Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Nitric Oxide Detection of Fe(DTC)3-hybrizided CdSe Quantum Dots Via Fluorescence Energy Transfer
- Chang-Yeoul Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):453-458. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.453
- 1,117 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
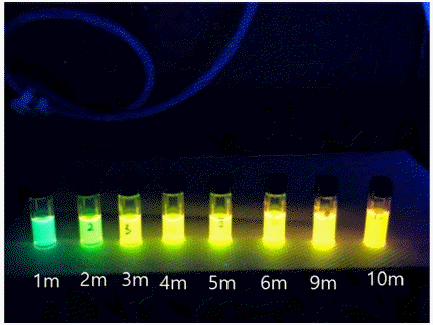
PDF We successfully synthesize water-dispersible CTAB-capped CdSe@ZnS quantum dots with the crystal size of the CdSe quantum dots controlled from green to orange colors. The quenching effect of Fe(DTC)3 is very efficient to turn off the emission light of quantum dots at four molar ratios of the CdSe quantum dots, that is, the effective covering the surface of quantum dots with Fe(DTC)3. However, the reaction with Fe(DTC)3 for more than 24 h is required to completely realize the quenching effect. The highly quenched quantum dots efficiently detect nitric oxide at nano-molar concentration of 110nM of NO with 34% of recovery of emission light intensity. We suggest that Fe(DTC)3-hybridized CdSe@ZnS quantum dots are an excellent fluorescence resonance energy transfer probe for the detection of nitric oxide in biological systems.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and analysis CdSe/ZnS quantum dot with a Core/shell Continuous Synthesis System Using a Microfluidic Reactor
- Myung Hwan Hong, So Young Joo, Lee-Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):132-136. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.132
- 1,892 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
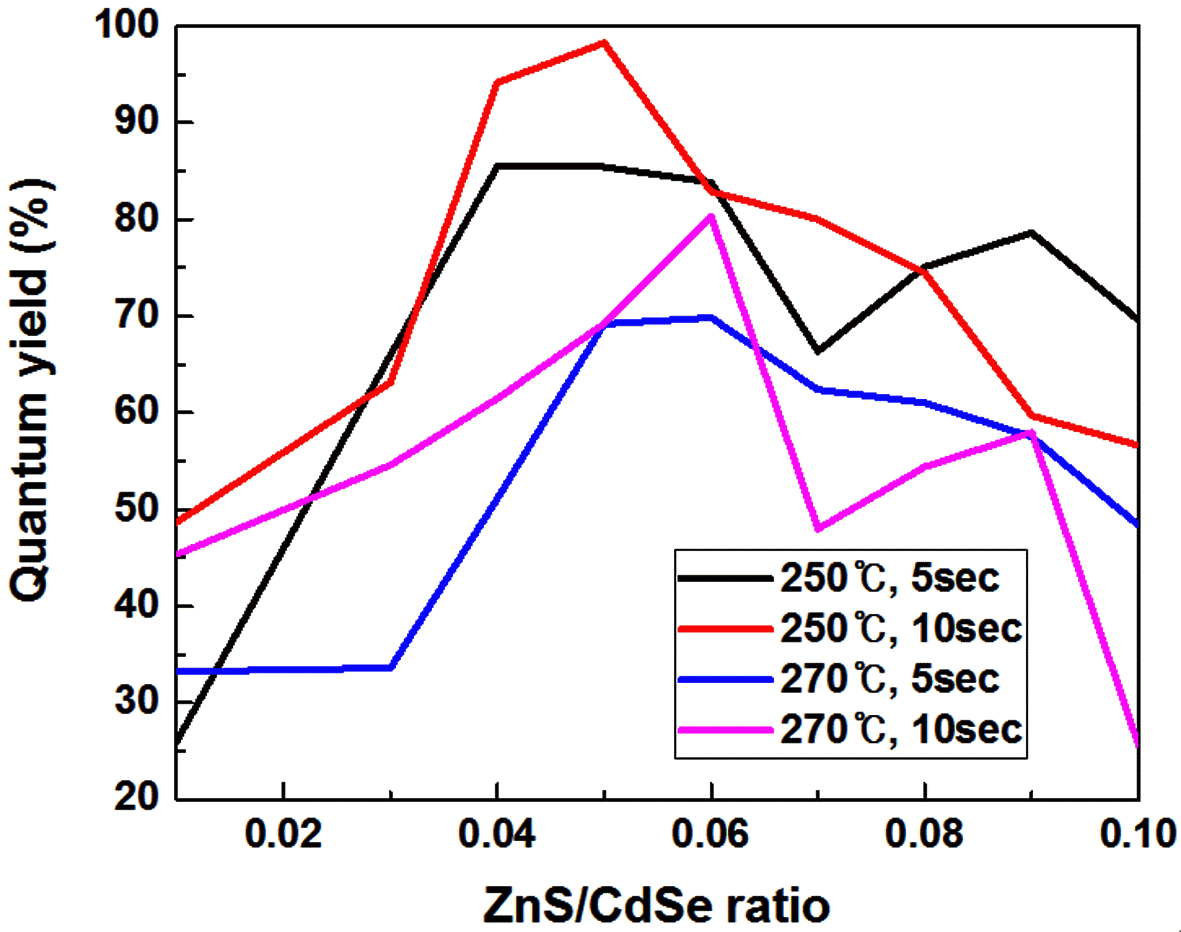
PDF Core/shell CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) are synthesized by a microfluidic reactor-assisted continuous reactor system. Photoluminescence and absorbance of synthesized CdSe/ZnS core/shell QDs are investigated by fluorescence spectrophotometry and online UV-Vis spectrometry. Three reaction conditions, namely; the shell coating reaction temperature, the shell coating reaction time, and the ZnS/CdSe precursor volume ratio, are combined in the synthesis process. The quantum yield of the synthesized CdSe QDs is determined for each condition. CdSe/ZnS QDs with a higher quantum yield are obtained compared to the discontinuous microfluidic reactor synthesis system. The maximum quantum efficiency is 98.3% when the reaction temperature, reaction time, and ZnS/CdSe ratio are 270°C, 10 s, and 0.05, respectively. Obtained results indicate that a continuous synthesis of the Core/shell CdSe/ZnS QDs with a high quantum efficiency could be achieved by isolating the reaction from the external environment.
- [Korean]
- Surface Treatment Method for Long-term Stability of CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots
- Hyun-Su Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum-Sung Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan-Gi Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):1-5. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.1
- 1,491 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
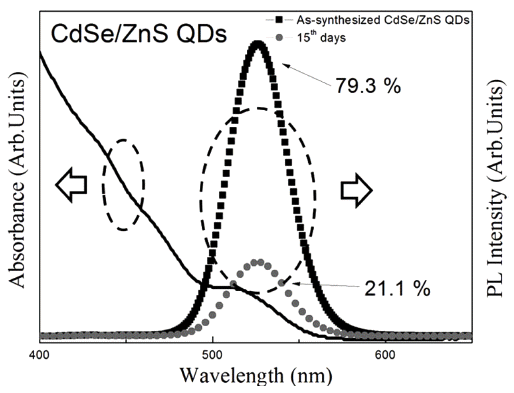
PDF We have investigated the washing method of as-synthesized CdSe/ZnS core/shell structure quantum dots (QDs) and the effective surface passivation method of the washed QDs using PMMA. The quantum yield (QY%) of assynthesized QDs decreases with time, from 79.3% to 21.1%, owing to surface reaction with residual organics. The decreased QY% is restored to the QY% of as-synthesized QDs by washing. However, the QY% of washed QDs also decreases with time, owing to the absence of surface passivation layer. On the other hand, the PMMA-treated QDs maintained a relatively higher QY% after washing than that of the washed QDs that were kept in toluene solution for 30 days. Formation of the PMMA coating layer on CdSe/ZnS QD surface is confirmed by HR-TEM and FT-IR. It is found that the PMMA surface coating, when combined with washing, is useful to be applied in the storage of QDs, owing to its long-term stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improvement of Short-Circuit Current of Quantum Dot Sensitive Solar Cell Through Various Size of Quantum Dots
Seung Hwan Ji, Hye Won Yun, Jin Ho Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2021; 31(1): 16. CrossRef - Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef - Study on Surface-defect Passivation of InP System Quantum Dots by Photochemical Method
Doyeon Kim, Hyun-Su Park, Hye Mi Cho, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(6): 489. CrossRef
- Improvement of Short-Circuit Current of Quantum Dot Sensitive Solar Cell Through Various Size of Quantum Dots
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and analysis CdSe Quantum dot with a Microfluidic Reactor Using a Combinatorial Synthesis System
- Myung Hwan Hong, Duk-Hee Lee, Lee-Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Nam-Hoon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):143-148. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.143
- 851 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
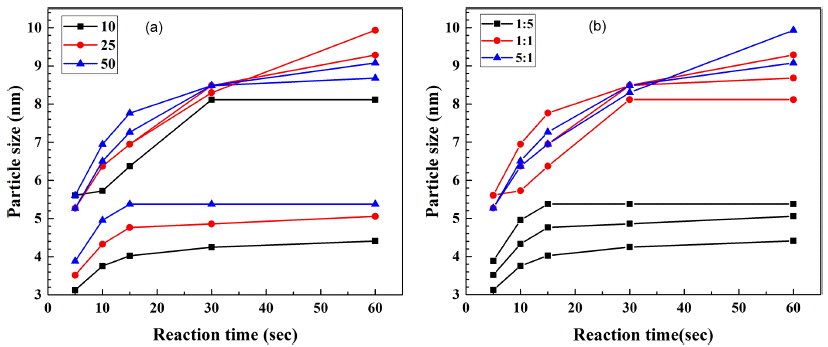
PDF A microfluidic reactor with computer-controlled programmable isocratic pumps and online detectors is employed as a combinatorial synthesis system to synthesize and analyze materials for fabricating CdSe quantum dots for various applications. Four reaction condition parameters, namely, the reaction temperature, reaction time, Cd/Se compositional ratio, and precursor concentration, are combined in synthesis condition sets, and the size of the synthesized CdSe quantum dots is determined for each condition. The average time corresponding to each reaction condition for obtaining the ultraviolet–visible absorbance and photoluminescence spectra is approximately 10 min. Using the data from the combinatorial synthesis system, the effects of the reaction conditions on the synthesized CdSe quantum dots are determined. Further, the data is used to determine the relationships between the reaction conditions and the CdSe particle size. This method should aid in determining and selecting the optimal conditions for synthesizing nanoparticles for diverse applications.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


