodes. In this work, we synthesize tin nano-powders with an amorphous carbon layer on the surface and surroundings of the powder by electrical wire explosion in alcohol-based liquid media at room temperature. The morphology and microstructures of the powders are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Xray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of the powder for use as an anode material for lithium-ion battery are evaluated by cyclic voltammetry and a galvanometric dischargecharge method. It is shown that the carbon-coated tin nano-powders prepared in hexanol media exhibit a high initial charge specific capacity of 902 mAh/g and a high capacity retention of 89% after 50 cycles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of carbon coating thickness to prevent crack generation in Sn nanoparticles during charge/discharge process and their electrochemical properties
Ji-Seub Choi, Yeon-Ju Lee, Hoi-Jin Lee, Gyu-Bong Cho, Jai-Won Byeon, Hyo-Jun Ahn, Ki-Won Kim, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2020; 843: 155892. CrossRef - Fabrication of multilayer graphene-encapsulated Sn/SnO2 nanocomposite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries and its electrochemical properties
Ju-Seok Song, Gyu-Bong Cho, Ki-Won Kim, Hyo-Jun Ahn, Hye-Sung Kim, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 736. CrossRef
- Optimization of carbon coating thickness to prevent crack generation in Sn nanoparticles during charge/discharge process and their electrochemical properties
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


