Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Bandgap Tuning and Quenching Effects of In(Zn)P@ZnSe@ZnS Quantum Dots
- Sang Yeon Lee, Su Hyun Park, Gyungsu Byun, Chang-Yeoul Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):226-235. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00003

- 2,922 View
- 44 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
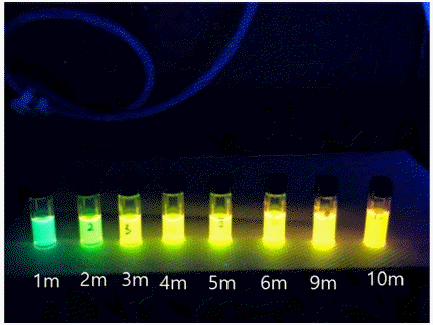
PDF - InP quantum dot (QDs) have attracted researchers’ interest due to their applicability in quantum dot light-emitting displays (QLED) or biomarkers for detecting cancers or viruses. The surface or interface control of InP QD core/shell has substantially increased quantum efficiency, with a quantum yield of 100% reached by introducing HF to inhibit oxide generation. In this study, we focused on the control of bandgap energy of quantum dots by changing the Zn/(In+Zn) ratio in the In(Zn)P core. Zinc incorporation can change the photoluminescent light colors of green, yellow, orange, and red. Diluting a solution of as-synthesized QDs by more than 100 times did not show any quenching effects by the Förster resonance energy transfer phenomenon between neighboring QDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing luminescence of QD thin films, polymer composite films, and LED devices by nanostructures
Hongcheng Yang, Junjie Hao, Mingyu Sun, Yujie Song, Kai Wang, Yujie Song, Xiao Wei Sun, Wenda Zhang
The Innovation.2026; 7(2): 101121. CrossRef
- Enhancing luminescence of QD thin films, polymer composite films, and LED devices by nanostructures
- [English]
- Nitric Oxide Detection of Fe(DTC)3-hybrizided CdSe Quantum Dots Via Fluorescence Energy Transfer
- Chang-Yeoul Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):453-458. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.453
- 1,116 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We successfully synthesize water-dispersible CTAB-capped CdSe@ZnS quantum dots with the crystal size of the CdSe quantum dots controlled from green to orange colors. The quenching effect of Fe(DTC)3 is very efficient to turn off the emission light of quantum dots at four molar ratios of the CdSe quantum dots, that is, the effective covering the surface of quantum dots with Fe(DTC)3. However, the reaction with Fe(DTC)3 for more than 24 h is required to completely realize the quenching effect. The highly quenched quantum dots efficiently detect nitric oxide at nano-molar concentration of 110nM of NO with 34% of recovery of emission light intensity. We suggest that Fe(DTC)3-hybridized CdSe@ZnS quantum dots are an excellent fluorescence resonance energy transfer probe for the detection of nitric oxide in biological systems.
- [English]
- Effect of SiC and WC additon on Oxidation Behavior of Spark-Plasma-Sintered ZrB2
- Chang-Yeoul Kim, Jae-Seok Choi, Sung-Churl Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):455-462. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.455
- 1,093 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
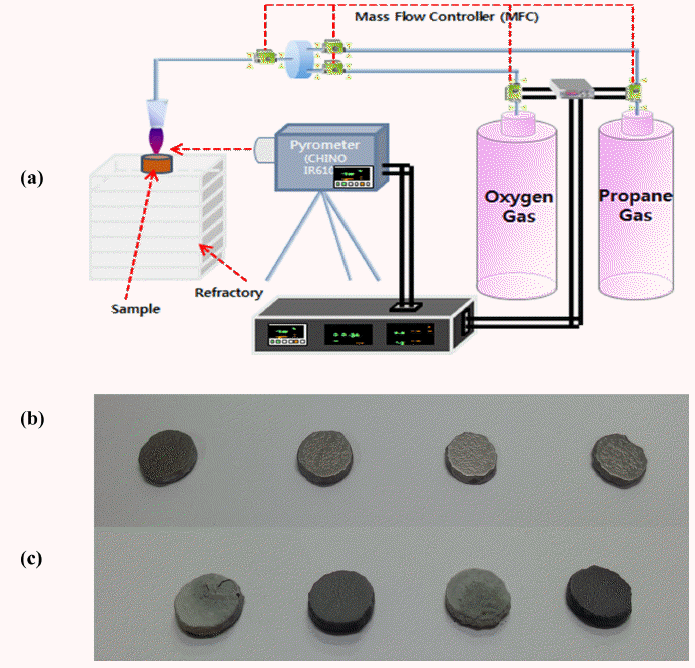
PDF ZrB2 ceramic and ZrB2 ceramic composites with the addition of SiC, WC, and SiC/WC are successfully synthesized by a spark plasma sintering method. During high-temperature oxidation, SiC additive form a SiO2 amorphous outer scale layer and SiC-deplete ZrO2 scale layer, which decrease the oxidation rate. WC addition forms WO3 during the oxidation process to result in a ZrO2/WO3 liquid sintering layer, which is known to improve the antioxidation effect. The addition of SiC and WC to ZrB2 reduces the oxygen effective diffusivity by one-fifth of that of ZrB2. The addition of both SiC and WC shows the formation of a SiO2 outer dense glass layer and ZrO2/WO3 layer so that the anti-oxidation effect is improved three times as much as that of ZrB2. Therefore, SiC- and WC-added ZrB2 has a lower two-order oxygen effective diffusivity than ZrB2; it improves the anti-oxidation performance 3 times as much as that of ZrB2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of TiC and WC Addition on the Mechanism and Kinetics of Isothermal Oxidation and High-Temperature Stability of ZrB2–SiC Composites
Pradyut Sengupta, Indranil Manna
High Temperature Corrosion of Materials.2024; 101(S1): 57. CrossRef
- Role of TiC and WC Addition on the Mechanism and Kinetics of Isothermal Oxidation and High-Temperature Stability of ZrB2–SiC Composites
- [Korean]
- Titanate Nanotube Formation and Nanostructure Development from the Reaction of TiO2 Nanopowder and Alkalihydroxide
- Eun-Ju Jin, Doh-Hyung Riu, Seung-Hun Huh, Chang-Yeoul Kim, Hae-Jin Hwang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2008;15(2):125-135.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2008.15.2.125

- 698 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - [ TiO_2 ] nanotubes for photocatalytic application have been synthesized by hydrothermal method. TiO_2 nanotubes are formed by washing process after reaction in alkalic solution. Nanotubes with different morphology have been fabricated by changing NaOH concentration, temperature and time. TiO_2 nanoparticles were treated inside NaOH aqueous solution in a Teflon vessel at 110°C for 20 h, after which they were washed with HCl aqueous solution and deionized water. Nanotube with the most perfect morphology was formed from 0.1 N HCl washing treatment. TiO_2 nanotube was also obtained when the precursor was washed with other washing solutions such as NH_4OH, NaCl, K_2SO_4, and Na_2SO_3. Therefore, it was suggested that Na+ ion combined inside the precursor compound slowly comes out from the structure, leaving nanosheet morphology of TiO_2 compounds, which in turn become the nanotube in the presence of hydroxyl ion. To stabilize the sheet morphology, the different type of washing treatment solution might be considered such as amine class compounds.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coating Property of Hybrid Structured Photo-Electrode to Increase Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells Efficiency
Min-Hee Kim, Hyung-Woo Lee, Young-Keun Jeong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2010; 17(6): 449. CrossRef
- Coating Property of Hybrid Structured Photo-Electrode to Increase Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells Efficiency
- [English]
- Design of Nanocluster Based Material with Catalytic Properties
- Nakayama Tadachika, Chang-Yeoul Kim, Sekino Tohru, Yong-Ho Choa, Kusunose Takafumi, Hayashi Yamato, Niibara Koichi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2001;8(3):197-200.

- 343 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Modified inert gas condensation method was used to produce the nanocluster composites of CuO/CeO_2. High-resolution TEM, SEM and catalytic measurements have been used to characterize the samples and study the synergistic effect between the CuO phase and CeO_2(ceria) support. By varying the He pressure, the heating temperature and configuration of the heating boats inside the modified gas condensation chamber, nanoclusters of varying sizes, shapes and composition can be produced. The composition and nanostructured morphology were shown to influence the catalytic properties of the system. A copper content around 10 at% with a morphology that favors high-energy surfaces of ceria is shown to be beneficial for a high catalytic activity.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


