Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Comparison and Characterization of Silodosin-loaded Solid Dispersions Prepared by Various Solid Dispersion Preparation Methods
- Su Man Lee, Da Young Song, Kyeong Soo Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):263-271. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00143
- 1,581 View
- 37 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
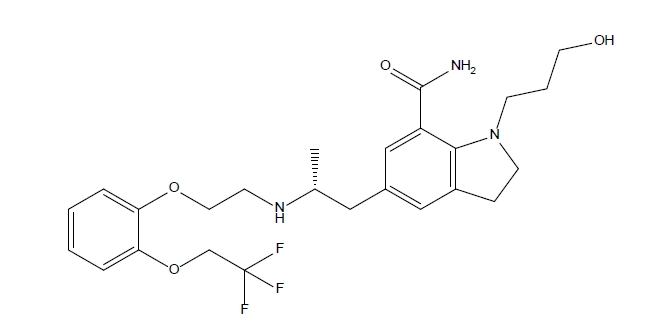
PDF - This study focused on improving the solubility of silodosin, a drug poorly soluble in water, by utilizing solid dispersions. Three types of dispersions were examined and compared against the drug powder: surface-attached (SA), solvent-wetted (SW), and solvent-evaporated (SE). Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was identified as the most effective polymer in enhancing solubility. These dispersions were prepared using spray-drying techniques with silodosin and PVA as the polymer, employing solvents such as water, ethanol, and a water-acetone mix. The physicochemical properties and solubility of the dispersions were evaluated. The surface-attached dispersions featured the polymer on a crystalline drug surface, the solvent-wetted dispersions had the amorphous drug on the polymer, and the solvent-evaporated dispersions produced nearly round particles with both components amorphous. Testing revealed that the order of improved solubility was: solvent-evaporated, solvent-wetted, and surface-attached. The results demonstrated that the preparation method of the solid dispersions significantly impacted their physicochemical properties and solubility enhancement.
- [Korean]
- Preparation and Evaluation of Ketoconazole-loaded Solid-SNEDDS (Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System) using Various Solidification Carriers
- Da Young Song, Kyeong Soo Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):493-501. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.493
- 982 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
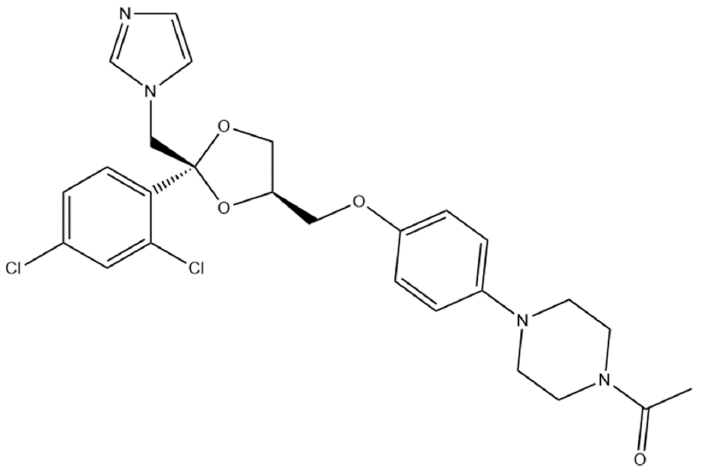
PDF This study aimed to develop a solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (solid-SNEDDS) to enhance the formulation of ketoconazole (KTZ), a BCS Class II drug with poor solubility. Ketoconazole, which is insoluble above pH 3, requires solubilization for effective delivery. This SNEDDS comprises oil, surfactant, and co-surfactant, which spontaneously emulsify in the gastrointestinal tract environment to form nanoemulsions with droplet sizes less than 100 nm. The optimal SNE-vehicle composition of oleic acid, TPGS, and PEG 400 at a 10:80:10 weight ratio was determined based on the smallest droplet size achieved. This composition was used to prepare liquid SNEDDS containing ketoconazole. The droplet size and polydispersity index (PDI) of the resulting liquid SNEDDS were analyzed. Subsequently, solid-SNEDDS was fabricated using a spray-drying method with solidifying carriers such as silicon dioxide, crospovidone, and magnesium alumetasilicate. The physicochemical properties of the solid-SNEDDS were characterized by scanning electron microscopy and powder X-ray diffraction, and its solubility, droplet size, and PDI were evaluated. In particular, the solid-SNEDDS containing ketoconazole and crospovidone in a 2:1 weight ratio exhibited significantly enhanced solubility, highlighting its potential for improved medication adherence and dissolution rates.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


