Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Hydrogen Reduction Behavior and Microstructure Characteristics of Ball-milled CuO-Co3O4 Powder Mixtures
- Ju-Yeon Han, Gyuhwi Lee, Hyunji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):410-414. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.410

- 376 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The hydrogen reduction behavior of the CuO-Co3O4 powder mixture for the synthesis of the homogeneous Cu-15at%Co composite powder has been investigated. The composite powder is prepared by ball milling the oxide powders, followed by a hydrogen reduction process. The reduction behavior of the ball-milled powder mixture is analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and temperature-programmed reduction at different heating rates in an Ar-10%H2 atmosphere. The scanning electron microscopy and XRD results reveal that the hydrogen-reduced powder mixture is composed of fine agglomerates of nanosized Cu and Co particles. The hydrogen reduction kinetics is studied by determining the degree of peak shift as a function of the heating rate. The activation energies for the reduction of the oxide powders estimated from the slopes of the Kissinger plots are 58.1 kJ/mol and 65.8 kJ/mol, depending on the reduction reaction: CuO to Cu and Co3O4 to Co, respectively. The measured temperature and activation energy for the reduction of Co3O4 are explained on the basis of the effect of pre-reduced Cu particles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Porous Cu-Co using Freeze Drying Process of Camphene Slurry with Oxide Composite Powders
Gyuhwi Lee, Ju-Yeon Han, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 193. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Porous Cu-Co using Freeze Drying Process of Camphene Slurry with Oxide Composite Powders
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Mo-Cu by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of Metal Oxide Powders
- Hyunji Kang, Ju-Yeon Han, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):1-5. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.1

- 500 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, porous Mo-5 wt% Cu with unidirectionally aligned pores is prepared by freeze drying of camphene slurry with MoO3-CuO powders. Unidirectional freezing of camphene slurry with dispersion stability is conducted at -25°C, and pores in the frozen specimens are generated by sublimation of the camphene crystals. The green bodies are hydrogen-reduced at 750°C and sintered at 1000°C for 1 h. X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that MoO3-CuO composite powders are completely converted to a Mo-and-Cu phase without any reaction phases by hydrogen reduction. The sintered bodies with the Mo-Cu phase show large and aligned parallel pores to the camphene growth direction as well as small pores in the internal walls of large pores. The pore size and porosity decrease with increasing composite powder content from 5 to 10 vol%. The change of pore characteristics is explained by the degree of powder rearrangement in slurry and the accumulation behavior of powders in the interdendritic spaces of solidified camphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristic Evaluation of WC Hard Materials According to Ni Content Variation by a Pulsed Current Activated Sintering Process
Hyun-Kuk Park
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2020; 30(12): 672. CrossRef - Effect of α-lath size on the mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V using core time hydrogen heat treatment
Gye-Hoon Cho, Jung-Min Oh, Hanjung Kwon, Jae-Won Lim
Materials Science and Technology.2020; 36(7): 858. CrossRef
- Characteristic Evaluation of WC Hard Materials According to Ni Content Variation by a Pulsed Current Activated Sintering Process
- [Korean]
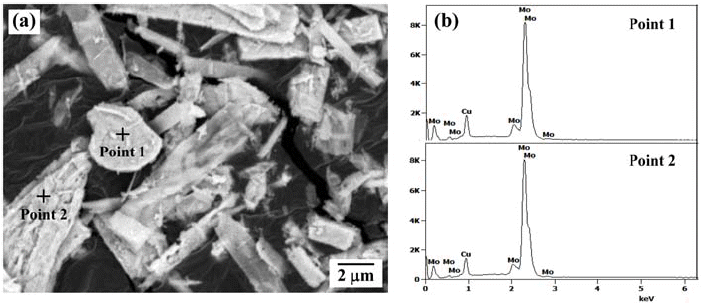
- Fabrication of Mo-Cu Powders by Ball Milling and Hydrogen Reduction of MoO3-CuO Powder Mixtures
- Hyunji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):322-326. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.322
- 438 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The hydrogen reduction behavior of MoO3-CuO powder mixture for the synthesis of homogeneous Mo-20 wt% Cu composite powder is investigated. The reduction behavior of ball-milled powder mixture is analyzed by XRD and temperature programmed reduction method at various heating rates in Ar-10% H2 atmosphere. The XRD analysis of the heat-treated powder at 300°C shows Cu, MoO3, and Cu2MoO5 phases. In contrast, the powder mixture heated at 400°C is composed of Cu and MoO2 phases. The hydrogen reduction kinetic is evaluated by the amount of peak shift with heating rates. The activation energies for the reduction, estimated by the slope of the Kissinger plot, are measured as 112.2 kJ/mol and 65.2 kJ/mol, depending on the reduction steps from CuO to Cu and from MoO3 to MoO2, respectively. The measured activation energy for the reduction of MoO3 is explained by the effect of pre-reduced Cu particles. The powder mixture, hydrogen-reduced at 700°C, shows the dispersion of nano-sized Cu agglomerates on the surface of Mo powders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Mo-Cu nanocomposite powder by hydrogen reduction of copper nitrate coated MoO3 powder mixture
Ji Won Choi, Ji Young Kim, Youngmin Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Materials Letters.2024; 377: 137565. CrossRef - Fabrication of Porous Mo-Cu by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of Metal Oxide Powders
Hyunji Kang, Ju-Yeon Han, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Hydrogen Reduction Behavior and Microstructure Characteristics of Ball-milled CuO-Co3O4 Powder Mixtures
Ju-Yeon Han, Gyuhwi Lee, Hyunji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(5): 410. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Mo-Cu nanocomposite powder by hydrogen reduction of copper nitrate coated MoO3 powder mixture
- [Korean]
- Effect of Freezing and Sintering Condition of CuO-SnO2/Camphene Slurries on the Pore Structure of Porous Cu-Sn
- Joo-Hyung Kim, Sung-Tag Oh, Chang-Yong Hyun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):49-53. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.49

- 371 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The present study demonstrates the effect of freezing conditions on the pore structure of porous Cu-10 wt.% Sn prepared by freeze drying of CuO-SnO2/camphene slurry. Mixtures of CuO and SnO2 powders are prepared by ball milling for 10 h. Camphene slurries with 10 vol.% of CuO-SnO2 are unidirectionally frozen in a mold maintained at a temperature of -30°C for 1 and 24 h, respectively. Pores are generated by the sublimation of camphene at room temperature. After hydrogen reduction and sintering at 650°C for 2 h, the green body of the CuO-SnO2 is completely converted into porous Cu-Sn alloy. Microstructural observation reveals that the sintered samples have large pores which are aligned parallel to the camphene growth direction. The size of the large pores increases from 150 to 300 μm with an increase in the holding time. Also, the internal walls of the large pores contain relatively small pores whose size increases with the holding time. The change in pore structure is explained by the growth behavior of the camphene crystals and rearrangement of the solid particles during the freezing process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Porous Ni by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of NiO/Camphene Slurry
Jae-Hun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh, Chang-Yong Hyun
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 6. CrossRef - Fabrication of Al2O3 Dispersed Porous Cu by Freeze Drying of CuO-Al2O3/Camphene Slurry
Hyunji Kang, Doh-Hyung Riu, Sung-Tag Oh
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(1): 25. CrossRef - Porous W-Ni Alloys Synthesized from Camphene/WO3-NiO Slurry by Freeze Drying and Heat Treatment in Hydrogen Atmosphere
Sung Hyun Park, Seong-Min Park, So-Jeong Park, Bo-Yeong Park, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(2): 108. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Porous Ni by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of NiO/Camphene Slurry
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Cu-Ni by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of CuO-NiO Powder Mixture
- Han Gil Seo, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):34-38. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.34

- 354 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cu-Ni alloys with unidirectionally aligned pores were prepared by freeze-drying process of CuO-NiO/camphene slurry. Camphene slurries with dispersion stability by the addition of oligomeric polyester were frozen at -25°C, and pores in the frozen specimens were generated by sublimation of the camphene during drying in air. The green bodies were hydrogen-reduced at 300°C and sintered at 850°C for 1 h. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that CuO-NiO composite powders were completely converted to Cu-Ni alloy without any reaction phases by hydrogen reduction. The sintered samples showed large and aligned parallel pores to the camphene growth direction, and small pores in the internal wall of large pores. The pore size and porosity decreased with increase in CuO-NiO content from 5 to 10 vol%. The change of pore characteristics was explained by the degree of powder rearrangement in slurry and the accumulation behavior of powders in the interdendritic spaces of solidified camphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancement in electrical conductivity of pastes containing submicron Ag-coated Cu filler with palmitic acid surface modification
Eun Byeol Choi, Jong-Hyun Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 67. CrossRef - Investigation for Microstructure and Hardness of Welded Zone of Cu-Ni Alloy using W92-Ni-Fe Sintering Tool
Tae-Jin Yoon, Sang-Won Park, Myung-Chang Kang, Joong-Suk Noh, Sung-Wook Chung, Chung-Yun Kang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 181. CrossRef - Controlling Structural and Electrical Properties of Pt Nanopowder-Dispersed SiO2Film
Jae Ho Lee, In Joo Shin, Sung Woo Lee, Hyeong Cheol Kim, Byung Joon Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(5): 355. CrossRef
- Enhancement in electrical conductivity of pastes containing submicron Ag-coated Cu filler with palmitic acid surface modification
TOP
 kpmi
kpmi


 First
First Prev
Prev


